Abstract
Some anti-phosphocholine antibodies protect mice against challenge with certain, but not all, pneumococcal types. We found that both their isotype and reactivity with the cell wall C-polysaccharide of encapsulated pneumococci, as measured by immunodiffusion, were important in predicting the protective activity of anti-phosphocholine antibodies. We propose that the specificity of the protective antibodies includes the backbone of the phosphocholine-containing structure.
Full text
PDF


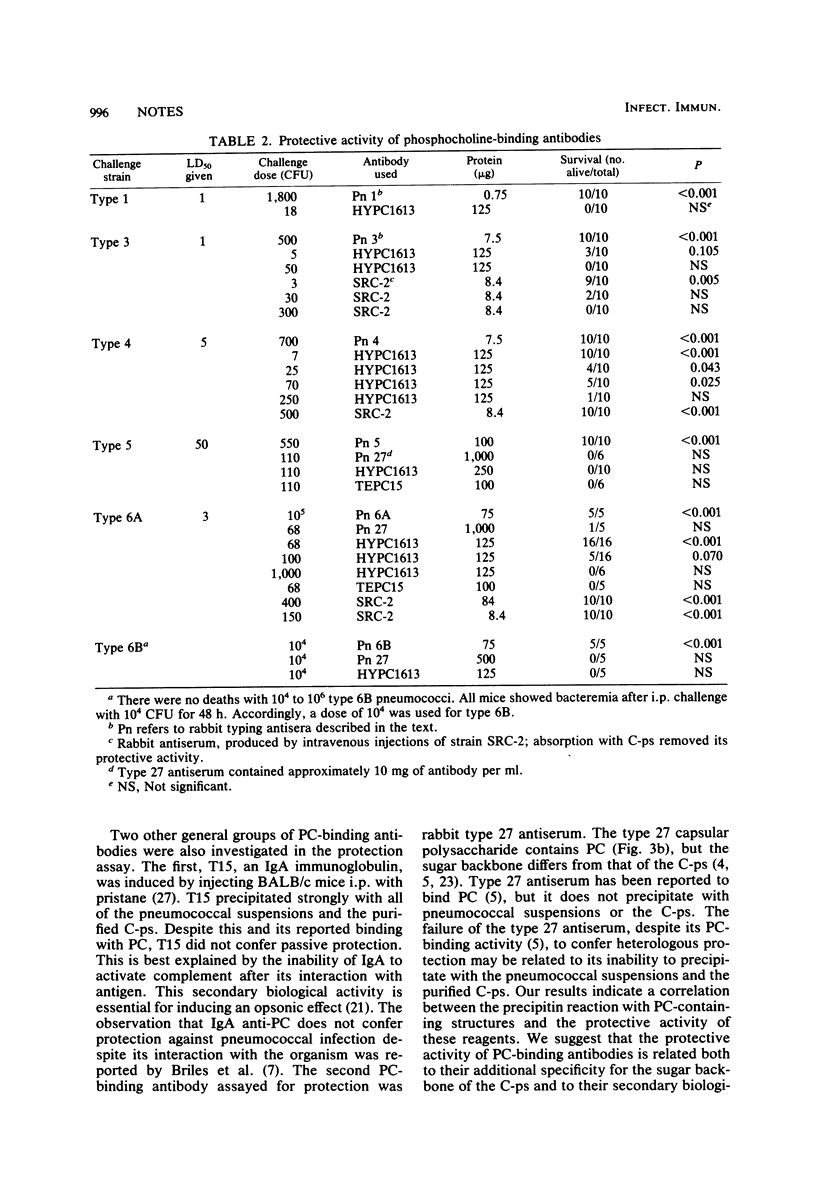



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Au C. C., Einsenstein T. K. Evaluation of the role of the pneumococcal Forssman antigen (F-polysaccharide) in the cross-serotype protection induced by pneumococcal subcellular preparations. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):169–173. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.169-173.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au C. C., Eisenstein T. K. Nature of the cross-protective antigen in subcellular vaccines of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):160–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.160-168.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery O. T., Morgan H. J. IMMUNOLOGICAL REACTIONS OF THE ISOLATED CARBOHYDRATE AND PROTEIN OF PNEUMOCOCCUS. J Exp Med. 1925 Aug 31;42(3):347–353. doi: 10.1084/jem.42.3.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett L. G., Glaudemans C. P. Binding studies with antibodies having phosphorylcholine specificity and fragments derived from their homologous Streptococcus pneumoniae type 27 capsular polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2356–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Claflin J. L., Schroer K., Forman C. Mouse Igg3 antibodies are highly protective against infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):88–90. doi: 10.1038/294088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Nahm M., Schroer K., Davie J., Baker P., Kearney J., Barletta R. Antiphosphocholine antibodies found in normal mouse serum are protective against intravenous infection with type 3 streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):694–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundish D. E., Baddiley J. Pneumococcal C-substance, a ribitol teichoic acid containing choline phosphate. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):573–582. doi: 10.1042/bj1100573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubos R. J. IMMUNIZATION OF EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS WITH A SOLUBLE ANTIGEN EXTRACTED FROM PNEUMOCOCCI. J Exp Med. 1938 Apr 30;67(5):799–808. doi: 10.1084/jem.67.5.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Parkes L., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Protection against group B meningococcal disease. I. Comparison of group-specific and type-specific protection in the chick embryo model. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):319–329. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara M. Immunological properties of anti-pneumococcus rabbit serum as heterophile antibodies. Jpn J Exp Med. 1968 Feb;38(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J., Johnson N. D., Douglas R., Hood L. IgG antibodies to phosphorylcholine exhibit more diversity than their IgM counterparts. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):29–34. doi: 10.1038/291029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaudemans C. P. The interaction of homogeneous, murine myeloma immunoglobulins with polysaccharide antigens. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1975;31:313–346. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60299-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel W. F., Adams M. H. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HETEROPHILE ANTIGEN AND SOMATIC POLYSACCHARIDE OF PNEUMOCOCCUS. J Exp Med. 1943 May 1;77(5):435–449. doi: 10.1084/jem.77.5.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodner K., Horsfall F. L. THE PROTECTIVE ACTION OF TYPE I ANTIPNEUMOCOCCUS SERUM IN MICE : I. THE QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF THE MOUSE PROTECTION TEST. J Exp Med. 1935 Aug 31;62(3):359–374. doi: 10.1084/jem.62.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y. Structural and immunological studies on the pneumococcal C polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):463–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger M., Sia R. H., Kendall F. E. SPECIFIC PRECIPITATION AND MOUSE PROTECTION IN TYPE I ANTIPNEUMOCOCCUS SERA. J Exp Med. 1930 Sep 30;52(4):477–483. doi: 10.1084/jem.52.4.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C., Young N. M. Structure of the complex polysaccharide C-substance from Streptococcus pneumoniae type 1. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 30;19(20):4712–4719. doi: 10.1021/bi00561a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Klemperer M. R., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. The enhancement of bacterial phagocytosis by serum. The role of complement components and two cofactors. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1275–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon M. A., Young N. M. Specificity for phosphorylcholine of six murine myeloma proteins reactive with Pneumococcus C polysaccharide and beta-lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1424–1429. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod C. M., Hodges R. G., Heidelberger M., Bernhard W. G. PREVENTION OF PNEUMOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA BY IMMUNIZATION WITH SPECIFIC CAPSULAR POLYSACCHARIDES. J Exp Med. 1945 Nov 30;82(6):445–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mold C., Nakayama S., Holzer T. J., Gewurz H., Du Clos T. W. C-reactive protein is protective against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1703–1708. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira E. B., Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y. Comparative studies on the binding properties of human and rabbit C-reactive proteins. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1396–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Antigen-binding myeloma proteins of mice. Adv Immunol. 1977;25:141–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poxton I. R., Tarelli E., Baddiley J. The structure of C-polysaccharide from the walls of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):1033–1042. doi: 10.1042/bj1751033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman G., Bornstein D. L., Austrian R. Capsulation of pneumococcus with soluble cell wall-like polysaccharide. II. Nonidentity of cell wall and soluble cell wall-like polysaccharides derived from the same and from different pneumococcal strains. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):600–617. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Barrera O., Sutton A., Robbins J. B. Preparation, characterization, and immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-protein conjugates. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):361–376. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillett W. S. ACTIVE AND PASSIVE IMMUNITY TO PNEUMOCOCCUS INFECTION INDUCED IN RABBITS BY IMMUNIZATION WITH R PNEUMOCOCCI. J Exp Med. 1928 Nov 30;48(6):791–804. doi: 10.1084/jem.48.6.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillett W. S. STUDIES ON IMMUNITY TO PNEUMOCOCCUS MUCOSUS (TYPE III) : III. INCREASED RESISTANCE TO TYPE III INFECTION INDUCED IN RABBITS BY IMMUNIZATION WITH R AND S FORMS OF PNEUMOCOCCUS. J Exp Med. 1927 Jul 31;46(2):343–356. doi: 10.1084/jem.46.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. R., Claflin J. L. Clonotypes of anti-phosphocholine antibodies induced with Proteus morganii (Potter). II. Heterogeneity, class, and idiotypic analyses of the repertoires in BALB/c and A/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):600–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Tomasz A. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by pneumococcal cell wall teichoic acid. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):174–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Forman C., Gray B. M., Briles D. E. Protection of mice from infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae by anti-phosphocholine antibody. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):184–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.184-188.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




