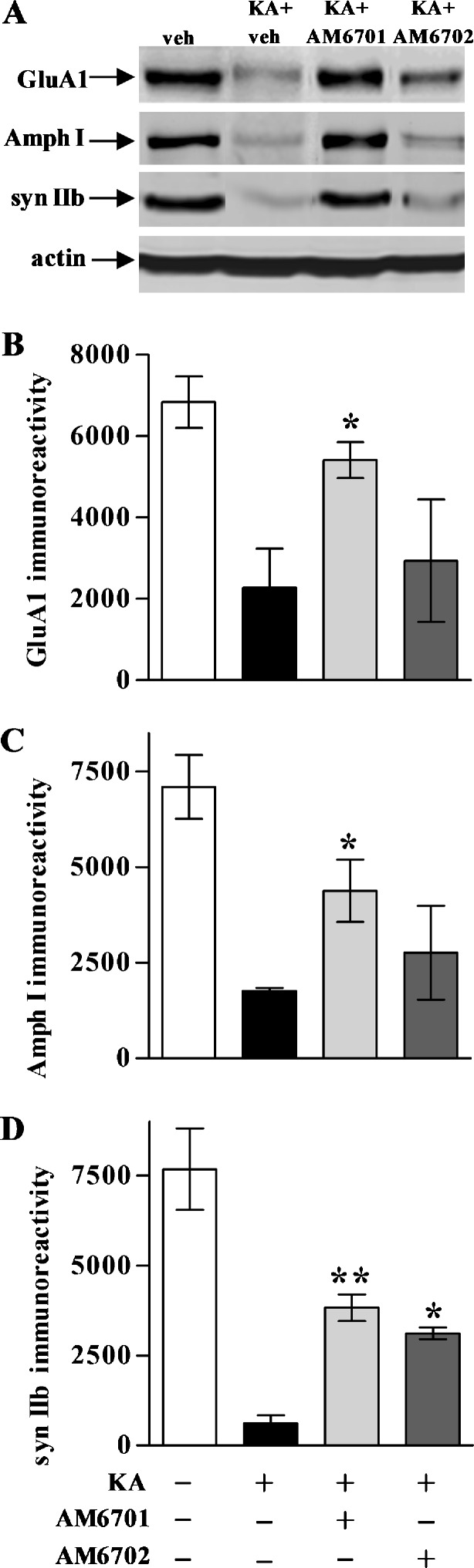
Fig. 4.
Synaptic protection in hippocampal slice cultures after kainic acid (KA)-induced excitotoxicity. Using the slice samples from Fig. 2, the slice cultures were treated with vehicle (veh) AM6701 or AM6702 for 1 h, and subsequently during the KA insult. Slices were harvested 24-h post-insult in groups of 6 to 8 each, and assessed by immunoblotting for the postsynaptic marker GluA1, the presynaptic markers amphiphysin I (Amph I) and synapsin IIb (syn IIb), and actin (a). Integrated optical densities for GluA1 (b) (analysis of variance, p = 0.019), Amph I (c) (p = 0.015), and syn IIb (d) (p < 0.01) are shown as means ± SEM across the treatment groups. Post hoc tests compared to KA only group: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01