Abstract
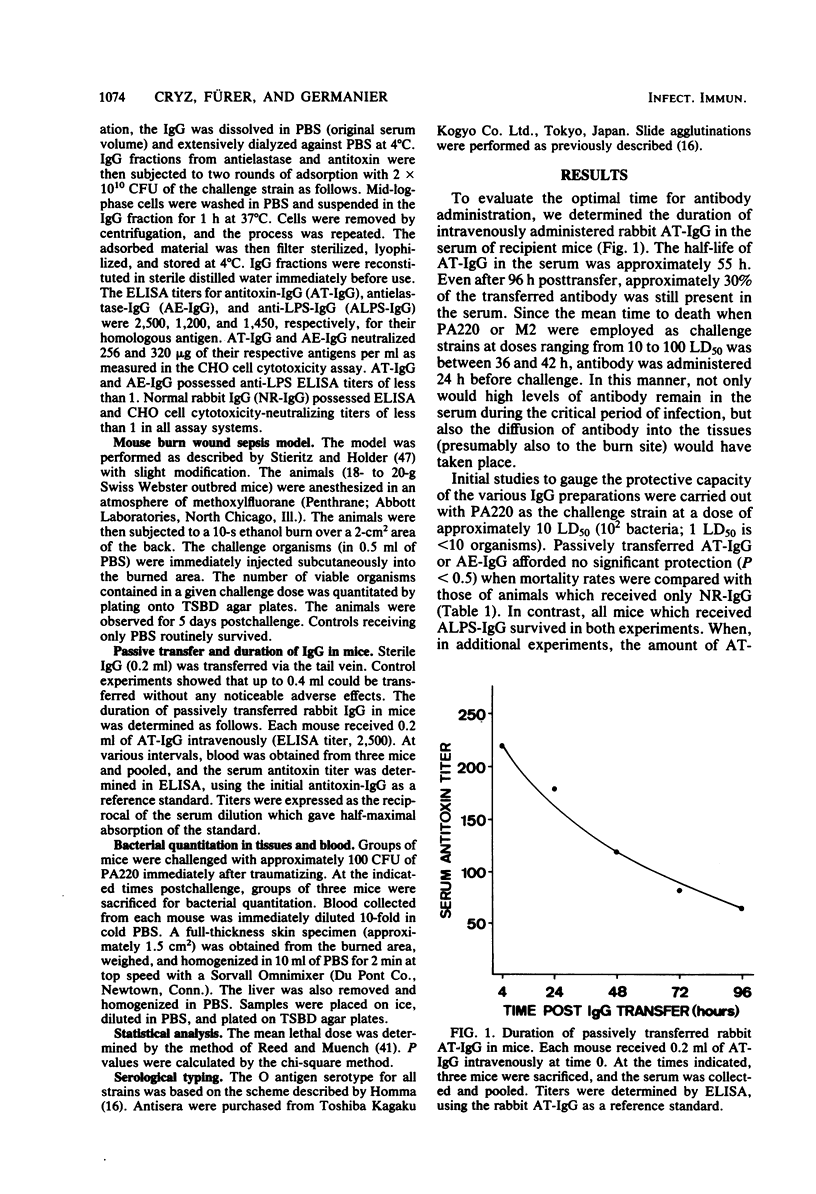
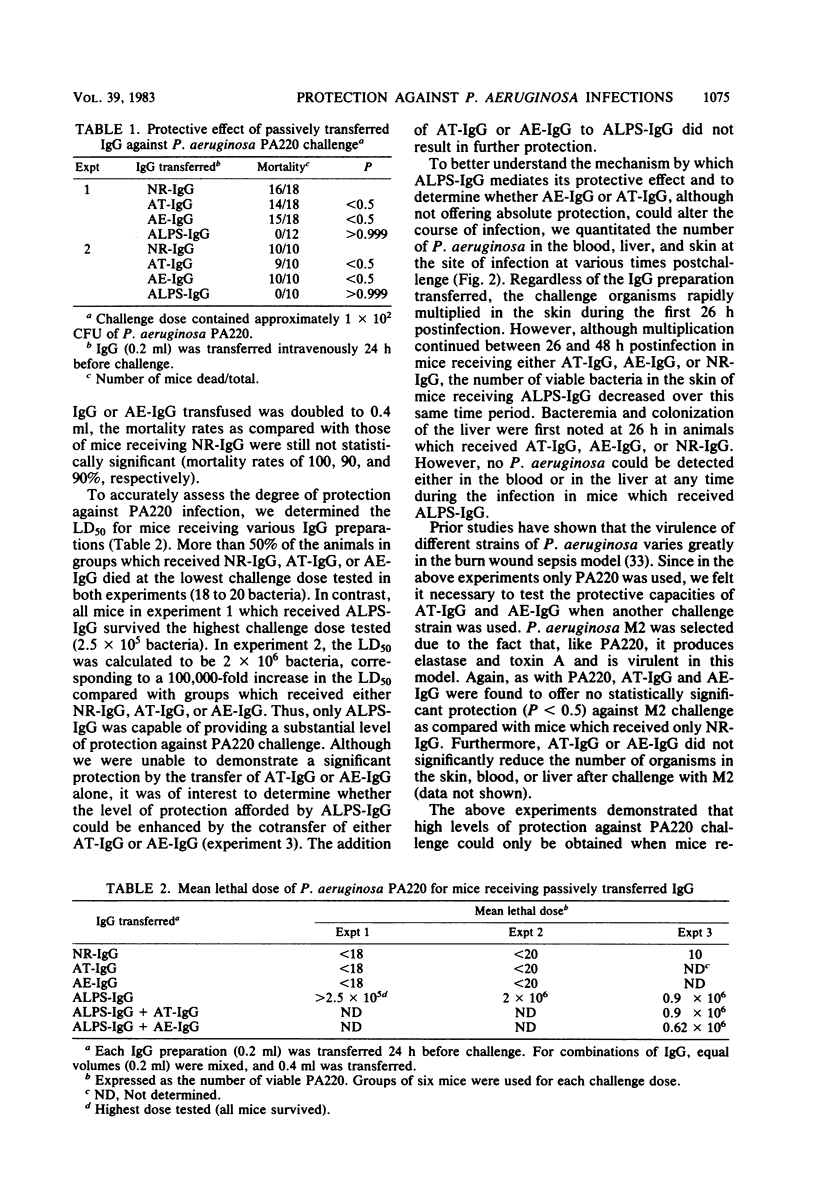
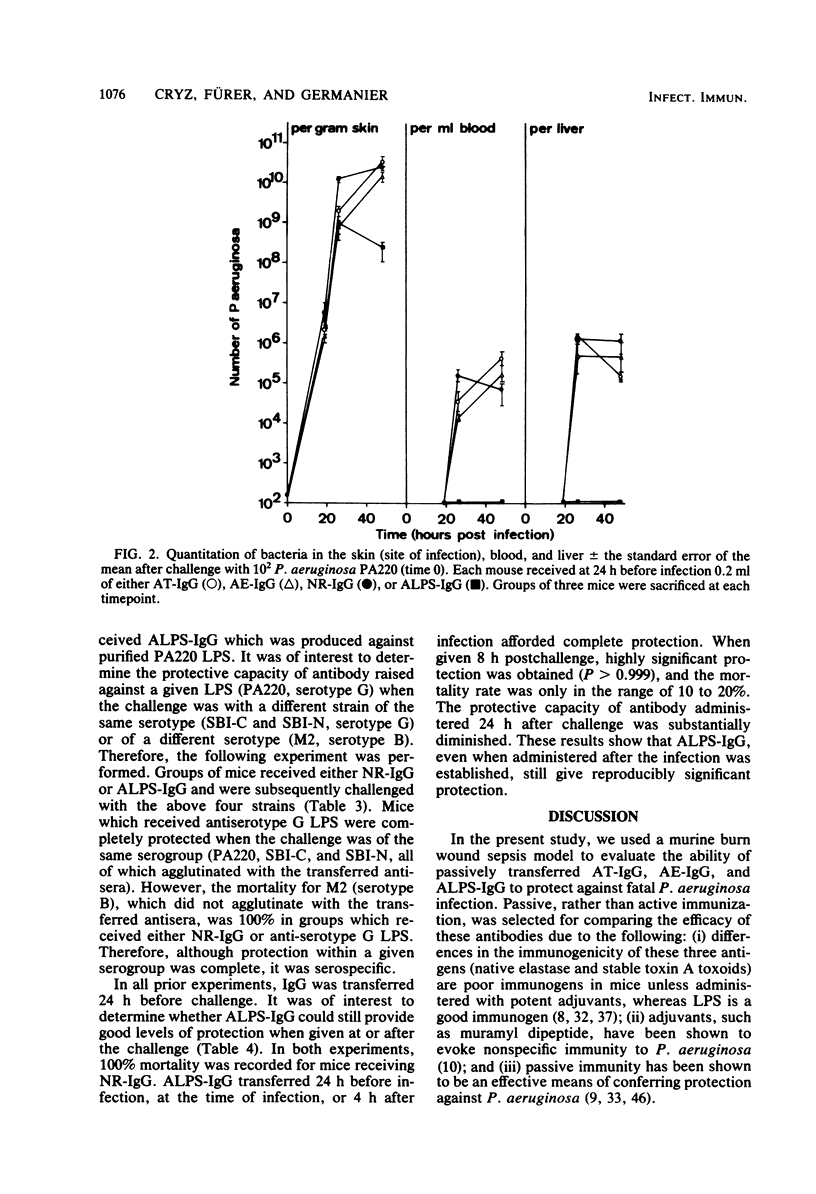
The protective capacity of passively transferred immunoglobulin G (IgG) fractions from antitoxin (AT-IgG), antielastase (AE-IgG), and antilipopolysaccharide (ALPS-IgG) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection was evaluated in a murine burn wound sepsis model. Complete protection was afforded by homologous ALPS-IgG against intermediate challenge doses (10 50% lethal doses) of P. aeruginosa PA220, whereas AT-IgG and AE-IgG offered no significant protection (P less than 0.5). The simultaneous transfer of AT-IgG or AE-IgG with ALPS-IgG gave no additional protection above that seen with ALPS-IgG alone. The transfer of ALPS-IgG did not dramatically alter bacterial multiplication in the skin at the site of infection. However, bacteremia and infection of the liver were prevented. In parallel experiments, AT-IgG or AE-IgG did not significantly alter either the course of the infection or the number of bacteria seen in the blood, liver, or skin when compared with controls. ALPS-IgG administered 24 h before infection, at the time of infection, or 4 h postinfection provided complete protection. Even when ALPS-IgG was transferred at a time when the infection was well established locally in the skin (8 h postinfection), highly significant protection (P greater than 0.999) was obtained. Protection afforded by ALPS-IgG was serotype specific. These results indicate that antibody to lipopolysaccharide is of critical importance for protection against P. aeruginosa challenge in a relevant animal model.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W., Fisher M. W. Immunological determinants of pseudomonas infections of man accompanying severe burn injury. J Trauma. 1970 Jul;10(7):565–574. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197007000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn M. J., Sokol P. A., Iglewski B. H. Influence of iron on yields of extracellular products in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):193–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.193-200.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges K., Lowbury E. J. Drug resistance in relation to use of silver sulphadiazine cream in a burns unit. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Feb;30(2):160–164. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.2.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H., Sokol P. A. Evidence for the role of toxin A in the pathogenesis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in humans. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):538–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowder J. G., Fisher M. W., White A. Type-specific immunity in pseudomonas diseases. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Jan;79(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowder J. G., Fisher M. W., White A. Type-specific immunity in pseudomonas diseases. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Jan;79(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe K. E., Bass J. A., Young V. M., Straus D. C. Antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproducts in cancer patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):115–122. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.115-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Friedman R. L., Pavlovskis O. R., Iglewski B. H. Effect of formalin toxoiding on Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A: biological, chemical, and immunochemical studies. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):759–768. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.759-768.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser-Smith E. B., Matthews T. R. Protective effect of muramyl dipeptide analogs against infections of Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Candida albicans in mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):676–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.676-683.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürer E., Cryz S. J., Jr, Dorner F., Nicolet J., Wanner M., Germanier R. Protection against colibacillosis in neonatal piglets by immunization of dams with procholeragenoid. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):887–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.887-894.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haghbin M., Armstrong D., Murphy M. L. Controlled prospective trial of Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in children with acute leukemia. Cancer. 1973 Oct;32(4):761–766. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197310)32:4<761::aid-cncr2820320405>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanessian S., Regan W., Watson D., Haskell T. H. Isolation and characterization of antigenic components of a new heptavalent Pseudomonas vaccine. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 17;229(7):209–210. doi: 10.1038/newbio229209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holby N., Olling S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Bactericidal effect of serum from normal individuals and patients with cystic fibrosis on P. aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis or other diseases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Apr;85(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Wheeler R., Montie T. C. Flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: animal protection studies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):276–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.276-280.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. E., Alexander J. W., Fisher M. Clinical evaluation of Pseudomonas hyperimmune globulin. J Surg Res. 1973 Feb;14(2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(73)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Gupta J. L. Controlled trials of a polyvalent pseudomonas vaccine in burns. Lancet. 1979 Nov 10;2(8150):977–982. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92559-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Abe C., Homma J. Y., Kawano M., Goto E. Corneal ulcers caused by protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1974 Oct;44(5):435–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y., Aoyama Y., Okada K., Morihara K. Effects of protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa on skin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Apr;45(2):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H., OKA T., INOUE H., EBATA M. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ELASTASE. ISOLATION, CRYSTALLIZATION, AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miler J. M., Spilsbury J. F., Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Lowbury E. J. A new polyvalent Pseudomonas vaccine. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):19–27. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan P., Holder I. A., MacMillan B. G. Burn wounds: microbiology, local host defenses, and current therapy. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1973 Jul;4(1):61–100. doi: 10.3109/10408367309151684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Burns R. P., Iglewski B. H. Corneal infections in mice with toxin A and elastase mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):547–555. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Edman D. C., Leppla S. H., Wretlind B., Lewis L. R., Martin K. E. Protection against experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in mice by active immunization with exotoxin A toxoids. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):681–689. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.681-689.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Iglewski B. H. Passive protection by antitoxin in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infections. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):596–602. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.596-602.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Wretlind B. Assessment of protease (elastase) as a Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor in experimental mouse burn infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):181–187. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.181-187.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Sidberry H. F., Sadoff J. C. High-molecular-weight polysaccharide antigen from Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype 2. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):461–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.461-468.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Sidberry H. F., Sadoff J. C. Protective immunity induced in mice by immunization with high-molecular-weight polysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):919–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.919-925.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Sidberry H. F., Zolyomi S., Sadoff J. C. Isolation and characterization of a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide from the slime of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):908–918. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.908-918.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Taylor N. S. Neutralizing antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in human sera: evidence for in vivo toxin production during infection. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):942–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.942-947.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Young L. S. Protective activity of antibodies to exotoxin A and lipopolysaccharide at the onset of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):276–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seid R. C., Jr, Sadoff J. C. Preparation and characterization of detoxified lipopolysaccharide-protein conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7305–7310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell K., Holder I. A., Leppla S. A., Saelinger C. B. Role of exotoxin and protease as possible virulence factors in experimental infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.839-845.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieritz D. D., Holder I. A. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: description of a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):688–691. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker H. L., McLeod C. G., Jr, Leppla S. H., Mason A. D., Jr Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A in experimental rat burn wound sepsis. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):828–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.828-830.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitecar J. P., Jr, Luna M., Bodey G. P. Pseudomonas bacteremia in patients with malignant diseases. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Oct;60(4):216–223. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197010000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Cryz S. J., Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Contribution of toxin A and elastase to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infections of rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1223–1228. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1223-1228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Relationship between heat-stable opsonins and type-specific lipopolysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):277–287. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



