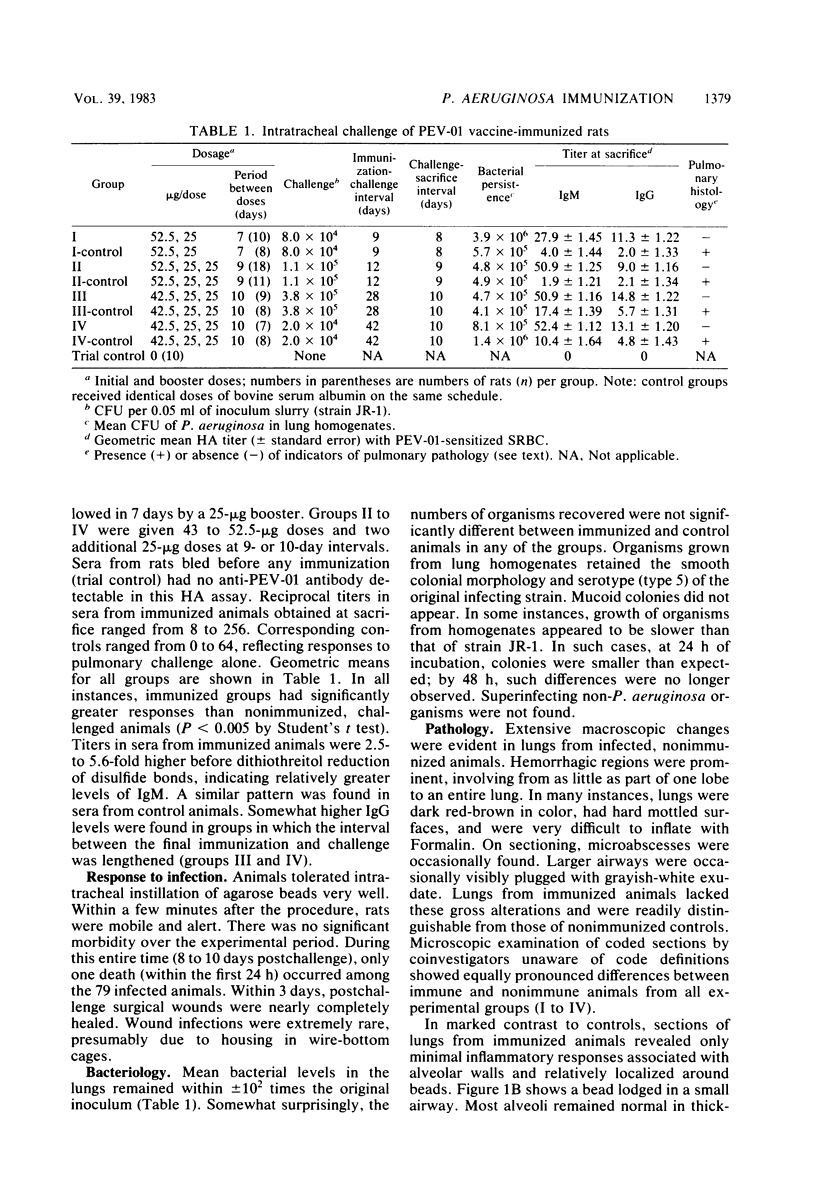
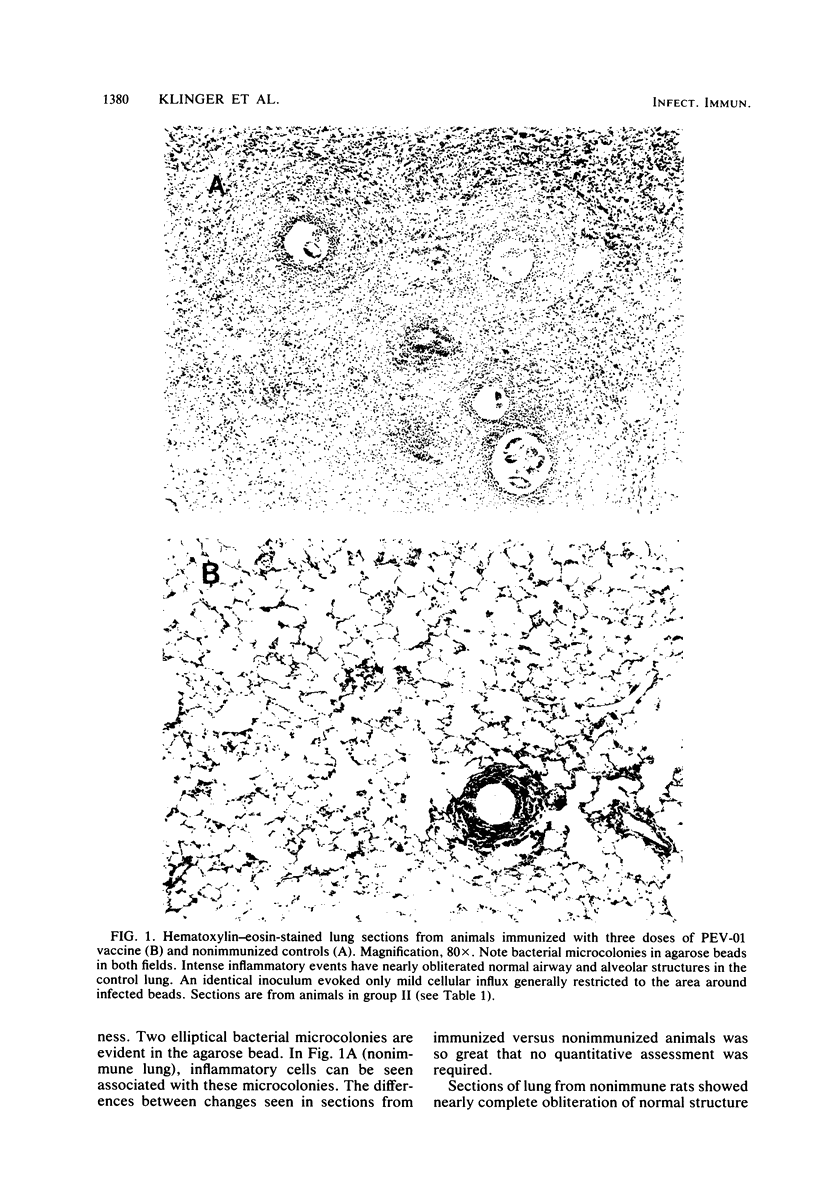
Abstract
Rats were immunized systemically with various doses of the polyvalent Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine PEV-01. After a series of two or three doses (25 to 50 micrograms each) at 8- to 11-day intervals, animals were challenged intratracheally by the agarose bead technique with a serotype 5 P. aeruginosa strain at periods of 9 to 42 days. Immunized animals developed circulating antibodies (primarily immunoglobulin M) against vaccine components at levels significantly higher than challenged, nonimmunized controls (P less than 0.005). Eight to ten days postinfection, histological sections of lungs from immunized animals showed only minimal inflammation associated with infectious foci (agarose beads) as compared with the extensive pathological changes of airways and parenchyma seen in infected nonimmunized control animals. However, no significant reduction in bacterial numbers was observed. Such protection lasted at least 6 weeks after the final immunization. It is speculated that the vaccine may contain components of cell surface proteins and virulence exoproducts.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W., Fisher M. W., MacMillan B. G. Immunological control of Pseudomonas infection in burn patients: a clinical evaluation. Arch Surg. 1971 Jan;102(1):31–35. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1971.01350010033008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alms T. H., Bass J. A. Immunization against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Induction of protection by an alcohol-precipitated fraction from the slime layer. J Infect Dis. 1967 Jun;117(3):249–256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdischewsky M., Pollack M., Young L. S., Chia D., Osher A. B., Barnett E. V. Circulating immune complexes in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Res. 1980 Jun;14(6):830–833. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198006000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash H. A., Woods D. E., McCullough B., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. A rat model of chronic respiratory infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):453–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Cundy K. R. Demonstration of cell envelope-bound exotoxin A in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):411–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.411-416.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haghbin M., Armstrong D., Murphy M. L. Controlled prospective trial of Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in children with acute leukemia. Cancer. 1973 Oct;32(4):761–766. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197310)32:4<761::aid-cncr2820320405>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanessian S., Regan W., Watson D., Haskell T. H. Isolation and characterization of antigenic components of a new heptavalent Pseudomonas vaccine. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 17;229(7):209–210. doi: 10.1038/newbio229209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidbrink P. J., Toews G. B., Gross G. N., Pierce A. K. Mechanisms of complement-mediated clearance of bacteria from the murine lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 May;125(5):517–520. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.5.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Abe C., Tanamoto K., Hirao Y., Morihara K., Tsuzuki H., Yanagawa R., Honda E., Aoi Y., Fujimoto Y. Effectiveness of immunization with single and multi-component vaccines prepared from a common antigen (OEP), protease and elastase toxoids of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on protection against hemorrhagic pneumonia in mink due to P. aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1978 Apr;48(2):111–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Wiik A. Antibacterial precipitins and autoantibodies in serum of patients with cystic fibrosis. Scand J Respir Dis. 1975 May;56(1):38–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Gupta J. L. Controlled trial of Pseudomonas immunoglobulin and vaccine in burn patients. Lancet. 1980 Dec 13;2(8207):1263–1265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92334-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Gupta J. L. Low mortality in burned patients in a Pseudomonas vaccine trial. Lancet. 1978 Aug 19;2(8086):401–403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91868-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Lowbury E. J., Miler J. J., Spilsbury J. F. A new Pseudomonas vaccine: preliminary trial on human volunteers. J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Jun;76(3):429–439. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400055364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Roe E. A. Protective properties and haemagglutinins in serum from humans and in serum from mice injected with a new polyvalent Pseudomonas vaccine. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Feb;56(1):34–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Straus D. C., Hilton C. B., Bass J. A. Antibodies to proteases and exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis: Demonstration by radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):49–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J., Chan R., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.546-556.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Studies on the permeability change produced in coliform bacteria by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2373–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Hsieh H. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 3. Characteristics of antitoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):520–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W. J., Jr, Williams M., Oliphint B., Geha R., Colten H. R. Hypogammaglobulinemia in patients with cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 31;302(5):245–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001313020501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane H., Holzel A., Brenchley P., Allan J. D., Wallwork J. C., Singer B. E., Worsley B. Immune complexes in cystic fibrosis. Br Med J. 1975 Feb 22;1(5955):423–428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5955.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1139/m77-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miler J. M., Spilsbury J. F., Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Lowbury E. J. A new polyvalent Pseudomonas vaccine. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):19–27. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan P., Holder I. A., MacMillan B. G. Burn wounds: microbiology, local host defenses, and current therapy. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1973 Jul;4(1):61–100. doi: 10.3109/10408367309151684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Hickey W. F., Blackwood L. L., Arnaut M. A. Active immunization with lipopolysaccharide Pseudomonas antigen for chronic Pseudomonas bronchopneumonia in guinea pigs. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1140–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI110358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Kuchmy D. Mechanism for pulmonary protection by lipopolysaccharide pseudomonas vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):191–198. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E. Lipopolysaccharide pseudomonas vaccine: efficacy against pulmonary infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):73–80. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Miler J. J. Evaluation of a new polyvalent Pseudomonas vaccine in respiratory infections. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1029–1034. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1029-1034.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Reynolds H. Y., Wood R. E., Robinson R. A., Levine A. S. Use of a Pseudomonas Aeruginosa vaccine in pateints with acute leukemia and cystic fibrosis. Am J Med. 1975 May;58(5):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90498-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirofsky B., Rosner E. R. DTT test: a new method to differentiate IgM and IgG erythrocyte antibodies. Vox Sang. 1974;27(5):480–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1974.tb02446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Anderson S. E., Jr Toxicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A for human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1092–1096. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1092-1096.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Taylor N. S. Serum antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin measured by a passive hemagglutination assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.58-61.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Young L. S. Protective activity of antibodies to exotoxin A and lipopolysaccharide at the onset of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):276–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiotz P. O., Hoiby N., Juhl F., Permin H., Nielsen H., Svehag S. E. Immune complexes in cystic fibrosis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Feb;85(1):57–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb03611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz D. R., Miller K. D. Elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: inactivation of complement components and complement-derived chemotactic and phagocytic factors. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):128–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.128-135.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell K., Holder I. A., Leppla S. A., Saelinger C. B. Role of exotoxin and protease as possible virulence factors in experimental infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.839-845.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAHBA A. H., DARRELL J. H. THE IDENTIFICATION OF ATYPICAL STRAINS OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Mar;38:329–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





