Abstract
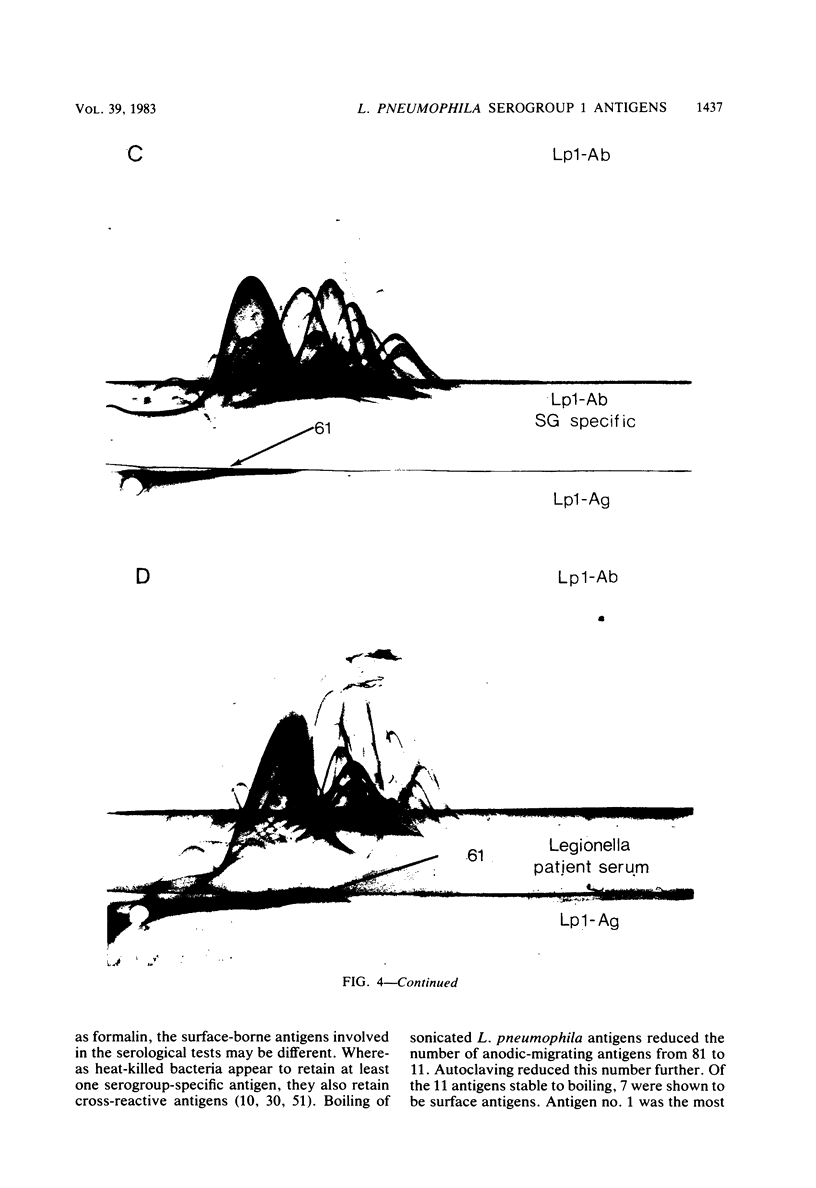
By crossed immunoelectrophoresis, 85 different antigens were demonstrated in sonicated preparations of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 (Lp1). The precipitin patterns of 82 anodic-migrating antigens were numbered and were designated the Lp1 reference system. Eleven antigens were stable to boiling, and seven of these were shown to be surface antigens. One heat-stable surface antigen (antigen no. 61) was highly reactive with limulus amoebocyte lysates and formed a precipitin resembling lipopolysaccharide. Serum from an isolation confirmed case of Lp1 infection and serogroup-specific rabbit antiserum reacted specifically with antigen no. 61, which was designated the serogroup-specific antigen. Normal human and rabbit sera commonly had antibodies to antigen no. 66 of the Lp1 reference system. This antigen is antigenically related to the "common antigen" of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsen N. H. Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods as tools for a polyvalent approach to standardization in the immunochemistry of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):949–960. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.949-960.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Sorg R. J., Thomason B. M., Hicklin M. D., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J., Wulf M. R. Recognition of a second serogroup of Legionella longbeachae. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):674–677. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.674-677.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. T., Jones P. W. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis and crossed-line immunoelectrophoresis of Salmonella dublin antigens. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):315–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Gorman G. W., Orrison L. H., Moss C. W., Steigerwalt A. G., Wilkinson H. W., Johnson S. E., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. Legionella jordanis: a new species of Legionella isolated from water and sewage. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):290–297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.290-297.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Pittman B., Harris P. P., Hebert G. A., Thomason B. M., Thacker L., Weaver R. E. Detection of Legionnaires disease bacteria by direct immunofluorescent staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):329–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.329-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., McKinney R. M., Meyer R. D., Edelstein M. A., Krause C. J., Finegold S. M. Immunologic diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease: cross-reactions with anaerobic and microaerophilic organisms and infections caused by them. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):652–655. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. A., Johnson W., Helms C. M. Ultrastructural localization and protective activity of a high-molecular-weight antigen isolated from Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):822–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.822-824.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. A., Johnson W. Immunological and biochemical relationships among flagella isolated from Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1, 2, and 3. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):602–610. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.602-610.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England A. C., 3rd, McKinney R. M., Skaliy P., Gorman G. W. A fifth serogroup of Legionella pneumophila. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):58–59. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Hertz J. B., Høiby N., Mogensen H. H. Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Salmonella typhi antigens and of corresponding antibodies in human sera. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Aug;88(4):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshy C. E., Klein G. C., Feeley J. C. Detection of antibodies to legionnaires disease organism by microagglutination and micro-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):327–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.327-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz J. B., Hølby N., Andersen V., Baekgaard P. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Bordetella pertussis antigens and of corresponding antibodies in human sera. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Dec;84B(6):386–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Axelsen N. H. Identification and quantitation of precipitins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Moss C. W., McDougal L. K., Bozeman F. M., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. The rickettsia-like organisms TATLOCK (1943) and HEBA (1959): bacteria phenotypically similar to but genetically distinct from Legionella pneumophila and the WIGA bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):45–52. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Thomason B. M., Harris P. P., Hicklin M. D., McKinney R. M. "Pittsburgh pneumonia agent": a bacterium phenotypically similar to Legionella pneumophila and identical to the TATLOCK bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):53–54. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Hertz J. B., Sompolinsky D. Antibody response in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection to a 'common antigen' from P. aeruginosa analysed by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Jun;88(3):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of Legionella pneumophila and Tatlockia micdadei (Legionella micdadei) by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):721–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.721-729.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B. Immunological studies of an antigen common to many gram-negative bacteria with special reference to E. coli. Characterization and biological significance. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(1):72–81. doi: 10.1159/000231293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. C. Cross-reaction to Legionella pneumophila antigen in sera with elevated titers to Pseudomonas pseudomallei. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):27–29. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.27-29.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Porschen R. K., Edelstein P. H., Bissett M. L., Harris P. P., Bondell S. P., Steigerwalt A. G., Weaver R. E., Ein M. E., Lindquist D. S. Legionella longbeachae species nova, another etiologic agent of human pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):739–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Thacker L., Harris P. P., Lewallen K. R., Hebert G. A., Edelstein P. H., Thomason B. M. Four serogroups of Legionnaires' disease bacteria defined by direct immunofluorescence. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):621–624. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W., Sommers H. M., Fikes B. J., Sasseville K. R., Yungbluth M. M., Wolf J. S. Legionella pneumophila serogroup six: isolation from cases of legionellosis, identification by immunofluorescence staining, and immunological response to infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.395-401.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen O. S. Serotyping of Pseudomonas aerunginosa. I. Studies on the production of anti O sera. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;73(3):373–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Steigerwalt A., Feeley J. C., Wong E. S., Martin W. T., Patton C. M., Brenner D. J. Legionella gormanii sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):718–721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.718-721.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Lattimer G. L., Page L. A., Fiset P. Legionnaires' disease: antigenic peculiarities, strain differences, and antibiotic sensitivities of the agent. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):260–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Myerowitz R. L., Rinaldo C. R., Jr New bacterial agent of pneumonia isolated from renal-transplant recipients. Lancet. 1979 Jul 14;2(8133):58–61. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold R. B., Fine J. A technique for quantitative measurement of endotoxin in human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):334–340. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiøtz P. O., Høiby N., Hertz J. B. Cross-reactions between Haemophilus influenzae and nineteen other bacterial species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Dec;87(6):337–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., DiGiorgio S., Darner J., Wilhelm A. Detection of Legionella pneumophila capsular-like envelope antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):637–642. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.637-642.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Salton M. R. Antigenic analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1273–1288. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1273-1288.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Siegel J., Salton M. R., Owen P. Immunochemical analysis of inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):306–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.306-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Hertz J. B., Høiby N., Jensen K., Mansa B., Pedersen V. B., Samra Z. An antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. 2. A biochemical study of a "common antigen" from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Oct;88(5):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. A manual of quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. Methods and applications. 1. General remarks on principles, equipment, reagents and procedures. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:15–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Cruce D. D., Broome C. V. Validation of Legionella pneumophila indirect immunofluorescence assay with epidemic sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.139-146.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Farshy C. E., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D., Yealy L. P. Measure of immunoglobulin G-, M-, and A-specific titers against Legionella pneumophila and inhibition of titers against nonspecific, gram-negative bacterial antigens in the indirect immunofluorescence test for legionellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):685–689. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.685-689.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D. Indirect immunofluorescence test for serodiagnosis of Legionnaires disease: evidence for serogroup diversity of Legionnaires disease bacterial antigens and for multiple specificity of human antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):379–383. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.379-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Schalla W. O., Arko R. J., Bullard J. C., Feeley J. C. Immunochemical, serologic, and immunologic properties of major antigens isolated from the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Observations bearing on the feasibility of a vaccine. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):634–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Galanos C., Kinsky S., Bradshaw R. A., Wessler S., Lüderitz O., Sarmiento M. E. Picogram-sensitive assay for endotoxin: gelation of Limulus polyphemus blood cell lysate induced by purified lipopolysaccharides and lipid A from Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 28;261(1):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]