Abstract
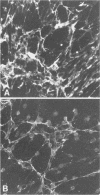
Clostridium difficile cytotoxin caused an irreversible dose- and time-dependent loss of fibronectin from the surfaces of human lung fibroblasts, paralleling the appearance of the cytopathic effect. Fibronectin was not required for the intoxication process. The results lend further support to a transmembrane connective link between fibronectin and the microfilaments.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali I. U., Hynes R. O. Effects of cytochalasin B and colchicine on attachment of a major surface protein of fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 15;471(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90388-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronsson B., Möllby R., Nord C. E. Clostridium difficile and antibiotic associated diarrhoea in Sweden. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;35:53–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Moon N., Chang T. W., Taylor N., Onderdonk A. B. Role of Clostridium difficile in antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Nov;75(5):778–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L., Onderdonk A. B. Clindamycin-induced enterocolitis in hamsters as a model of pseudomembranous colitis in patients. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):526–529. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.526-529.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Lin P. S., Gorbach S. L., Bartlett J. G. Ultrastructural changes of cultured human amnion cells by Clostridiu difficile toxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):795–798. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.795-798.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Shaffer S. J. Effects of Clostridium difficile toxin on tissue-cultured cells. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):218–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin I., Thelestam M. Intoxication of cultured human lung fibroblasts with Clostridium difficile toxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):67–74. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.67-74.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R. H., Symonds J. M., Dimock F., Brown J. D., Arabi Y., Shinagawa N., Keighley M. R., Alexander-Williams J., Burdon D. W. Identification of Clostridium difficile as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1978 Mar 18;1(6114):695–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6114.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Ash J. F., Singer S. J. Transmembrane linkage of fibronectin to intracellular actin-containing filaments in cultured human fibroblasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:414–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Ali I. U., Destree A. T., Mautner V., Perkins M. E., Senger D. R., Wagner D. D., Smith K. K. A large glycoprotein lost from the surfaces of transformed cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:317–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T., Mautner V. M., Ali I. U. Synthesis, secretion, and attachment of LETS glycoprotein in normal and transformed cells. J Supramol Struct. 1977;7(3-4):397–408. doi: 10.1002/jss.400070311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. Relationships between fibronectin (LETS protein) and actin. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurkinen M., Wartiovaara J., Vaheri A. Cytochalasin B releases a major surface-associated glycoprotein, fibronectin, from cultured fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jan;111(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Price A. B., Honour P., Borriello S. P. Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1978 May 20;1(8073):1063–1066. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90912-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby J. M., Wilkins T. D. Production of antitoxins to two toxins of Clostridium difficile and immunological comparison of the toxins by cross-neutralization studies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):374–376. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.374-376.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. F., Godman G. C., Tanenbaum S. W. Action of cytochalasin D on cells of established lines. II. Cortex and microfilaments. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):406–423. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Vaheri A. Thrombin stimulates the production and release of a major surface-associated glycoprotein (fibronectin) in cultures of human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Mar 15;112(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pena S. D., Hughes R. C. Fibronectin-plasma membrane interactions in the adhesion and spreading of hamster fibroblasts. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):80–83. doi: 10.1038/276080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I. The fibronexus: a transmembrane association of fibronectin-containing fibers and bundles of 5 nm microfilaments in hamster and human fibroblasts. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):675–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N. M., Pellett S., Wilkins T. D. Purification and characterization of toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1032–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1032-1040.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N. S., Thorne G. M., Bartlett J. G. Comparison of two toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1036-1043.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Brönnegård M. Interaction of cytopathogenic toxin from Clostridium difficile with cells in tissue culture. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;(Suppl 22):16–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Olden K. Fibronectins--adhesive glycoproteins of cell surface and blood. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):179–184. doi: 10.1038/275179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]