Abstract
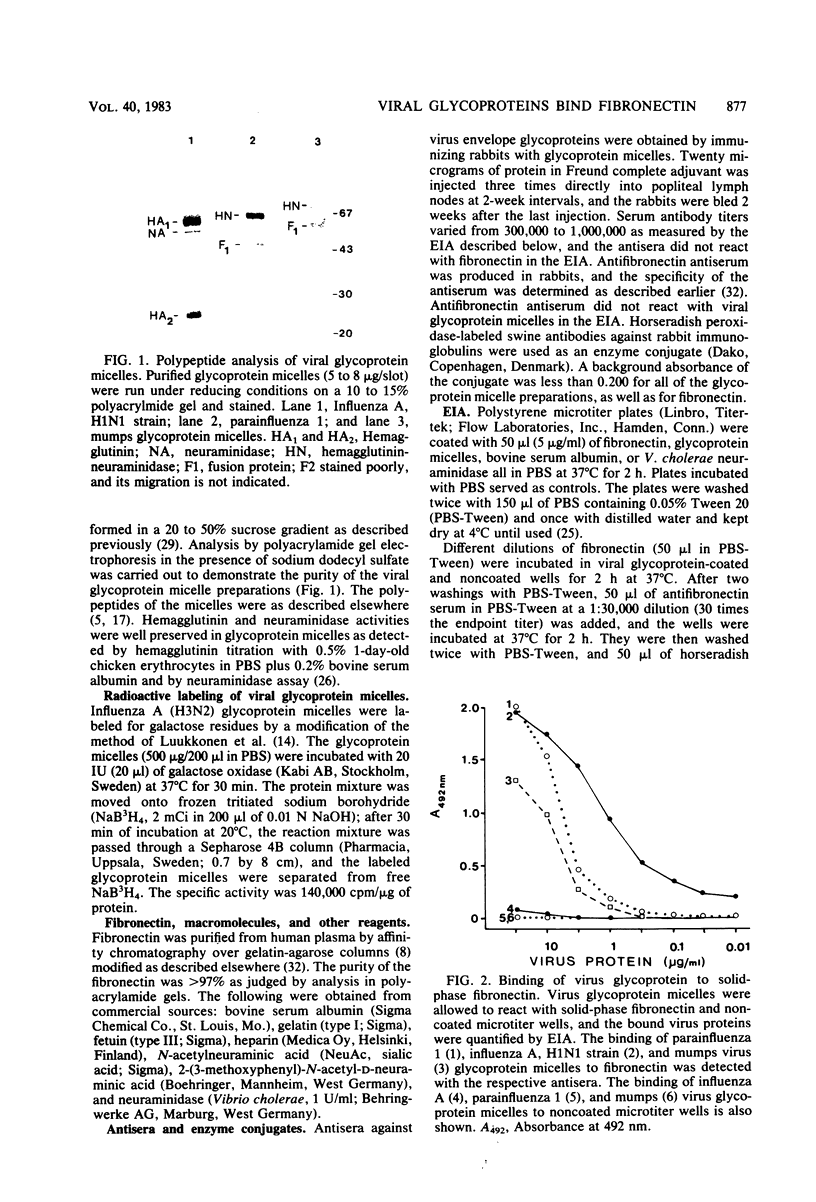
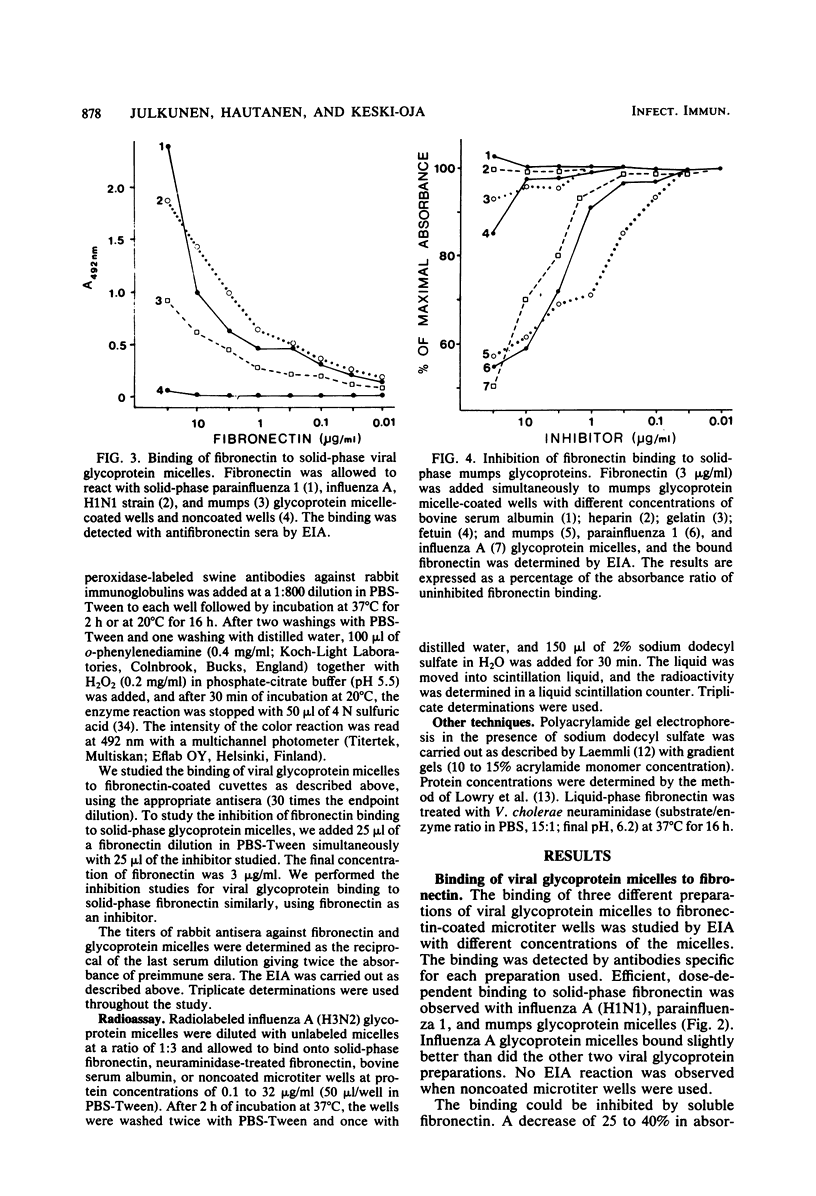
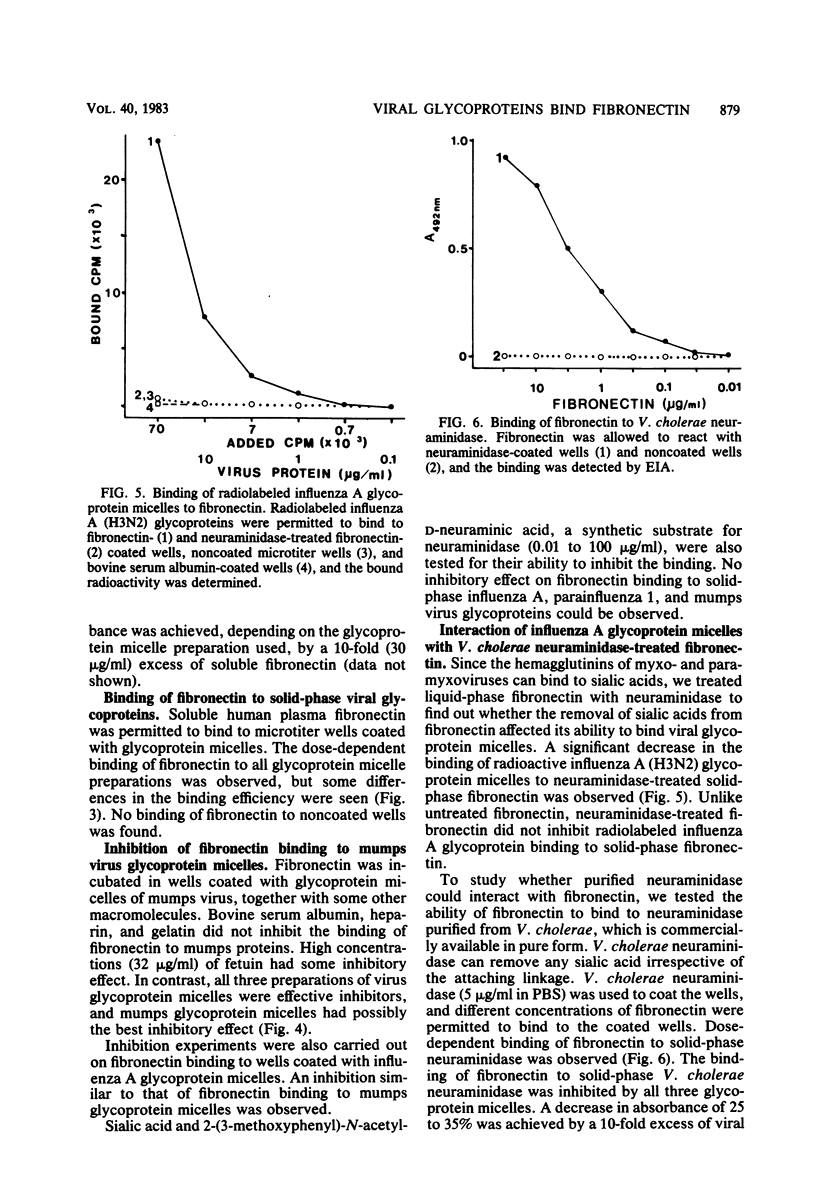
An interaction between fibronectin and viral envelope glycoprotein micelles isolated from influenza A, parainfluenza 1, and mumps viruses was found by enzyme immunoassay. All three different glycoprotein micelles bound efficiently to solid-phase fibronectin. When fibronectin was permitted to bind to solid-phase viral glycoproteins, dose-dependent binding was observed. Soluble glycoprotein micelles inhibited the binding of fibronectin to immobilized glycoprotein preparations. The binding was not observed when fibronectin was pretreated with neuraminidase, suggesting that the sugar moieties of fibronectin are responsible for the affinity. This affinity may play a role in virus-cell interactions or in the opsonization of certain viruses during infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structure of the complex oligosaccharides of fetuin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):789–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock F. A., Saba T. M., Weber P., Laffin R. Biochemical and immunological characterization of human opsonic alpha2SB glycoprotein: its identity with cold-insoluble globulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4287–4291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choppin P. W., Scheid A. The role of viral glycoproteins in adsorption, penetration, and pathogenicity of viruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Jan-Feb;2(1):40–61. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessau W., Jilek F., Adelmann B. C., Hörmann H. Similarity of antigelatin factor and cold insoluble globulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 28;533(1):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90566-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enegren B. J., Burness A. T. Chemical structure of attachment sites for viruses on human erythrocytes. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):536–537. doi: 10.1038/268536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E., Miller E. J. Affinity of fibronectin to collagens of different genetic types and to fibrinogen. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1584–1595. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Ruoslahti E., Engvall E. Binding of fibronectin to actin is inhibited by gelatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun;100(4):1515–1522. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90690-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Paulson J. C. Sendai virus utilizes specific sialyloligosaccharides as host cell receptor determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):601–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M., Johnson R. T. A comparison of the structural polypeptides of five strains of mumps virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jan;46(1):15–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morein B., Helenius A., Simons K., Pettersson R., Käriäinen L., Schirrmacher V. Effective subunit vaccines against an enveloped animal virus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):715–718. doi: 10.1038/276715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Fibronectin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:111–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan R. J., Loughlin M., Labat D. D., Howe C. Properties of influenza C virus grown in cell culture. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):875–882. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.875-882.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Prendergast E., Mosher D. F. Fibronectin mediates attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to human neutrophils. Blood. 1982 Apr;59(4):681–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E., Hayman E. G. Fibronectin: current concepts of its structure and functions. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):95–128. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Blumenstock F. A., Weber P., Kaplan J. E. Physiologic role of cold-insoluble globulin in systemic host defense: implications of its characterization as the opsonic alpha 2-surface-binding glycoprotein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:43–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A. Immobilization of viral and mycoplasma antigens and of immunoglobulins on polystyrene surface for immunoassays. J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(3):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santer U. V., Yee-Foon J., Glick M. C. A rapid assay for neuraminidase. The detection of two differences in activity associated with virus transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 12;523(2):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Isolation and purification of the envelope proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.263-271.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Helenius A., Leonard K., Sarvas M., Gething M. J. Formation of protein micelles from amphiphilic membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5306–5310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki S., Yamashita K., Suzuki K., Iwanaga S., Kobata A. The sugar chains of cold-insoluble globulin. A protein related to fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8548–8553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Kurkinen M., Lehto V. P., Linder E., Timpl R. Codistribution of pericellular matrix proteins in cultured fibroblasts and loss in transformation: fibronectin and procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4944–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peterson P. K., Smith D. E., Nguyen B. Y., Hoidal J. R., Wilkinson B. J., Verhoef J., Furcht L. T. Human fibronectin binding to staphylococcal surface protein and its relative inefficiency in promoting phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.811-819.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters G., Kuijpers L., Kacaki J., Schuurs A. Solid-phase enzyme-immunoassay for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Oct;29(10):873–879. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.10.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Bass J. A., Johanson W. G., Jr, Straus D. C. Role of adherence in the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):694–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.694-699.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. Role of fibronectin in the prevention of adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to buccal cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):784–790. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrann M. Methylation analysis of the carbohydrate portion of fibronectin isolated from human plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 14;84(1):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




