Abstract
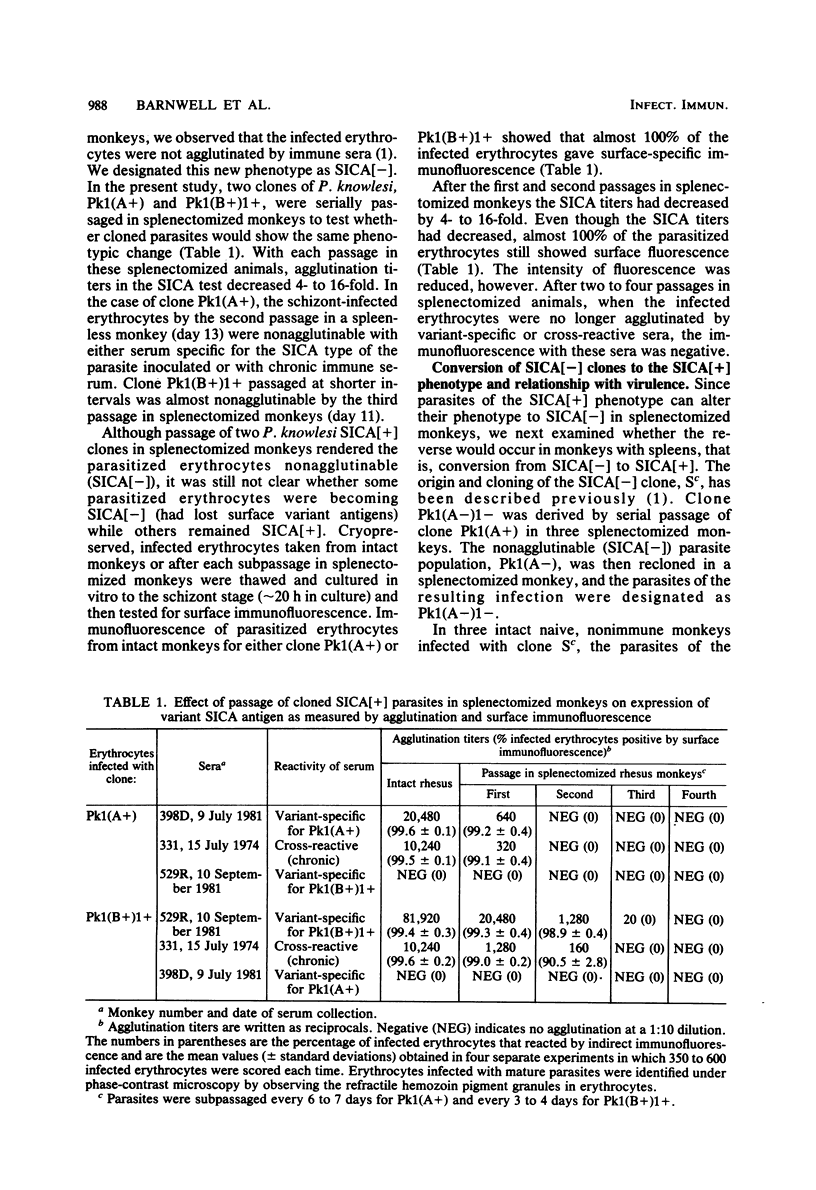
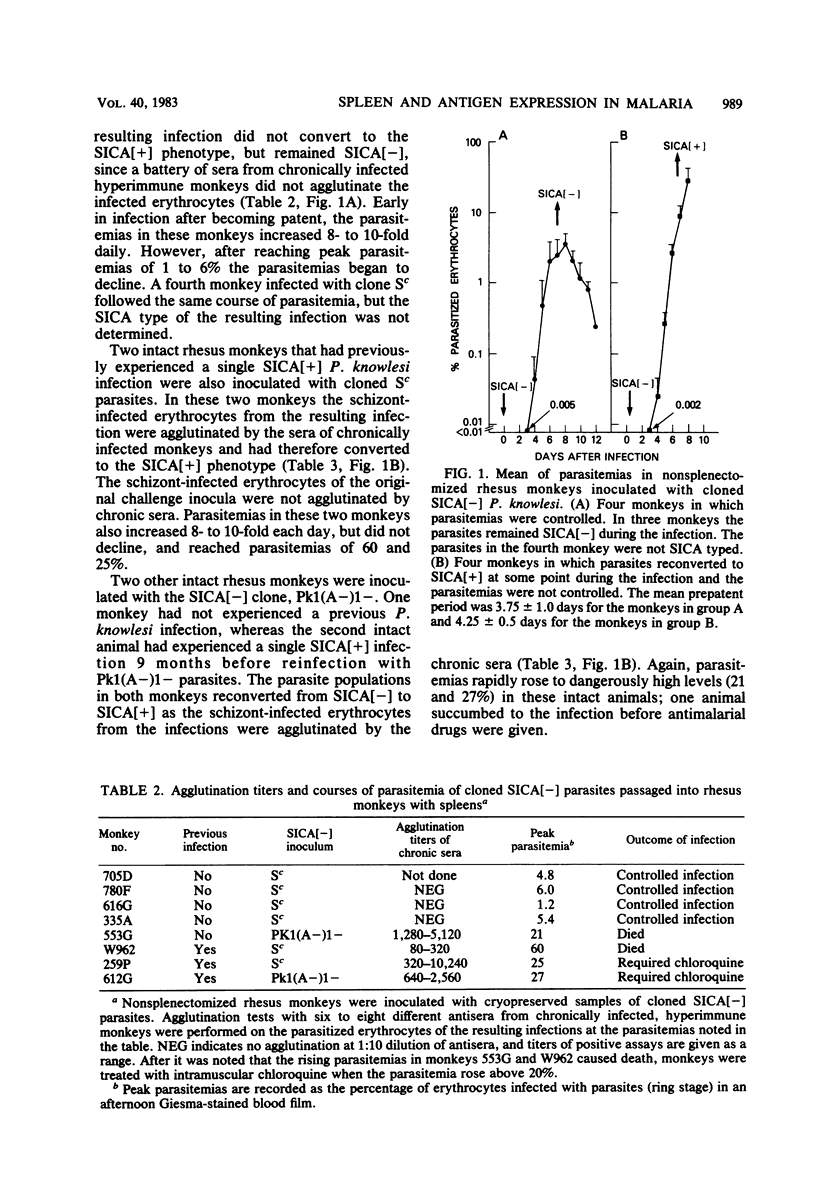
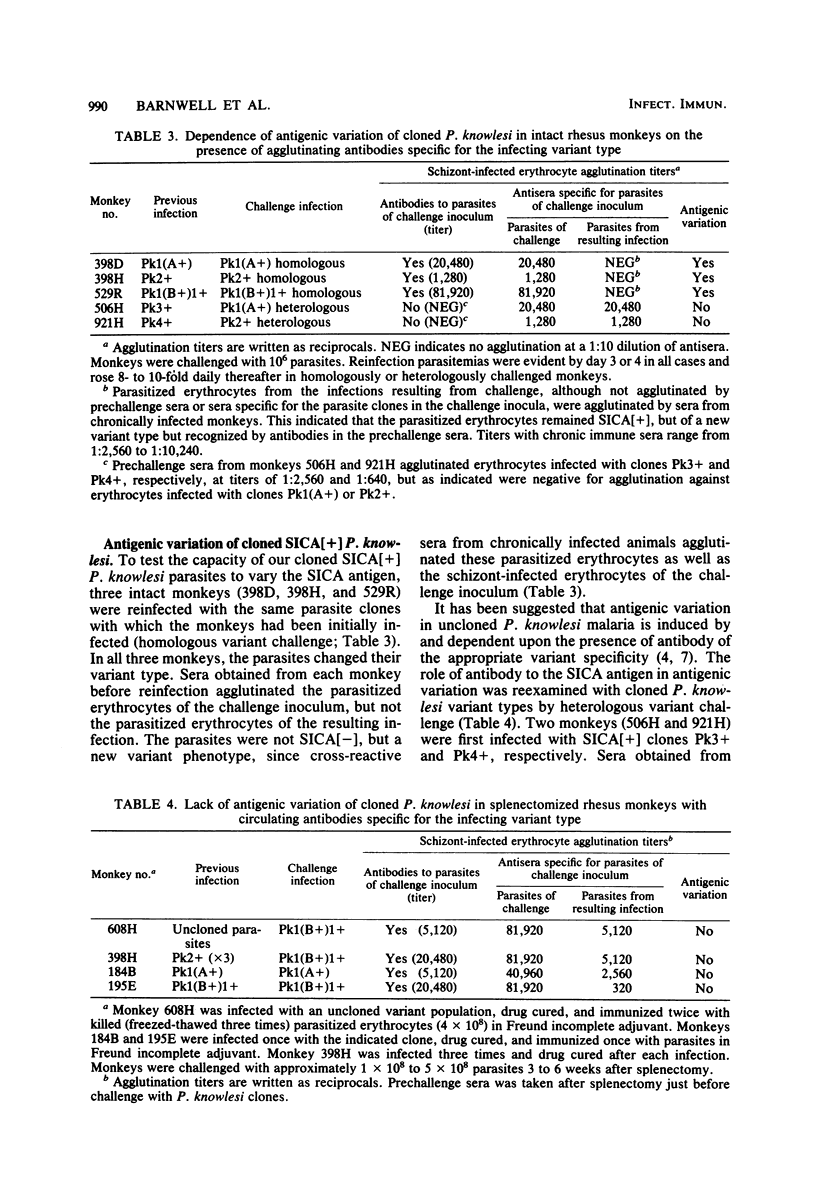
Variant antigens appear on the surface of Plasmodium knowlesi-infected erythrocytes as the asexual parasite matures and are detected by antibody-mediated schizont-infected cell agglutination (SICA). We now show that cloned parasites can undergo antigenic variation in nonsplenectomized monkeys. In addition, we previously described a new P. knowlesi phenotype in which uncloned parasites passaged in splenectomized monkeys were no longer agglutinable by immune sera. We have designated this new phenotype SICA[-] and the one expressing the variant antigen SICA[+]. Cloned parasites can also switch from SICA[+] to SICA[-] in splenectomized monkeys. The switch from SICA[+] to SICA[-] is a gradual process that requires sequential subpassage in several monkeys. After passage in one monkey, the agglutination titer decreased 4- to 16-fold. Decreased agglutination was associated with decreased antibody binding on all infected erythrocytes as measured by fluorescein-conjugated anti-rhesus monkey immunoglobulin. The asexual malaria parasite can therefore alter its expression of variant antigen in response to the host environment (antivariant antibody or splenectomy). When cloned SICA[-] parasites were inoculated into intact monkeys, two courses of parasitemia were observed: fulminant parasitemia (greater than 20%) and parasitemia that was controlled. Fulminant infections were associated with conversion of the parasite from SICA[-] to SICA[+], i.e., from nonexpression to expression of the variant antigen on the erythrocyte surface. Parasitized erythrocytes remained SICA[-] in those infections that were controlled. It appears, therefore, that the expression of the variant antigen on the erythrocyte surface may influence parasite virulence.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnwell J. W., Howard R. J., Miller L. H. Altered expression of Plasmodium knowlesi variant antigen on the erythrocyte membrane in splenectomized rhesus monkeys. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):224–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgen P. J., Cross G. A., Bridgen J. N-terminal amino acid sequences of variant-specific surface antigens from Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1976 Oct 14;263(5578):613–614. doi: 10.1038/263613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown I. N., Brown K. N., Hills L. A. Immunity to malaria: the antibody response to antigenic variation by Plasmodium knowlesi. Immunology. 1968 Jan;14(1):127–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N. Antibody induced variation in malaria parasites. Nature. 1973 Mar 2;242(5392):49–50. doi: 10.1038/242049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N., Hills L. A. Immunity to malaria. I. Protection against Plasmodium knowlesi shown by monkeys sensitized with drug-suppressed infections or by dead parasites in Freund's adjuvant. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Oct;28(2):304–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N. Immunity to malaria: antigenic variation in chronic infections of Plasmodium knowlesi. Nature. 1965 Dec 25;208(5017):1286–1288. doi: 10.1038/2081286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N., Trigg P. I., Phillips R. S., Hills L. A. Immunity to malaria. II. Serological response of monkeys sensitized by drug-suppressed infection or by dead parasitized cells in Freund's complete adjuvant. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Oct;28(2):318–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher G. A., Cohen S. Antigenic variation and protective immunity in Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Immunology. 1972 Oct;23(4):503–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIN W., CONTACOS P. G., COATNEY G. R., KIMBALL H. R. A NATURALLY ACQUITED QUOTIDIAN-TYPE MALARIA IN MAN TRANSFERABLE TO MONKEYS. Science. 1965 Aug 20;149(3686):865–865. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3686.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):240–244. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY A. R. ANTIGENIC VARIATION IN CLONES OF TRYPANOSOMA BRUCEI. I. IMMUNOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS OF THE CLONES. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1965 Mar;59:27–36. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1965.11686278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H., Frasch A. C., Bernards A., Borst P., Cross G. A. Novel expression-linked copies of the genes for variant surface antigens in trypanosomes. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):78–80. doi: 10.1038/284078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Characterization of a protein correlated with the production of knob-like protrusions on membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4650–4653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse S. A., Miller L. H. Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Ultrastructure of parasitized erythrocytes in cardiac vessels. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Sep;20(5):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meryman H. T., Hornblower M. A method for freezing and washing red blood cells using a high glycerol concentration. Transfusion. 1972 May-Jun;12(3):145–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1972.tb00001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed J. R. Antigens and antigenic variability of the African trypanosomes. J Protozool. 1974 Nov;21(5):639–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udeinya I. J., Schmidt J. A., Aikawa M., Miller L. H., Green I. Falciparum malaria-infected erythrocytes specifically bind to cultured human endothelial cells. Science. 1981 Jul 31;213(4507):555–557. doi: 10.1126/science.7017935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. Antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):613–617. doi: 10.1038/273613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Rossan R. N. Immunological studies on simian malaria. 3. Immunity to challenge and antigenic variation in P. knowlesi. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1969;63(4):507–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Young J. R., Majiwa P. A. Genomic rearrangements correlated with antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):847–849. doi: 10.1038/282847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J., Miller L. H., Schmidt L. H. Spleen function in quartan malaria (due to Plasmodium inui): evidence for both protective and suppressive roles in host defense. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jan;135(1):86–93. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



