Abstract
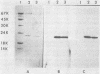
A total of 136 isolates of Staphylococcus aureus were tested for production of staphylococcal enterotoxin F (SEF) and pyrogenic exotoxin C (PEC), both of which have been identified as reliable indicators of toxic shock syndrome (TSS)-associated strains. SEF and PEC production by isolates from TSS-associated and other sources was tested independently in two laboratories, after which the two sets of data were compared. A 100% concordance between SEF and PEC production was obtained. The TSS toxin candidates were produced by 30 of 136 isolates, and in all instances SEF and PEC were made concurrently by the same strains; in no case was one toxin made and not the other. In the five groups of S. aureus tested, toxins were detected as follows: 23 of 25 (92%) acute TSS isolates, 2 of 48 (4.2%) genital non-TSS isolates, 2 of 16 (12.5%) recovered TSS isolates, 1 of 23 (4.3%) clinical nongenital isolates, and 2 of 24 (8.3%) enterotoxigenic food outbreak isolates. Comparison of purified SEF and purified PEC by immunological and biochemical criteria by immunodiffusion, isoelectric focusing, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and Western blot analysis show that the toxins are immunologically identical and strongly suggest that the two nominal TSS toxins are in fact a single protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G. Vaginal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):442–449. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.442-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Falkow S. Protein antigens from Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic-shock syndrome. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7466361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. A purified group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Physiochemical and biological properties including the enhancement of susceptibility to endotoxin lethal shock. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):611–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnemann C. C., Jr, Staneck J. L., Hornstein S., Barden T. P., Rauh J. L., Bonventre P. F., Buncher C. R., Beiting A. The epidemiology of genital colonization with Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):940–944. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Dan B. B., Shands K. N., Broome C. V. Toxic-shock syndrome not associated with menstruation. A review of 54 cases. Lancet. 1982 Jan 2;1(8262):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R., Gould S., Bergdoll M. Detecting the enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):946–950. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.946-950.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Enhancement of host susceptibility to lethal endotoxin shock by staphylococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):123–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.123-128.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Purification and characterization of staphylococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type B. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6204–6208. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Schoettle D. J., Watson D. W. Nonspecific T-lymphocyte mitogenesis by pyrogenic exotoxins from group A streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1075–1077. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1075-1077.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Schmid G. P., Dan B. B., Blum D., Guidotti R. J., Hargrett N. T., Anderson R. L., Hill D. L., Broome C. V., Band J. D. Toxic-shock syndrome in menstruating women: association with tampon use and Staphylococcus aureus and clinical features in 52 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1436–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]