Abstract
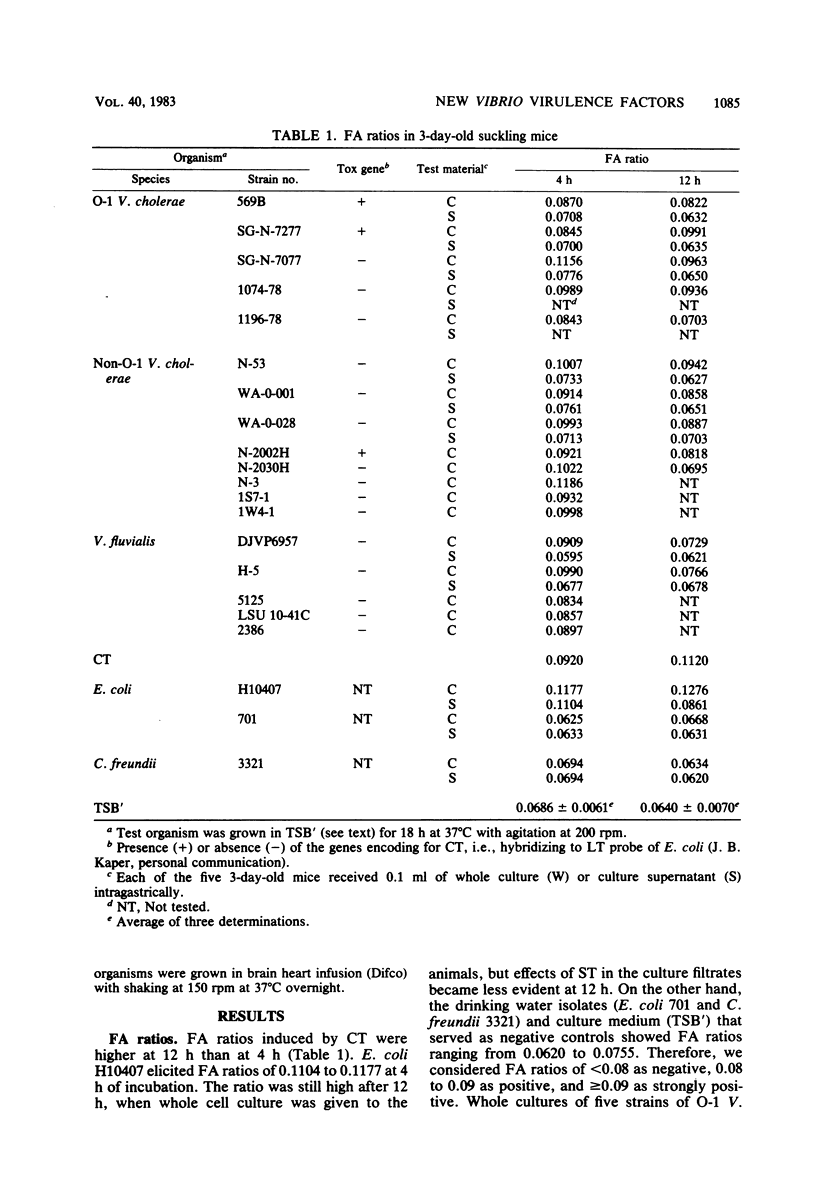
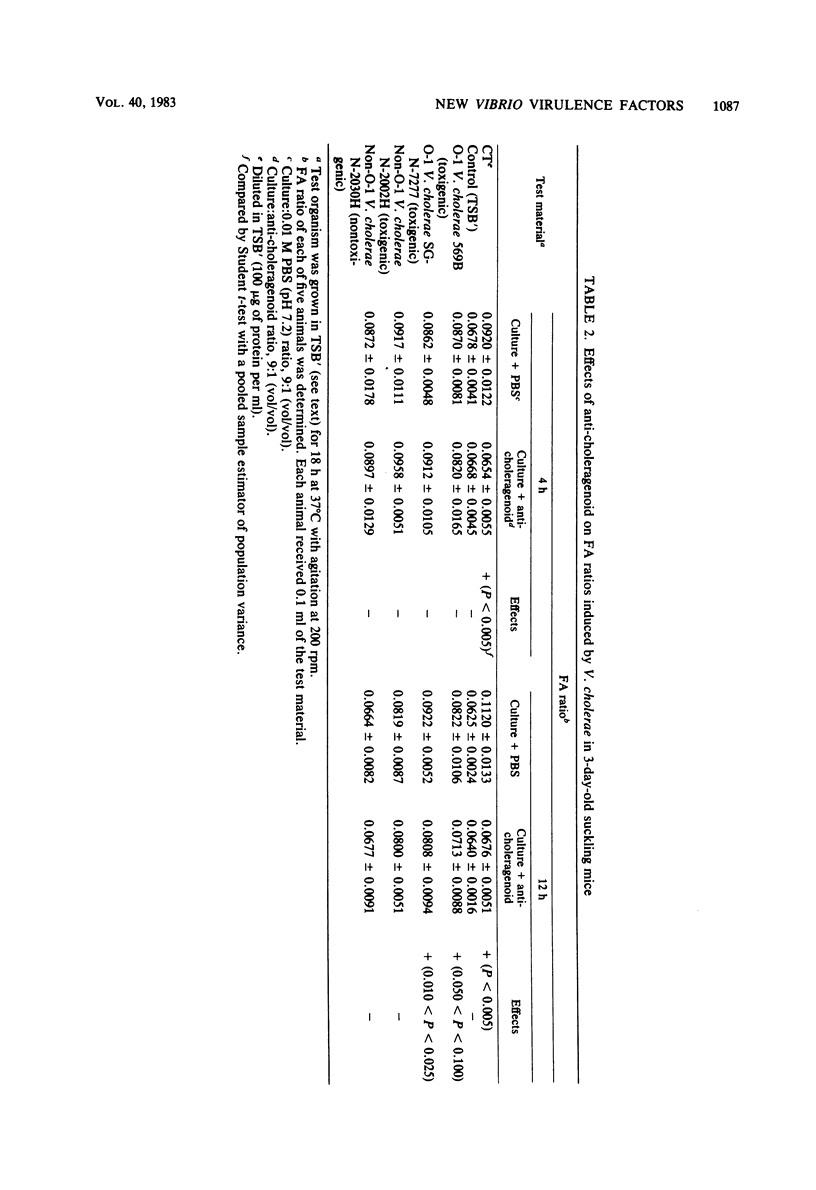
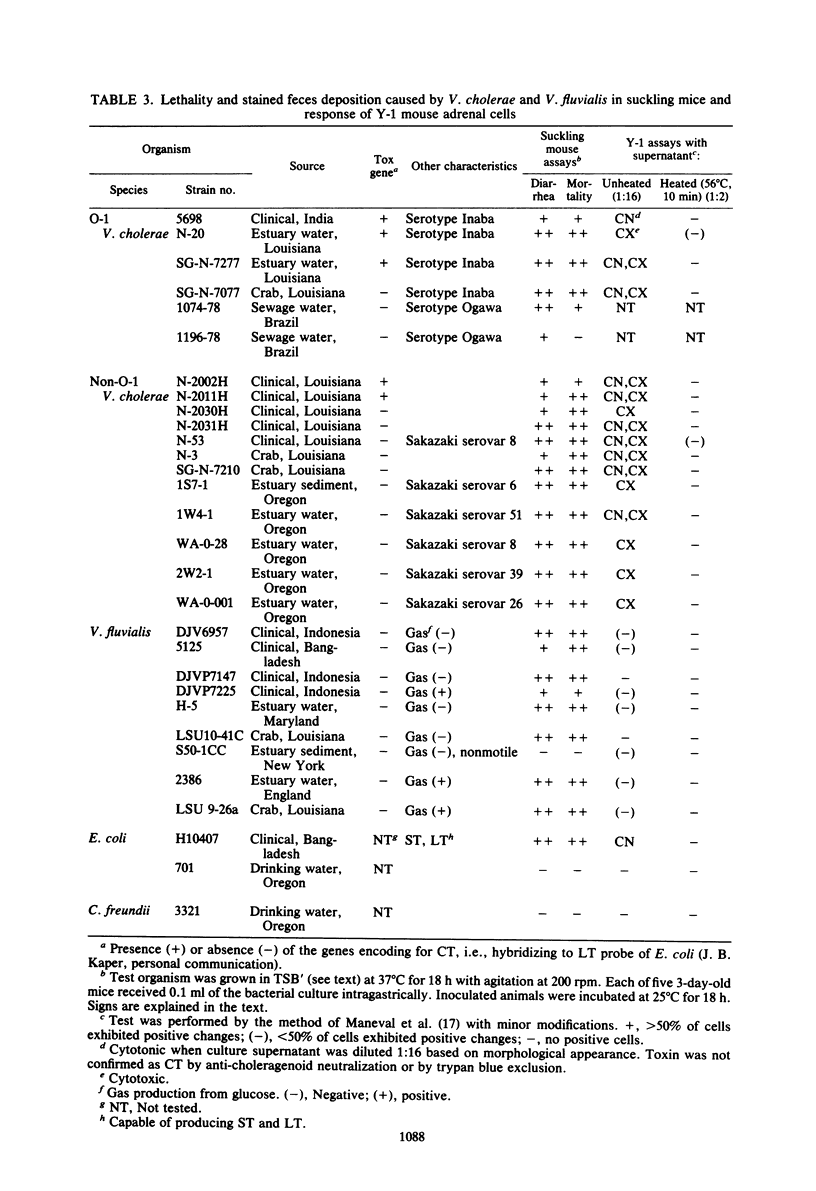
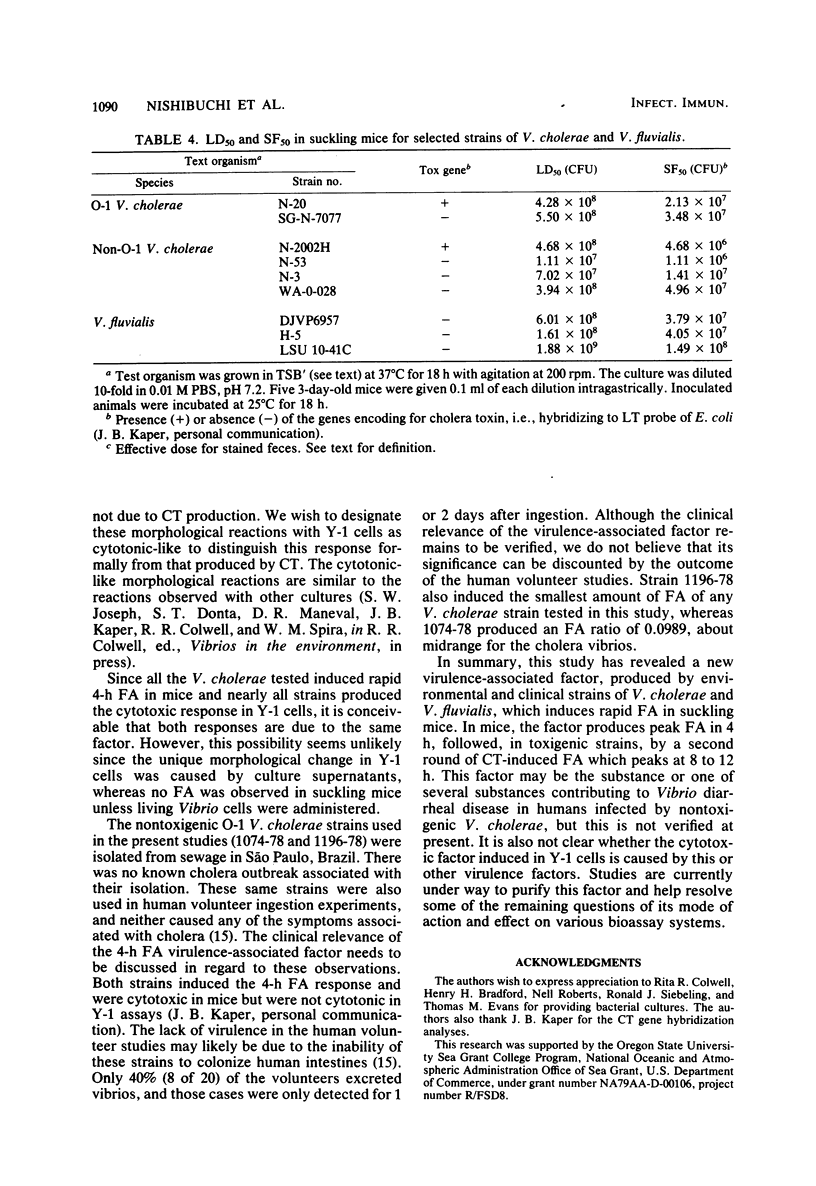
Non-O-1 and O-1 Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio fluvialis isolated from clinical and environmental sources were examined for virulence factor production in 3-day-old suckling mice and in Y-1 tissue culture. The responses of the suckling mice to intragastrically administered bacterial cultures were measured by intestinal fluid accumulation (FA), diarrhea, and mortality. Regardless of the O-serovar, source of isolation, or ability to produce cholera toxin, all strains of V. cholerae stimulated increased FA, which was measurable in the mice at 4 h post-inoculation. The factor(s) causing these symptoms was found to be distinct from cholera toxin by the kinetics of FA and serological difference from cholera toxin based on in vivo neutralization tests. In most instances, FA was followed by high rates of mortality. Y-1 mouse adrenal tumor cell assays also showed that many V. cholerae produced extracellular heat-labile cytotoxic factor(s), and many cholera toxin-negative strains also caused a cytotonic-like morphological response. The majority of V. fluvialis strains produced smaller amounts of cytotoxic factor(s) but no cytotoxic reactions. The factor which stimulates rapid FA in suckling mice could be one of several virulence-associated factors contributing to diarrheal disease by nontoxigenic vibrios, but this is not verified at present.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baselski V., Briggs R., Parker C. Intestinal fluid accumulation induced by oral challenge with Vibrio cholerae or cholera toxin in infant mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):704–712. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.704-712.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya S., Bose A. K., Ghosh A. K. Permeability and enterotoxic factors of nonagglutinable vibrios Vibrio alcaligenes and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Dec;22(6):1159–1161. doi: 10.1128/am.22.6.1159-1161.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaicumpa W., Rowley D. Experimental cholera in infant mice: protective effects of antibody. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):480–485. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P. A permeability factor (toxin) found in cholera stools and culture filtrates and its neutralization by convalescent cholera sera. Nature. 1965 Aug 7;207(997):614–616. doi: 10.1038/207614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P., Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Production of cholera-like enterotoxin by a Vibrio cholerae non-O1 strain isolated from the environment. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.90-97.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draskovicová M., Karolcek J., Winkler Experimental Toxigenicity of NAG Vibrios. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1977 Feb;237(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Monospecific equine antiserum against cholera exo-enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Dec;2(6):691–697. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.6.691-697.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Motility as a virulence factor for Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):890–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.890-897.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Protection of suckling mice from experimental cholera by maternal immunization: comparison of the efficacy of whole-cell, ribosomal-derived, and enterotoxin immunogens. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.167-172.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of environmental and nontoxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.661-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. V., Shread P., Furniss A. L., Bryant T. N. Taxonomy and description of Vibrio fluvialis sp. nov. (synonym group F vibrios, group EF6). J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;50(1):73–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Cisneros L., Saah A., Nalin D. R., Gill D. M., Craig J. P., Young C. R., Ristaino P. The pathogenicity of nonenterotoxigenic Vibrio cholerae serogroup O1 biotype El Tor isolated from sewage water in Brazil. J Infect Dis. 1982 Mar;145(3):296–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.3.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden J. M., Nematollahi W. P., Hill W. E., McCardell B. A., Twedt R. M. Virulence of three clinical isolates of Vibrio cholerae non-O-1 serogroup in experimental enteric infections in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):616–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.616-619.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Fung P. Y., Whipp S. C., Isaacson R. E. Effects of age and ambient temperature on the responses of infant mice to heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: assay modifications. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):36–39. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.36-39.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oashi M., Shimada T., Fukumi H. In vitro production of enterotoxin and hemorrhagic principle by Vibrio cholerae, NAG. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1972 Jun;25(3):179–194. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.25.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V. Production of enterotoxin by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):908–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.908-911.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V., Toma S. Prevalence of enterotoxigenicity in human and nonhuman isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):334–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.334-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Allen D. A., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W., Daily O. P. Biochemical characteristics and virulence of environmental group F bacteria isolated in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):715–720. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.715-720.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S. J., Sanyal S. C. Enterotoxicity of the so-called NAG vibrios. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1978;58(2):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twedt R. M., Madden J. M., Hunt J. M., Francis D. W., Peeler J. T., Duran A. P., Hebert W. O., McCay S. G., Roderick C. N., Spite G. T. Characterization of Vibrio cholerae isolated from oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1475–1478. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1475-1478.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. H., Yalow R., Berson S. A. Detection of Australia antigen and antibody by means of radioimmunoassay techniques. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):550–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Willis D. L., Berry L. J. Role of motility in experimental cholera in adult rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):387–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.387-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinnaka Y., Carpenter C. C., Jr An enterotoxin produced by noncholera vibrios. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1972 Dec;131(6):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



