Abstract
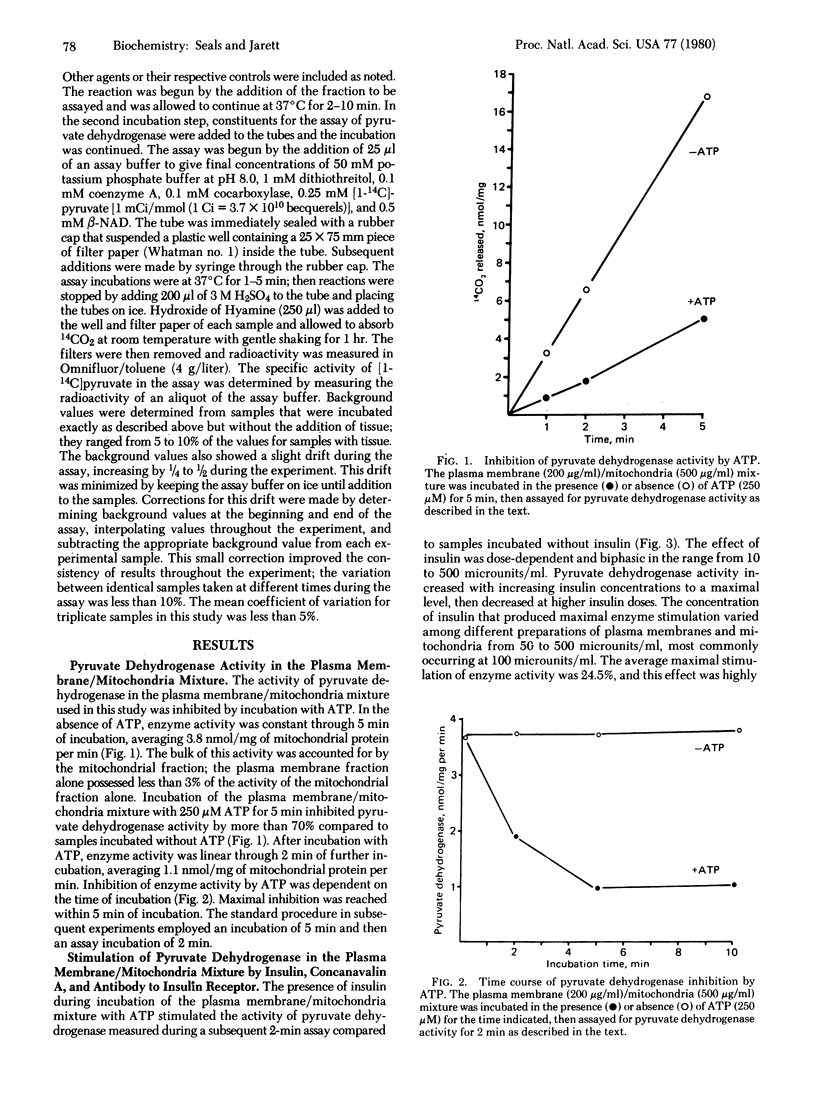
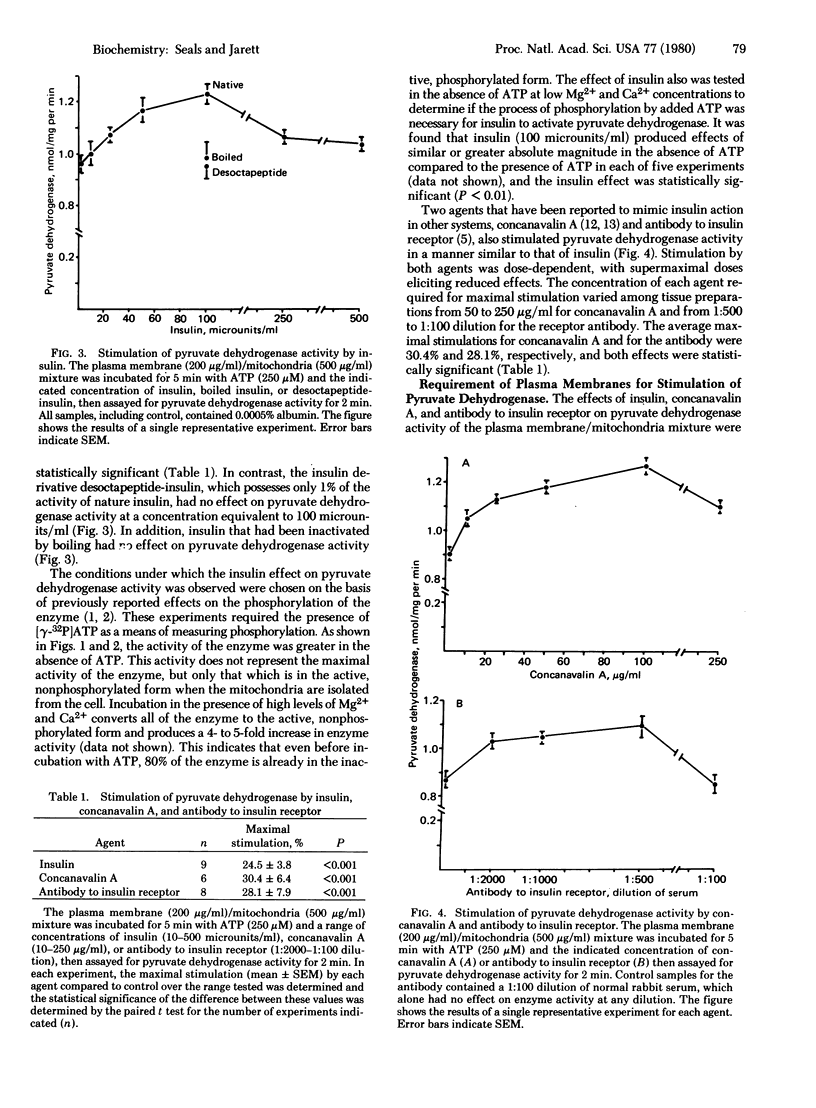
The addition of insulin to a mixture of plasma membrane and mitochondrial fractions from rat adipocytes results in a decrease in the phosphorylation of a mitochondrial protein identified as the α subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase [pyruvate:lipoamide oxidoreductase (decarboxylating and acceptor-acetylating), EC 1.2.4.1] (Seals, J. R., McDonald, J. M. & Jarett, L. (1979) J. Biol. Chem. 254, 6991-6996). This study confirms the prediction that a corresponding increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase activity can be effected by insulin treatment of this preparation. Incubation of the plasma membrane/mitochondria mixture with ATP inhibited pyruvate dehydrogenase activity as measured in a subsequent enzyme assay. The presence of insulin during this incubation with ATP resulted in a 24.5% stimulation of enzyme activity compared to incubation without insulin (n = 9, P < 0.001). The effect was specific for biologically active insulin and was insulin dose-dependent in the physiological range of insulin. Supermaximal doses of insulin produced reduced effects. An insulin effect of similar magnitude could also be observed when the plasma membrane/mitochondria mixture was incubated without ATP. Two insulin mimickers, concanavalin A and antibody to insulin receptor, stimulated pyruvate dehydrogenase by 30.4% (n = 6, P <0.001) and 28.1% (n = 8, P<0.001), respectively. Both of these agents also produced reduced effects at supermaximal concentrations. The effects of all three agents required plasma membranes and could not be produced by treatment of mitochondria alone. The results suggest that a mechanism common to all three agents is responsible for transmitting the stimulation from the plasma membrane to the mitochondrial components of the mixture.
Keywords: phosphorylation, concanavalin A, antibody to insulin receptor, pyruvate dehydrogenase (lipoamide)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper R. H., Randle P. J., Denton R. M. Regulation of heart muscle pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. Biochem J. 1974 Dec;143(3):625–641. doi: 10.1042/bj1430625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coore H. G., Denton R. M., Martin B. R., Randle P. J. Regulation of adipose tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase by insulin and other hormones. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1250115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Tell G. P. Insulin-like activity of concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin--direct interactions with insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Coore H. G., Martin B. R., Randle P. J. Insulin activates pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 26;231(21):115–116. doi: 10.1038/newbio231115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Hughes W. A. Pyruvate dehydrogenase and the hormonal regulation of fat synthesis in mammalian tissues. Int J Biochem. 1978;9(8):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(78)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Randle P. J., Martin B. R. Stimulation by calcium ions of pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):161–163. doi: 10.1042/bj1280161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N. Stimulation by insulin and prostaglandin E1 of glucose metabolism and inhibition of lipolytic action of theophylline on fat cells in the absence of K+. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):548–554. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D. Does insulin need a second messenger? Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):148–155. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepp D., Challoner D. R., Williams R. H. Studies on the action of insulin in isolated adipose tissue cells. I. Stimulation of incorporation of 32P-labeled inorganic phosphate into mononucleotides in the absence of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4020–4026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Incorporation of 32Pi into pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate in mitochondria from control and insulin-treated adipose tissue. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):471–473. doi: 10.1038/264471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illiano G., Cuatrecasas P. Modulation of adenylate cyclase activity in liver and fat cell membranes by insulin. Science. 1972 Feb 25;175(4024):906–908. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4024.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illiano G., Tell G. P., Siegel M. E., Cuatrecasas P. Guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and the action of insulin and acetylcholine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2443–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNGAS R. L., BALL E. G. Studies on the metabolism of adipose tissue. XII. The effects of insulin and epinephrine on free fatty acid and glycerol production in the presence and absence of glucose. Biochemistry. 1963 Mar-Apr;2:383–388. doi: 10.1021/bi00902a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Antibodies to purified insulin receptor have insulin-like activity. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1283–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.663609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Smith R. M. The stimulation of adipocyte plasma membrane magnesium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase by insulin and concanavalin A. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5195–5199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L. Subcellular fractionation of adipocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:60–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungas R. L. Role of cyclic-3',5'-amp in the response of adipose tissue to insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):757–763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Sarver J. A. Insulin-sensitive phosphodiesterase. Its localization, hormonal stimulation, and oxidative stabilization. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7826–7835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahl M. E. Insulin action at the molecular level. Facts and speculations. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):695–702. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J., Lawrence J. C., Walkenbach R. J., Roach P. J., Hazen R. J., Huang L. C. Insulin control of glycogen synthesis. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:425–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavis V. R., Williams R. H. Lipolytic effects of high concentrations of insulin on isolated fat cells. Enhancement of the response to lipolytic hormones. Diabetes. 1973 Aug;22(8):629–636. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.8.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter A. B., Weinberg M., Isohashi F., Utter M. F. Relationshiop between phosphorylation and activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat liver mitochondria and the absence of such a relationship for pyruvate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2716–2723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. X. Regulation of the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from beef kidney mitochondria by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):234–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. M., Bruns D. E., Jarett L. Characterization of calcium binding to adipocyte plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5345–5351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. M., Bruns D. E., Jarett L. The ability of insulin to alter the stable calcium pools of isolated adipocyte subcellular fractions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):114–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche T. E., Reed L. J. Monovalent cation requirement for ADP inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 19;59(4):1341–1348. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90461-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., McDonald J. M., Jarett L. Direct effect of insulin on the labeling of isolated plasma membranes by [gamma32P] ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1365–1372. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91372-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., McDonald J. M., Jarett L. Insulin effect on protein phosphorylation of plasma membranes and mitochondria in a subcellular system from rat adipocytes. I. Identification of insulin-sensitive phosphoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6991–6996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Denton R. M., Pask H. T., Randle P. J. Calcium and magnesium ions as effectors of adipose-tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):225–237. doi: 10.1042/bj1400225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica V., Cuatrecasas P. Effects of insulin, epinephrine, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate on pyruvate dehydrogenase of adipose tissue. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2282–2291. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F. The Banting Memorial Lecture 1976. Insulin today. Diabetes. 1977 Apr;26(4):322–340. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.4.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Mukherjee C., Jungas R. L. Studies on the mechanism of activation of adipose tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase by insulin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):73–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turakulov Ia Kh, Gainutdinov M. Kh, Lavina I. I., Akhmatov M. S. Insulinzavisimyi tsitoplazmaticheskii reguliator transporta ionov Ca2+ v mitokhondriiakh pecheni. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1977;234(6):1471–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


