Abstract
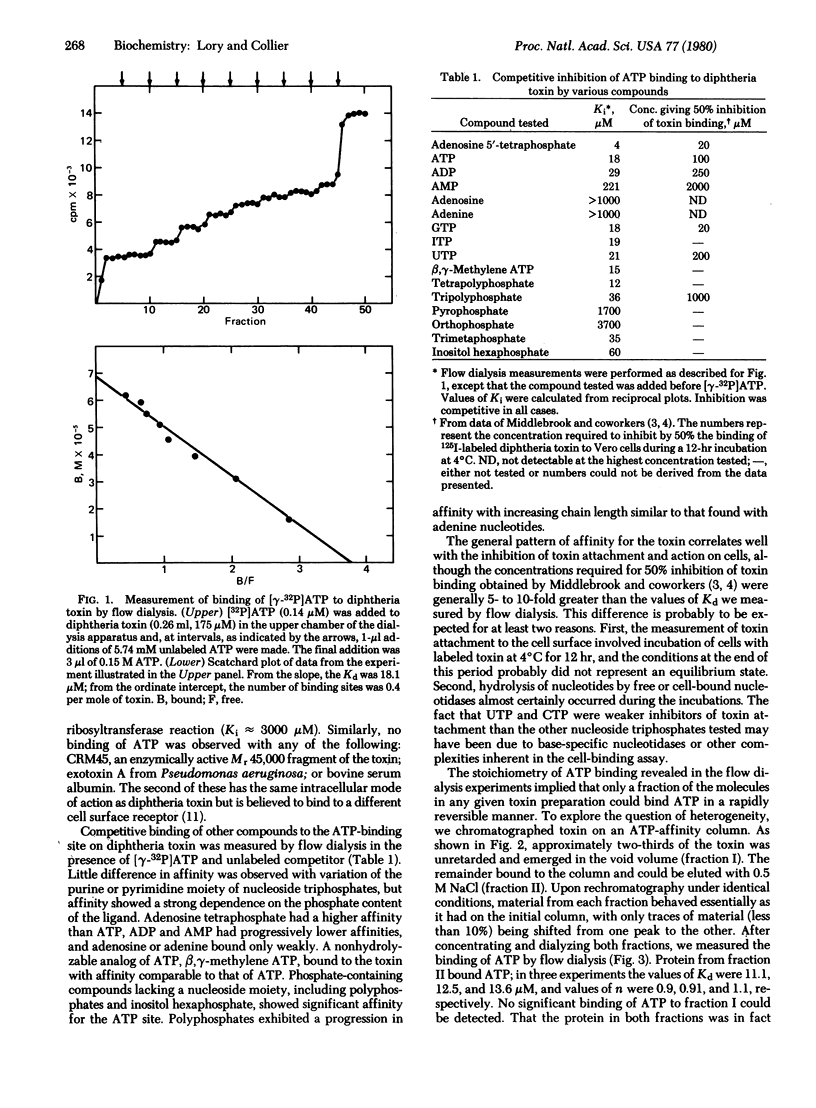
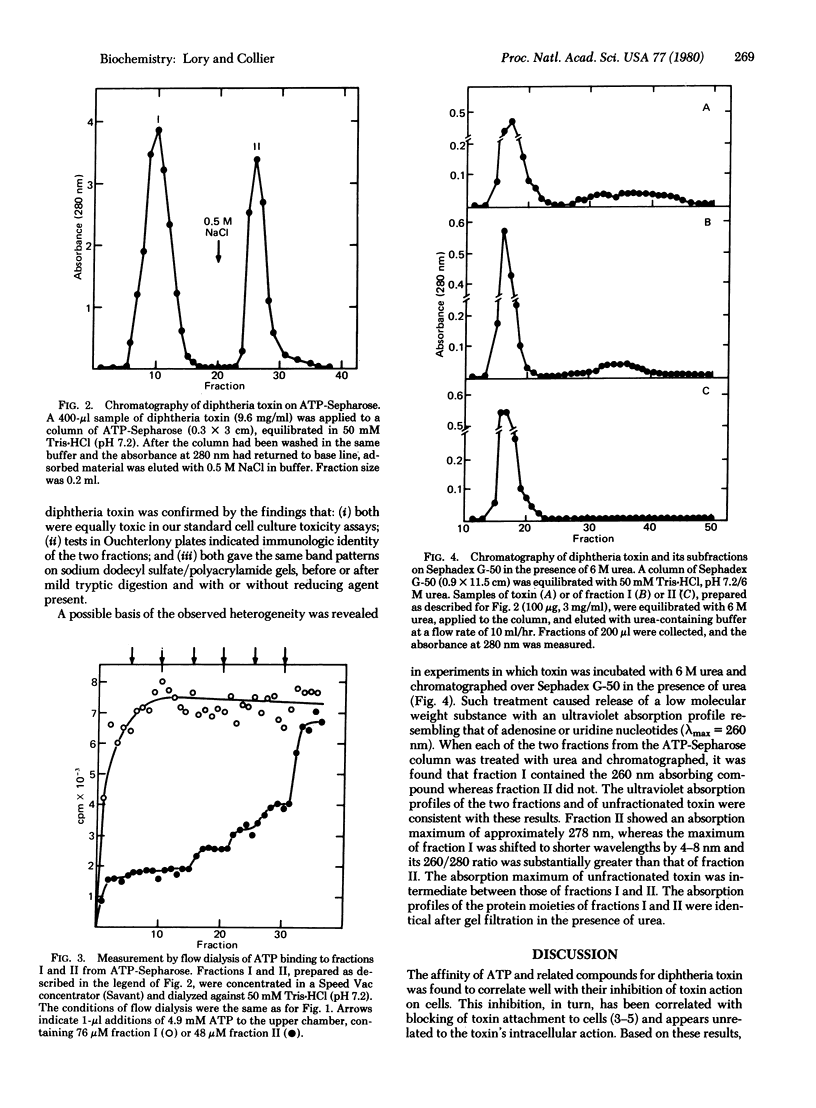
We have used flow dialysis to demonstrate binding of ATP and related compounds to diphtheria toxin. The results define a new site on the toxin molecule (the P site), which has distinctly different properties from the NAD+-binding site of the fragment A moiety. The relative affinities of various compounds for the P site are similar to their capacities to inhibit toxin attachment to cell surfaces and its action on cells. This suggests that the P site may correspond to the binding site for cell surface receptors. Affinity of nucleotides for the toxin depends strongly on the number of phosphates, although both nucleoside and phosphate moieties contribute to the interaction. A substantial fraction of the toxin in any given preparation did not bind ATP in a rapidly reversible manner and was not retained on ATP-Sepharose. This fraction, which varied in magnitude from preparation to preparation, was isolated and shown to contain an endogenous, firmly bound nucleotide or nucleotide-like compound. The presence of this compound may explain some of the physical heterogeneity within individual preparations of purified toxin as well as variations in physical and biological properties among various preparations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgoyne R. D., Wolstenholme J., Stephen J. The preparation of stable, biologically active B fragment of diphtheria toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):920–925. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90743-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T., Neville D. M., Jr Demonstration of diphtheria toxin receptors on surface membranes from both toxin-sensitive and toxin-resistant species. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6866–6871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Collier R. J. The mechanism of ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 catalyzed by fragment A from diphtheria toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 11;483(2):248–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colowick S. P., Womack F. C. Binding of diffusible molecules by macromolecules: rapid measurement by rate of dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):774–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Steinhaus D. M. Modification of diphtheria toxin by NAD. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(3):316–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittelson T. R., Gill D. M. Diphtheria toxin: specific competition for cell receptors. Nature. 1973 Mar 30;242(5396):330–332. doi: 10.1038/242330b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel J., Collier R. J., Chung D. W. Interaction of fragment A from diphtheria toxin with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2088–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B., Leppla S. H. Association of diphtheria toxin with Vero cells. Demonstration of a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7325–7330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Protection of mammalian cells from diphtheria toxin by exogenous nucleotides. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):285–290. doi: 10.1139/m79-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosbach K. AMP and NAD as "General Ligands". Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:229–242. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. G., Stevens M. F., Thomas D. Observations on crystalline diphtheria toxin: the optical density per Lf unit at 276 m-omega. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Feb;47(1):45–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Hart D. A., Holmes R. K., Holmes K. V., Eidels L. Immunoprecipitation and partial characterization of diphtheria toxin-binding glycoproteins from surface of guinea pig cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):685–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A. Studies on diphtheria toxin. The effect of GTP on the toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of rat liver aminoacyl transferase. II. Chem Biol Interact. 1971 Apr;3(2):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(71)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Harper A. A. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. II. Kinetic studies on intoxication of HeLa cells by diphtheria toxin and related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3845–3850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Iglewski B. H. Comparative toxicities of diphtherial toxin and Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A: evidence for different cell receptors. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Oct;108(2):333–337. doi: 10.1099/00221287-108-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanen J., Muyldermans G., Beugnier N. Competitive antagonists of the action of diphtheria toxin in HeLa cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 15;66(2):261–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80518-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



