Abstract
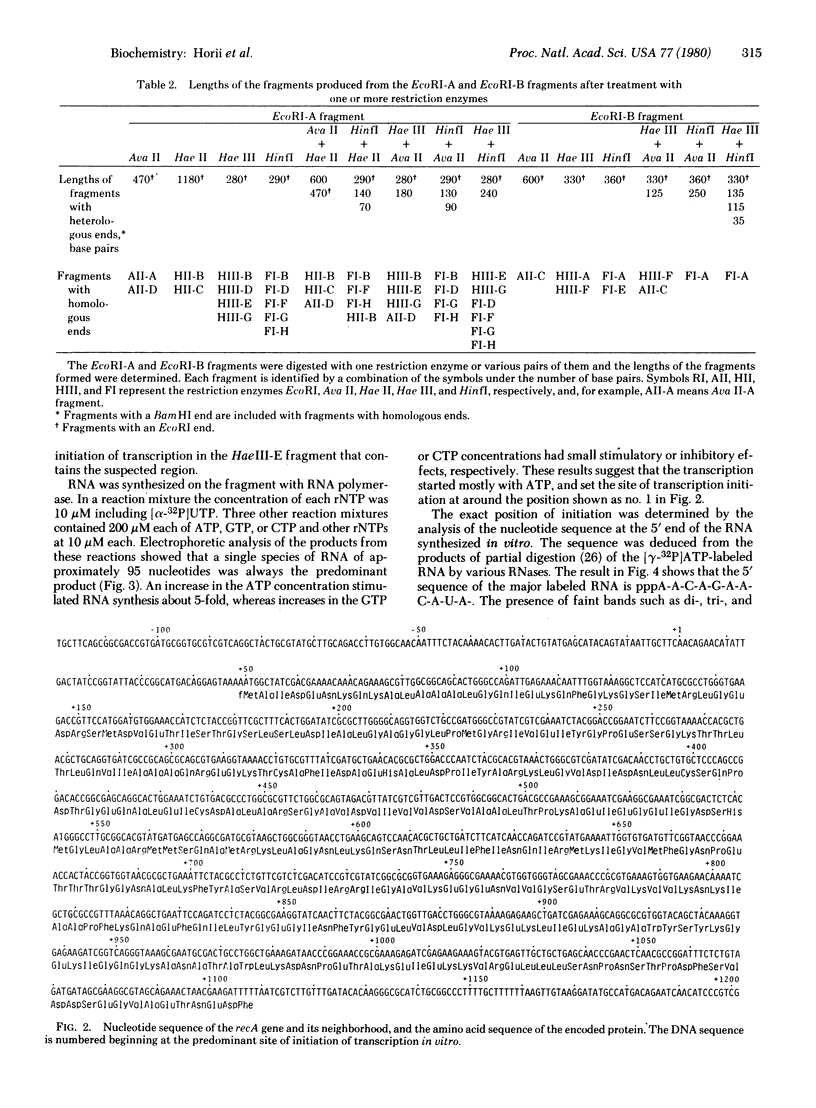
The restriction map of a BamHI DNA fragment that contains the recA gene of Escherichia coli has been established and a large portion of the fragment's nucleotide sequence has been determined. The coding region of the recA gene contains 1059 nucleotide residues and encodes a single protein of 353 amino acid residues. The amino acid sequence of the first five residues of the NH2 terminus of the recA protein agrees with the sequence predicted from the DNA sequence except for the absence of formylmethionine in the purified protein. Immediately after the coding sequence, there is a G+C-rich sequence with dyad symmetry followed by an A+T-rich sequence. These could signal termination of transcription. The site of initiation for synthesis in vitro of the recA messenger RNA has been determined by analysis of the 5' nucleotide sequence of [gamma-32P]ATP-labeled transcripts. The promoter region shos a high degree of symmetry and contains sequences commonly found in recognition and binding sites for RNA polymerase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks K., Clark A. J. Behavior of lambda bacteriophage in a recombination deficienct strain of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):283–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.283-293.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK A. J., MARGULIES A. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:451–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerson P. T., West S. C. Identification of protein X of Escherichia coli as the recA+/tif+ gene product. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Sep 21;155(1):77–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00268563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Mount D. W. Identification of the recA (tif) gene product of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5280–5284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Pardee A. B. DNA synthesis inhibition and the induction of protein X in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):459–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J. The induction of protein X in DNA repair and cell division mutants of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):567–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertman I., Luria S. E. Transduction studies on the role of a rec+ gene in the ultraviolet induction of prophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jan 28;23(2):117–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Boyce R. P. DNA repair and genetic recombination: studies on mutants of Escherichia coli defective in these processes. Radiat Res. 1966;(Suppl):156+–156+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins S. T., Bennett P. M. Effect of mutations in deoxyribonucleic acid repair pathways on the sensitivity of Escherichia coli K-12 strains to nitrofurantoin. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1214–1216. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1214-1216.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Kleid D. G. Escherichia coli protein X is the recA gene product. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6251–6252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K. Protein X is the product of the recA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5275–5279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Weinstock G. M., Lehman I. R. Initiation of general recombination catalyzed in vitro by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2615–2619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura A., Tomizawa J. I. Studies on radiation-sensitive mutants of E. coli. 3. Participation of the rec system in induction of mutation by ultraviolet irradiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1968;103(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00271151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita M., Oka A. The structure of a transcriptional unit on colicin E1 plasmid. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;97(2):435–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W. A mutant of Escherichia coli showing constitutive expression of the lysogenic induction and error-prone DNA repair pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):300–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Wabiko H., Tsurimoto T., Horii T., Masukata H., Ogawa H. Characteristics of purified recA protein and the regulation of its synthesis in vivo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):909–915. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A. Fine cleavage map of a small colicin E1 plasmid carrying genes responsible for replication and colicin E1 immunity. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):916–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.916-924.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site at an early T7 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):784–788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W., Craig N. L. Escherichia coli recA gene product inactivates phage lambda repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4714–4718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Breitmeyer J. B., Tabachnik N. F., Myers P. A. A second specific endonuclease from Haemophilus aegyptius. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 5;91(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D., Shimatake H., Brady C., Wulff D. L. The relationship between function and DNA sequence in an intercistronic regulatory region in phage lambda. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):414–423. doi: 10.1038/272414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., de Chrombrugghe B., Musso R. Determination of nucleotide sequences beyond the sites of transcriptional termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):717–721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupp W. D. Physical map of the recA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3144–3148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H., Gray C., Herrmann K. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site from the DNA of bacteriophage fd. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):737–741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., DasGupta C., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Purified Escherichia coli recA protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G., Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Guilley H. New rapid gel sequencing method for RNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):833–836. doi: 10.1038/269833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Ogawa H. Breakage of DNA in rec+ and Rec- bacteria by disintegration of radiophosphorus atoms in DNA and possible cause of pleiotropic effects of RecA mutation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:243–251. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. ATP-dependent renaturation of DNA catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):126–130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Isolation of a sequence-specific endonuclease (BamI) from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 5;97(1):123–125. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]