Abstract
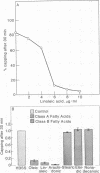
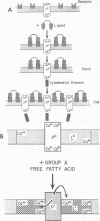
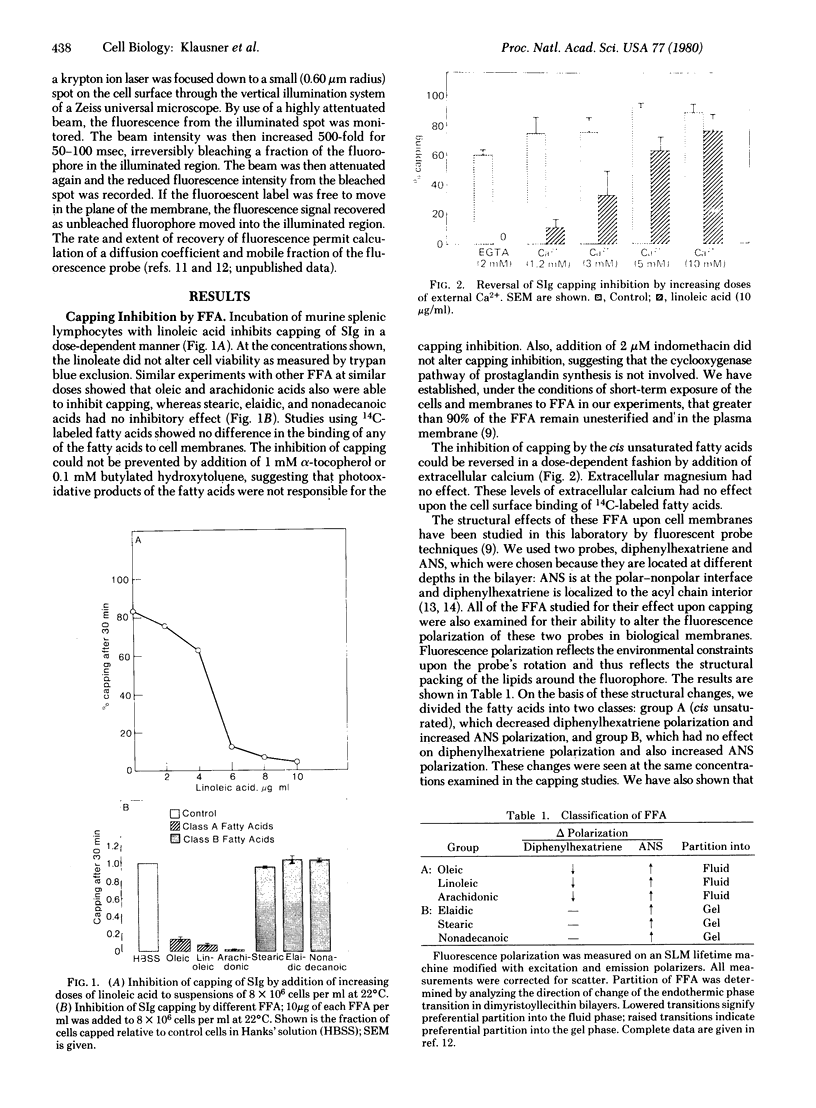
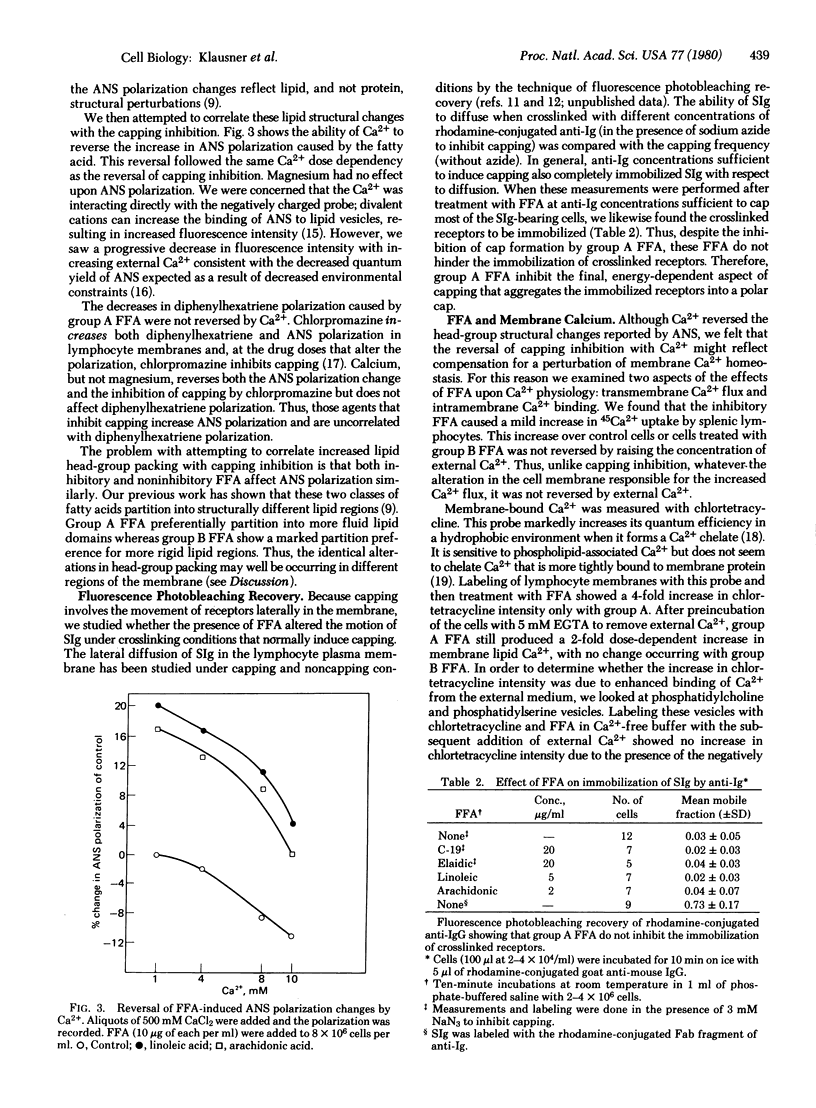
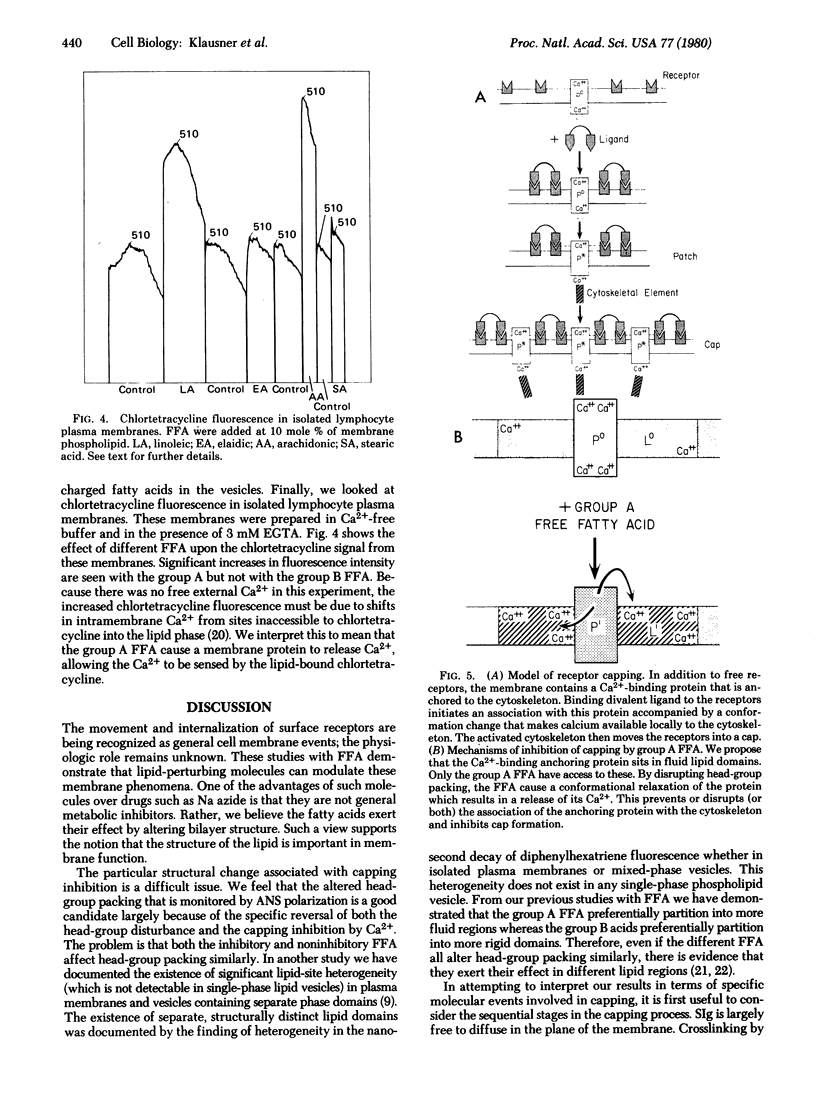
When low concentrations (2-5 mole %) of cis unsaturated free fatty acids (group A) are intercalated into lymphocyte plasma membrane, capping is inhibited. No effect is seen with trans unsaturated or saturated fatty acids (group B). The capping inhibition is reversible with increasing doses of extracellular calcium. Fluorescence photobleaching recovery has shown that the group A free fatty acids do not inhibit the receptor immobilization associated with patch formation, but inhibit the final energy-dependent movement of the patched receptors into a cap. We have also shown that the group A free fatty acids cause a shift in membrane-bound calcium to the lipid phase from probable protein-associated sites. We have incorporated these findings into a model for capping and membrane-cytoskeletal interactions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Singer S. J. Transmembrane interactions and the mechanism of capping of surface receptors by their specific ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5031–5035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye L. D., Edidin M. The rapid intermixing of cell surface antigens after formation of mouse-human heterokaryons. J Cell Sci. 1970 Sep;7(2):319–335. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K. Calcium binding to brain plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 6;363(2):202–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemonnier F., Mescher T. M., sherman L., Burakoff S. The induction of cytolytic T lymphocytes with purified plasma membranes. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1114–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loor F., Forni L., Pernis B. The dynamic state of the lymphocyte membrane. Factors affecting the distribution and turnover of surface immunoglobulins. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Jun;2(3):203–212. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C., Pangborn W., Nir S., Papahadjopoulos D. Specificity of Ca2+ and Mg2+ binding to phosphatidylserine vesicles and resultant phase changes of bilayer membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 19;506(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podo F., Blasie J. K. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of lecithin bimolecular leaflets with incorporated fluorescent probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle M. J., Miller K. W. Differential effects on phospholipid phase transitions produced by structurally related long-chain alcohols. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3314–3320. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Webb W. W., Elson E. L. Lateral transport of a lipid probe and labeled proteins on a cell membrane. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):307–309. doi: 10.1126/science.556653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Quantitative determination of the lateral diffusion coefficients of the hormone-receptor complexes of insulin and epidermal growth factor on the plasma membrane of cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5353–5357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. The disruption of immunoglobulin caps by local anesthetics. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Sep;6(2):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Hudson B. S., Simoni R. D. Conjugated polyene fatty acids as fluorescent probes: synthetic phospholipid membrane studies. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):819–828. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs G. W., Litman B. J. Microviscosity of the hydrocarbon region of the bovine retinal rod outer segment disk membrane determined by fluorescent probe measurements. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2766–2772. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett R. B., Wingate J. M., Carraway K. L. Calcium effects on erythrocyte membrane proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):1014–1020. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Karnovsky M. J. Ligand-induced movement of lymphocyte membrane macromolecules. V. Capping, cell movement, and microtubular function in normal and lectin-treated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1207–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Perkins W. D., Karnovsky M. J. Ligand-induced movement of lymphocyte membrane macromolecules. I. Analysis by immunofluorescence and ultrastructural radioautography. J Exp Med. 1972 Oct 1;136(4):885–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Petris S. Concanavalin A receptors, immunoglobulins, and theta antigen of the lymphocyte surface. Interactions with concanavalin A and with Cytoplasmic structures. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):123–146. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]