Abstract
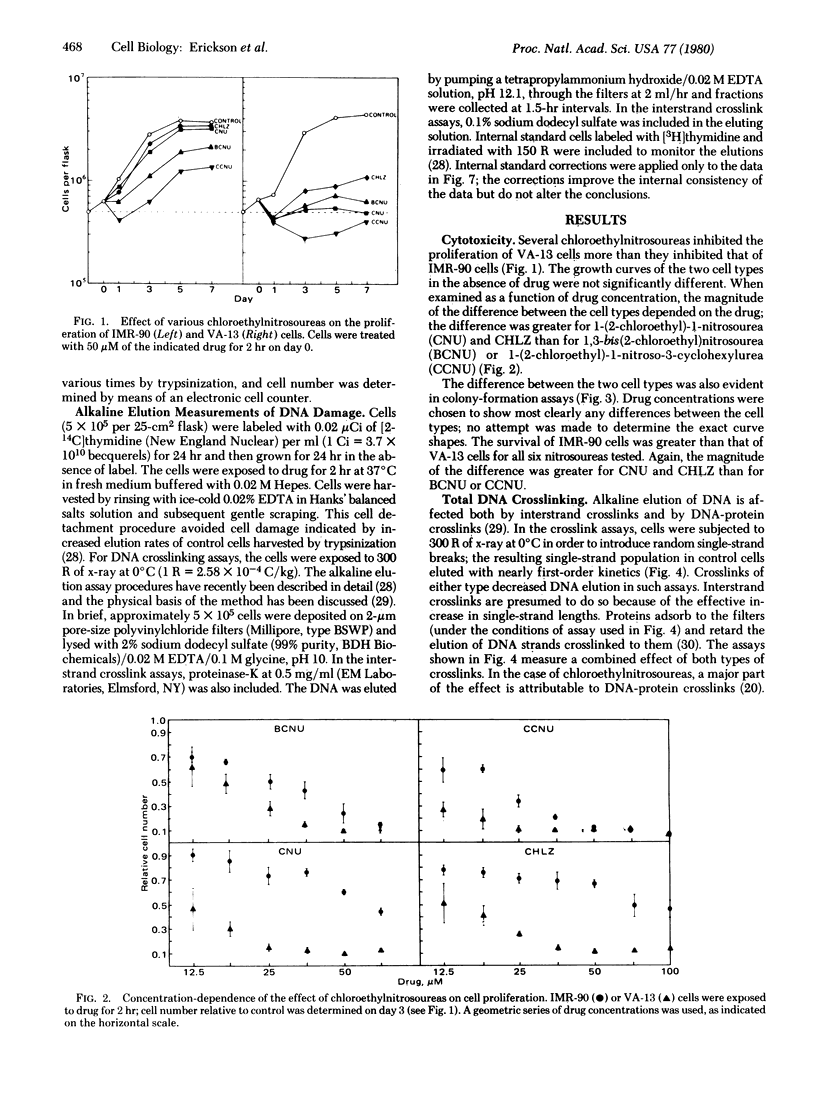
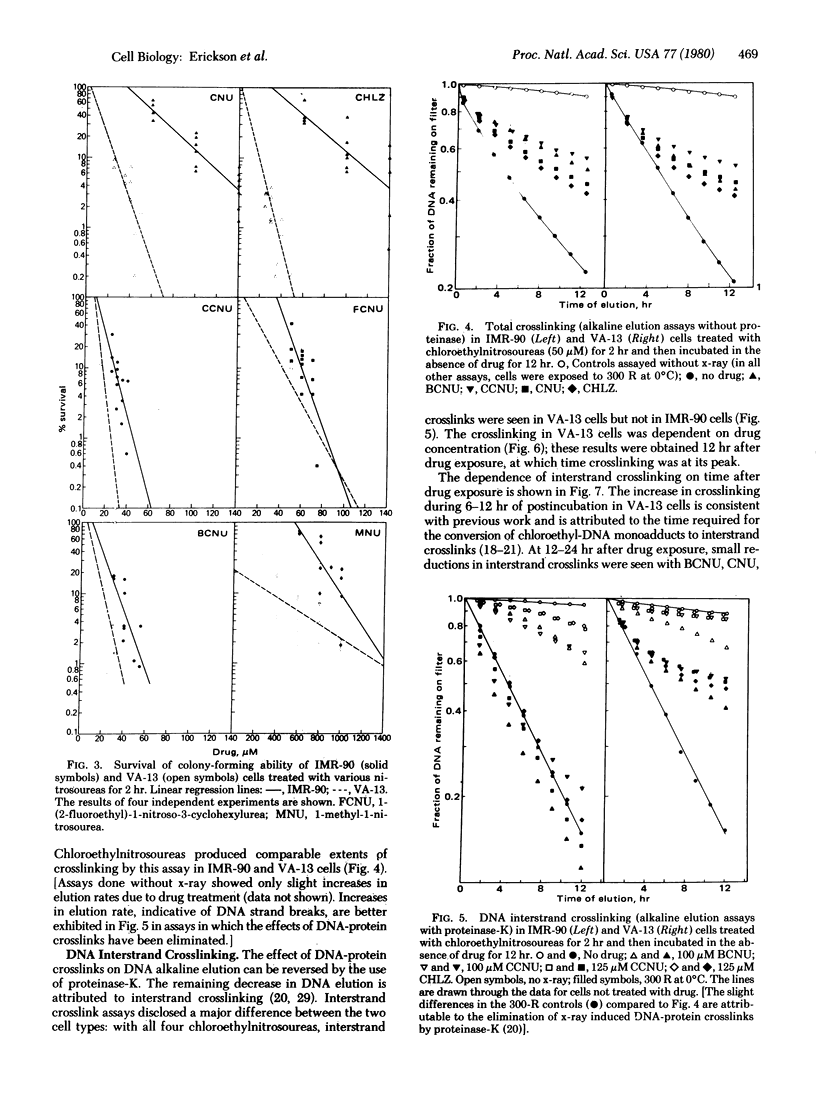
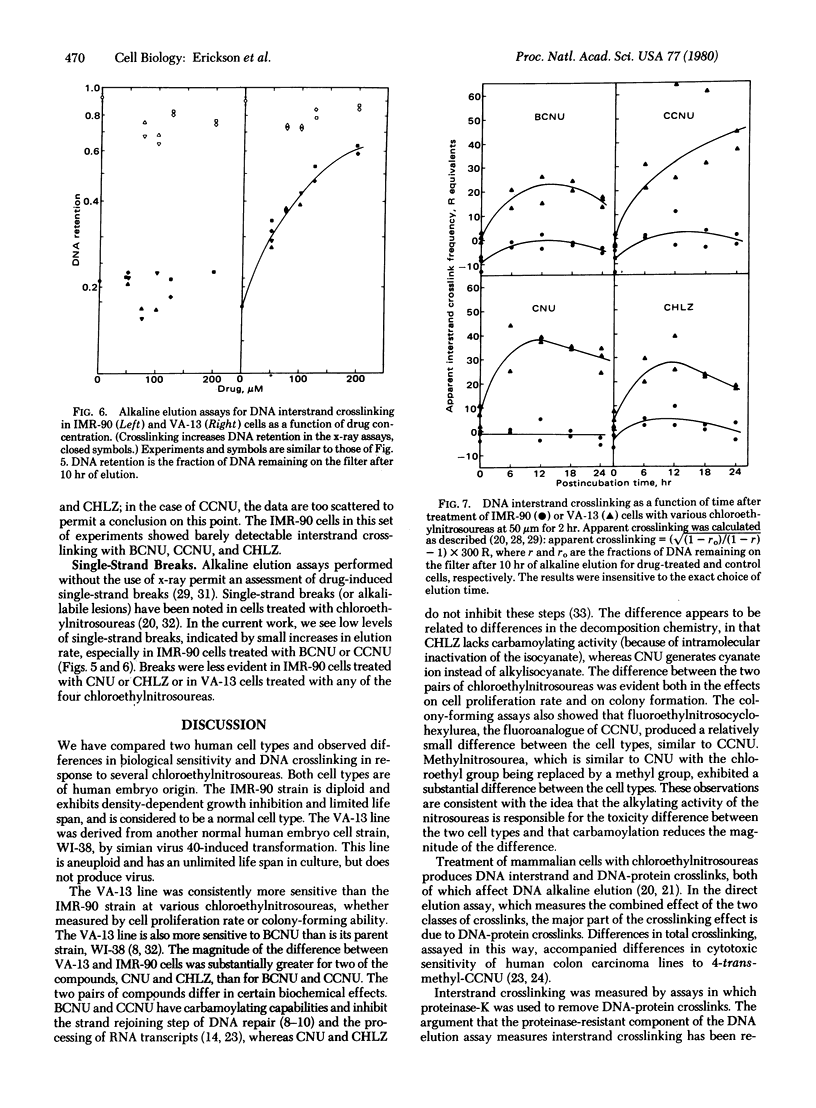
Normal (IMR-90) and simian virus 40-transformed (VA-13) human embryo cells were treated with antitumor nitrosoureas, and the effects on cell viability and cell DNA were compared. All six nitrosoureas tested were more toxic to VA-13 cells than to IMR-90 cells as measured by decrease in cell proliferation or in colony formation. The nitrosoureas capable of generating alkylisocyanates produced a smaller difference between the cell types than did derivatives lacking this capacity. DNA damage was measured by alkaline elution in cells treated with four chloroethylnitrosoureas. Whereas VA-13 cells exhibited dose-dependent interstrand crosslinking, little or none was detected in IMR-90 cells. The IMR-90 cells, however, exhibited at least as much DNA-protein crosslinking as did VA-13 cells. The results can be interpreted in terms of a possible difference in DNA repair between the cell lines.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson H. T., Karlan D., Penman S. A comparison of the effects of alkylating agents 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea, 1-(2-chloroethyl)-3-cyclohexyl-1-nitrosourea and nitrogen mustard on nuclear RNA synthesis and processing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 31;349(3):389–401. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baril B. B., Baril E. F., Laszlo J., Wheeler G. P. Inhibition of rat liver DNA polymerase by nitrosoureas and isocyanates. Cancer Res. 1975 Jan;35(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. O., Kohn K. W., Sharkey N. A., Ewig R. A. Differential cytotoxicity between transformed and normal human cells with combinations of aminonucleoside and hydroxyurea. Cancer Res. 1977 Jul;37(7 Pt 1):2126–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. K., Wasserman T. H. The nitrosoureas--thoughts for the future. Cancer Treat Rep. 1976 Jun;60(6):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang R. Y., Laszlo J., Keller P. Effects of nitrosoureas on human DNA polymerase activities from acute and chronic granulocytic leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):463–468. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvin M., Brundrett R. B., Cowens W., Jardine I., Ludlum D. B. A chemical basis for the antitumor activity of chloroethylnitrosoureas. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Mar 15;25(6):695–699. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90246-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. C., Bradley M. O., Kohn K. W. Differential inhibition of the rejoining of X-ray-induced DNA strand breaks in normal and transformed human fibroblasts treated with 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea in vitro. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):672–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. C., Bradley M. O., Kohn K. W. Measurements of DNA damage in Chinese hamster cells treated with equitoxic and equimutagenic doses of nitrosoureas. Cancer Res. 1978 Oct;38(10):3379–3384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. C., Bradley M. O., Kohn K. W. Strand breaks in DNA from normal and transformed human cells treated with 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3744–3750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. C., Osieka R., Kohn K. W. Differential repair of 1-(2-chloroethyl)-3-(4-methylcyclohexyl)-1-nitrosourea-induced DNA damage in two human colon tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):802–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewig R. A., Kohn K. W. DNA damage and repair in mouse leukemia L1210 cells treated with nitrogen mustard, 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea, and other nitrosoureas. Cancer Res. 1977 Jul;37(7 Pt 1):2114–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewig R. A., Kohn K. W. DNA-protein cross-linking and DNA interstrand cross-linking by haloethylnitrosoureas in L1210 cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Oct;38(10):3197–3203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Kohn K. W., Kann H. E., Jr Inhibition of the ligase step of excision repair by 2-chloroethyl isocyanate, a decomposition product of 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea. Cancer Res. 1978 Apr;38(4):1064–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARDI A. J., JENSEN F. C., KOPROWSKI H. SV40-INDUCED TRANFORMATION OF HUMAN DIPLOID CELLS: CRISIS AND RECOVERY. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Feb;65:69–83. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030650110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kann H. E., Jr Comparison of biochemical and biological effects of four nitrosoureas with differing carbamoylating activities. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2363–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kann H. E., Jr, Kohn K. W., Lyles J. M. Inhibition of DNA repair by the 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea breakdown product, 2-chloroethyl isocyanate. Cancer Res. 1974 Feb;34(2):398–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kann H. E., Jr, Kohn K. W., Widerlite L., Gullion D. Effects of 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and related compounds on nuclear RNA metabolism. Cancer Res. 1974 Aug;34(8):1982–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Erickson L. C., Ewig R. A., Friedman C. A. Fractionation of DNA from mammalian cells by alkaline elution. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4629–4637. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Ewig R. A. DNA-protein crosslinking by trans-platinum(II)diamminedichloride in mammalian cells, a new method of analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 28;562(1):32–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W. Interstrand cross-linking of DNA by 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and other 1-(2-haloethyl)-1-nitrosoureas. Cancer Res. 1977 May;37(5):1450–1454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery J. A. Chemistry and structure-activity studies of the nitrosoureas. Cancer Treat Rep. 1976 Jun;60(6):651–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. W., Murphy D. G., Cristofalo V. J., Toji L. H., Greene A. E., Dwight S. A. Characterization of a new human diploid cell strain, IMR-90. Science. 1977 Apr 1;196(4285):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.841339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osieka R., Houchens D. P., Goldin A., Johnson R. K. Chemotherapy of human colon cancer xenografts in athymic nude mice. Cancer. 1977 Nov;40(5 Suppl):2640–2650. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197711)40:5+<2640::aid-cncr2820400938>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panasci L. C., Green D., Nagourney R., Fox P., Schein P. S. A structure-activity analysis of chemical and biological parameters of chloroethylnitrosoureas in mice. Cancer Res. 1977 Aug;37(8 Pt 1):2615–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed D. J., May H. E., Boose R. B., Gregory K. M., Beilstein M. A. 2-chloroethanol formation as evidence for a 2-chloroethyl alkylating intermediate during chemical degradation of 1-(2-chloroethyl)-3-cyclohexyl-1-nitrosourea and 1-(2-chloroethyl)-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)-1-nitrosourea. Cancer Res. 1975 Mar;35(3):568–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schabel F. M., Jr Nitrosoureas: a review of experimental antitumor activity. Cancer Treat Rep. 1976 Jun;60(6):665–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. B., Osieka R., Kohn K. W. DNA cross-linking by in vivo treatment with 1-(2-chloroethyl)-3-(4-methylcyclohexyl)-1-nitrosourea of sensitive and resistant human colon carcinoma xenograms in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2448–2454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler K. T., Deen D. F., Wilson C. B., Williams M. E., Sheppard S. BCNU-modification of the in vitro radiation response in 9L brain tumor cells of rats. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1977 Jan-Feb;2(1-2):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(77)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



