Abstract
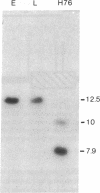
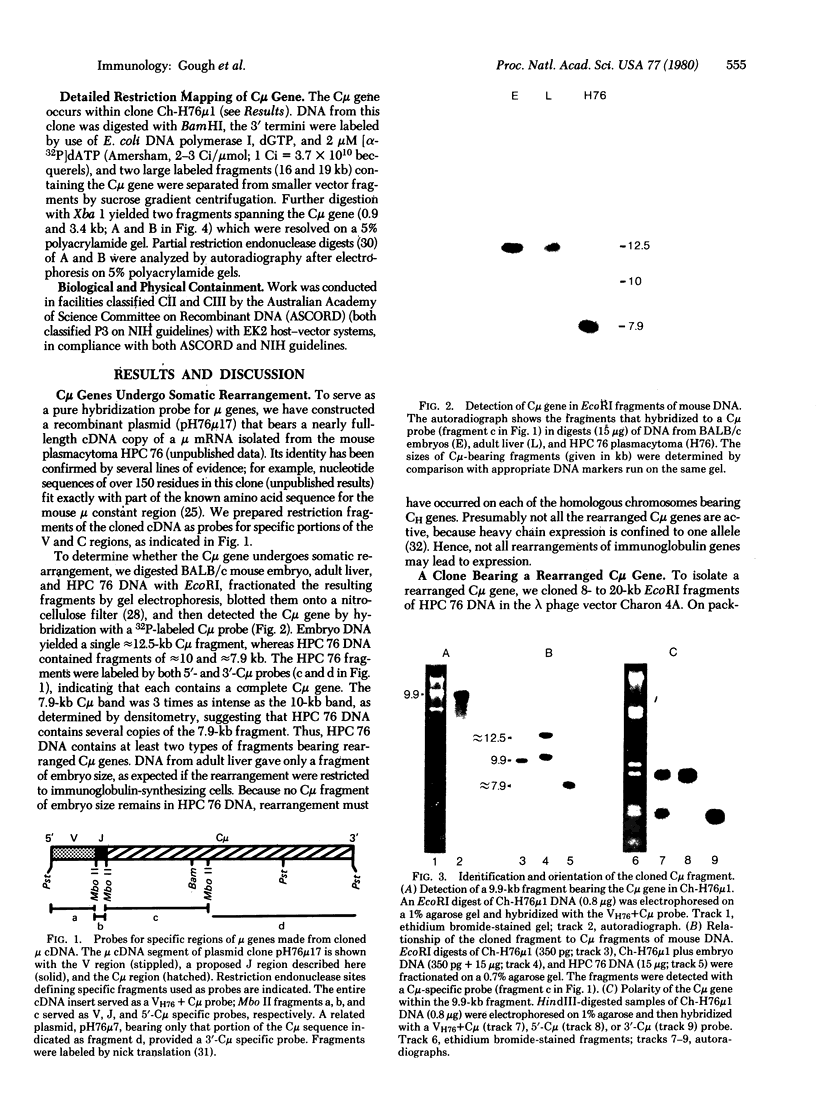
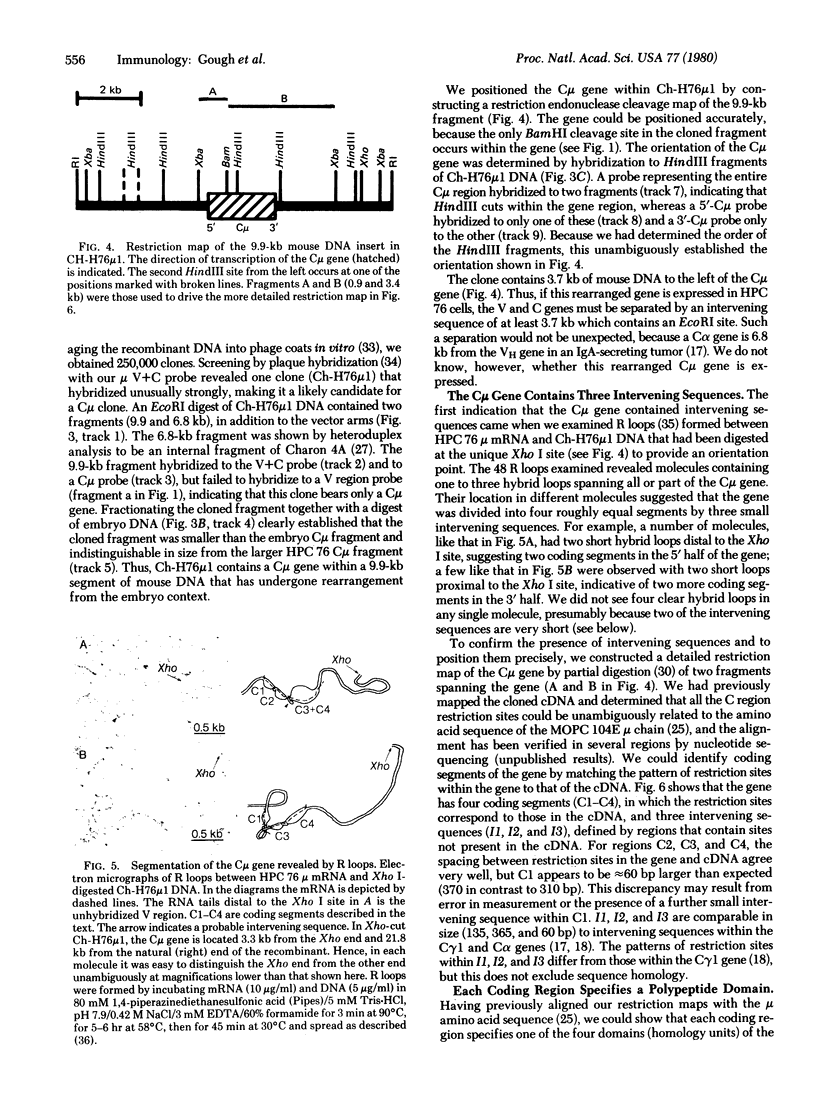
To elucidate the structure of the gene for the constant region of immunoglobulin mu chains, we have cloned a 9.9-kilobase-pair fragment of mouse DNA bearing a gene for the constant region of the mu chain (C mu gene) from an IgM-secreting mouse plasmacytoma. The sequence around this gene has apparently undergone somatic rearrangement; the gene occurs in an EcoRI restriction endonuclease fragment of a different size from that in embryo or liver DNA and no C mu-bearing fragment of embryo size remains in the plasmacytoma. The cloned sequence lacks a variable region gene; hence, if this C mu gene is active, its position within the clone indicates that the gene for the variable region of a heavy chain (VH gene) must be more than 3.7 kilobase pairs away. The C mu gene is divided by three intervening sequences into four coding segments, each of which encodes one of the domains (homology units) of the polypeptide. The nucleotide sequence coding for amino acids near the V-C junction is not present within the C mu clone or clones bearing homologous embryonic VH genes. This suggests that an immunoglobulin heavy chain, in common with light chains, is encoded not only by a V and C gene, but also by an independent joining region (JH) gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Hozumi N., Tonegawa S. Sequences of mouse immunoglobulin light chain genes before and after somatic changes. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Hirama M., Lenhard-Schuller R., Tonegawa S. A complete immunoglobulin gene is created by somatic recombination. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Tonegawa S. Variable and constant parts of the immunoglobulin light chain gene of a mouse myeloma cell are 1250 nontranslated bases apart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5652–5656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. Split genes and RNA splicing. Science. 1979 Apr 20;204(4390):264–271. doi: 10.1126/science.373120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Implications of RNA-RNA splicing in evolution of eukaryotic cells. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1257–1260. doi: 10.1126/science.364651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer W. J., Bennett J. C. The molecular basis of antibody formation: a paradox. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):864–869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P. W., Davis M. M., Kaback D. B., Davidson N., Hood L. Immunoglobulin heavy chain gene organization in mice: analysis of a myeloma genomic clone containing variable and alpha constant regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):857–861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. The genetic control of immunoglobulin synthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:1–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W., Scott D. W., Layton J. E. Genetics, cellular expression and function of IgD and IgM receptors. Immunol Rev. 1977;37:152–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M., Sibley C., Fuhrman J., Schilling J., Hood L. E. Amino acid sequence of a mouse immunoglobulin mu chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Cory S., Adams J. M. Cloned pairs of variable region genes for immunoglobulin heavy chains isolated from a clone library of the entire mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4627–4631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard-Schuller R., Hohn B., Brack C., Hirama M., Tonegawa S. DNA clones containing mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain genes isolated by in vitro packaging into phage lambda coats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie M. R., Gutman G. A., Warner N. L. The binding of murine IgM to Staphylococcal A protein. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(5):367–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOSSAL G. J., SZENBERG A., ADA G. L., AUSTIN C. M. SINGLE CELL STUDIES ON 19S ANTIBODY PRODUCTION. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:485–502. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Thomas M., Kramer R. A., Davis R. W. Unique arrangement of coding sequences for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S and 25 S ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as determined by R-loop and hybridization analysis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):387–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A. Evidence for noncontiguous variable and constant region genes in both germ line and myeloma DNA. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. N., Rudikoff S., Krutzsch H., Potter M. Structural evidence for independent joining region gene in immunoglobulin heavy chains from anti-galactan myeloma proteins and its potential role in generating diversity in complementarity-determining regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2890–2894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Hüppi K., Heinrich G., Tonegawa S. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):288–294. doi: 10.1038/280288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Rogers J. H., Hüppi K., Brack C., Traunecker A., Maki R., Wall R., Tonegawa S. Domains and the hinge region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain are encoded in separate DNA segments. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):627–633. doi: 10.1038/277627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder A., Edgell M. H., Polsky F., Tilghman S. M., Tiemeier D. C., Leder P. Multiple related immunoglobulin variable-region genes identified by cloning and sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3881–3885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder P. The arrangement and rearrangement of antibody genes. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):790–795. doi: 10.1038/276790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. In vitro packaging of a lambda Dam vector containing EcoRI DNA fragments of Escherichia coli and phage P1. Gene. 1977 May;1(3-4):255–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., White R. L., Davis R. W. Hybridization of RNA to double-stranded DNA: formation of R-loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Maxam A. M., Tizard R., Bernard O., Gilbert W. Sequence of a mouse germ-line gene for a variable region of an immunoglobulin light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Wang I. Y., Fudenberg H. H. Immunoglobulin structure and genetics. Identity between variable regions of a mu and a gamma2 chain. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7192–7199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]