Abstract
Azidonitrobenzoyl mono[125I]iodo scorpion toxin can be covalently attached to its receptor site in electrically excitable neuroblastoma cells or synaptosomes by photolysis. A polypeptide of Mr approximately 250,000 is specifically labeled in neuroblastoma cells. Labeling is blocked by unlabeled scorpion toxin and by depolarization. This polypeptide is not labeled in a variant neuroblastoma clone lacking voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Polypeptides of Mr approximately 250,000 and Mr approximately 32,000 are specifically labeled in synaptosomes. This labeling is also blocked by unlabeled toxin and by depolarization. These results identify specific polypeptides of Mr approximately 250,000 and Mr approximately 32,000 that are components of the sodium channel.
Full text
PDF
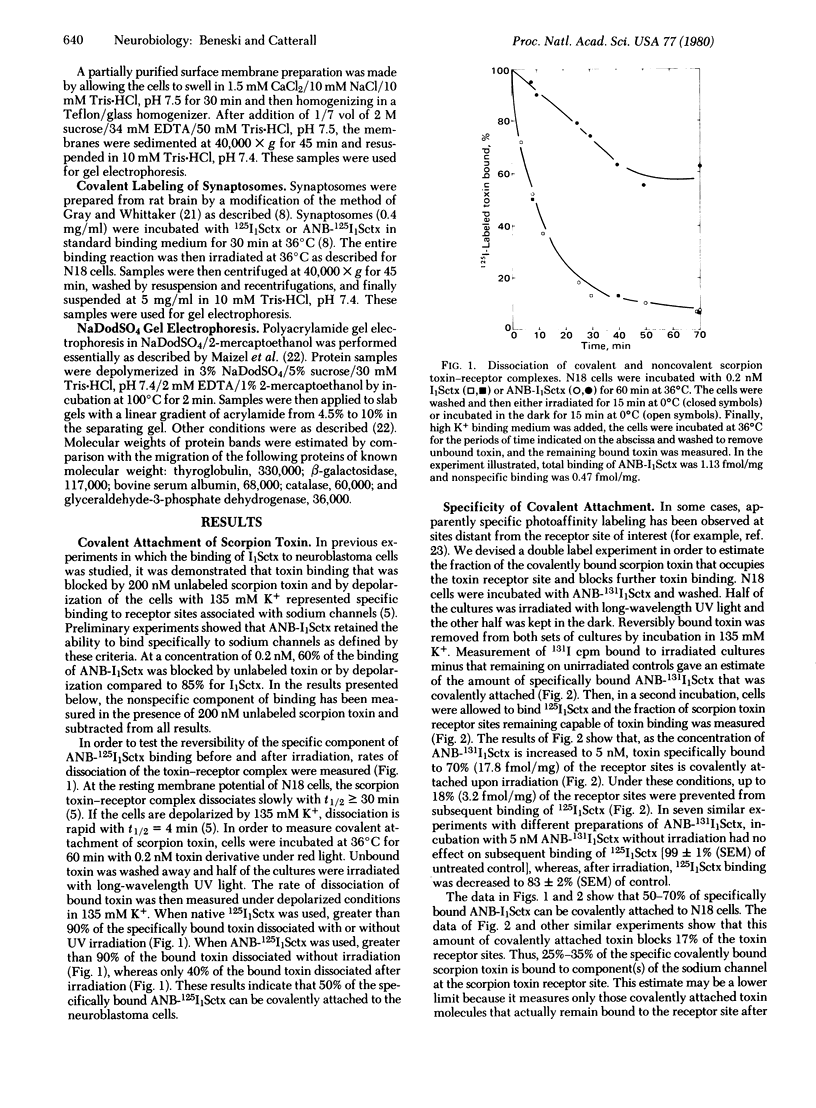
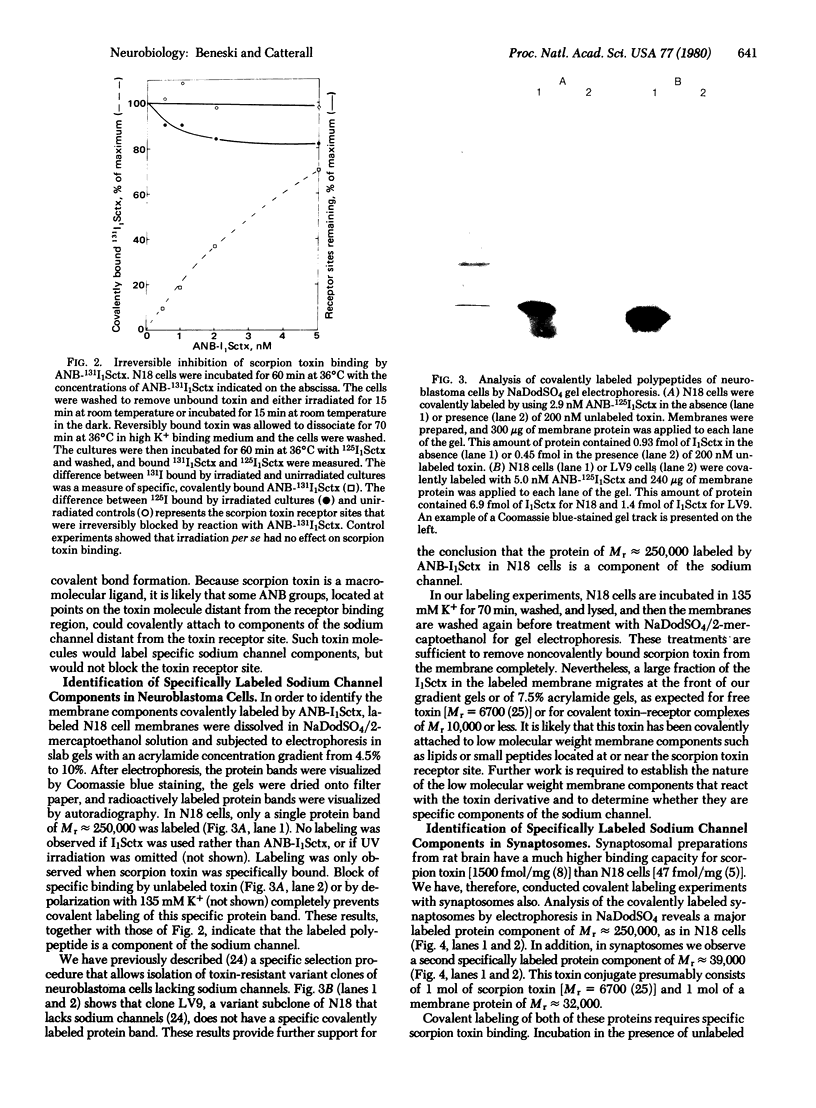


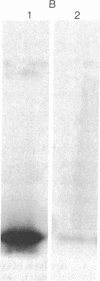
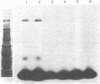
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R., Brabson J. S., Raftery M. A. Purification of the tetrodotoxin-binding component associated with the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from Electrophorus electricus electroplax membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer T. I., Raftery M. A. Solubilization and partial characterization of the tetrodotoxin binding component from nerve axons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):939–944. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Activation of the action potential Na+ ionophore by neurotoxins. An allosteric model. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8669–8676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Beress L. Sea anemone toxin and scorpion toxin share a common receptor site associated with the action potential sodium ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7393–7396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Binding of scorpion toxin to receptor sites associated with sodium channels in frog muscle. Correlation of voltage-dependent binding with activation. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Sep;74(3):375–391. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cooperative activation of action potential Na+ ionophore by neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1782–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Membrane potential-dependent binding of scorpion toxin to the action potential Na+ ionophore. Studies with a toxin derivative prepared by lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8660–8668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Morrow C. S., Hartshorne R. P. Neurotoxin binding to receptor sites associated with voltage-sensitive sodium channels in intact, lysed, and detergent-solubilized brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11379–11387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Purification of a toxic protein from scorpion venom which activates the action potential Na+ ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5528–5536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couraud F., Rochat H., Lissitzky S. Binding of scorpion and sea anemone neurotoxins to a common site related to the action potential Na+ ionophore in neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1525–1530. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Miyakawa T., Fox C. F., Pruss R. M., Aharonov A., Herschman H. R. Specific radiolabeling of a cell surface receptor for epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2790–2794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Wang J. H. Solubilization of a specific tetrodotoxin-binding component from garfish olfactory nerve membrane. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4565–4569. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques Y., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Molecular properties of the action potential Na+ ionophore in neuroblastoma cells. Interactions with neurotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7383–7392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji T. H. A novel approach to the identification of surface receptors. The use of photosensitive hetero-bifunctional cross-linking reagent. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1566–1570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji T. H. The application of chemical crosslinking for studies on cell membranes and the identification of surface reporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 23;559(1):39–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jover E., Martin-Moutot N., Couraud F., Rochat H. Scorpion toxin: specific binding to rat synaptosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):377–382. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Cowburn D. The affinity-labeling of partially purified acetylcholine receptor from electric tissue of Electrophorus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3636–3640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Roberts M. F., Dennis E. A., Allison W. S. Photoactivated heterobifunctional cross-linking reagents which demonstrate the aggregation state of phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5650–5654. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens J. R., Haley B. E. A study of adenosine 3'-5' cyclic monophosphate binding sites of human erythrocyte membranes using 8-azidoadenosine 3'-5' cyclic monophosphate, a photoaffinity probe. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(1):91–102. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray R., Morrow C. S., Catterall W. A. Binding of scorpion toxin to receptor sites associated with voltage-sensitive sodium channels in synaptic nerve ending particles. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7307–7313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B. The binding of saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin to excitable tissue. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;79:1–50. doi: 10.1007/BFb0037088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoho A. E., Kiefer H., Roeder P. E., Singer S. J. The mechanism of photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2567–2571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West G. J., Catterall W. A. Selection of variant neuroblastoma clones with missing or altered sodium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4136–4140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]