Abstract
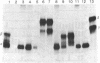
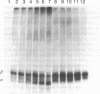
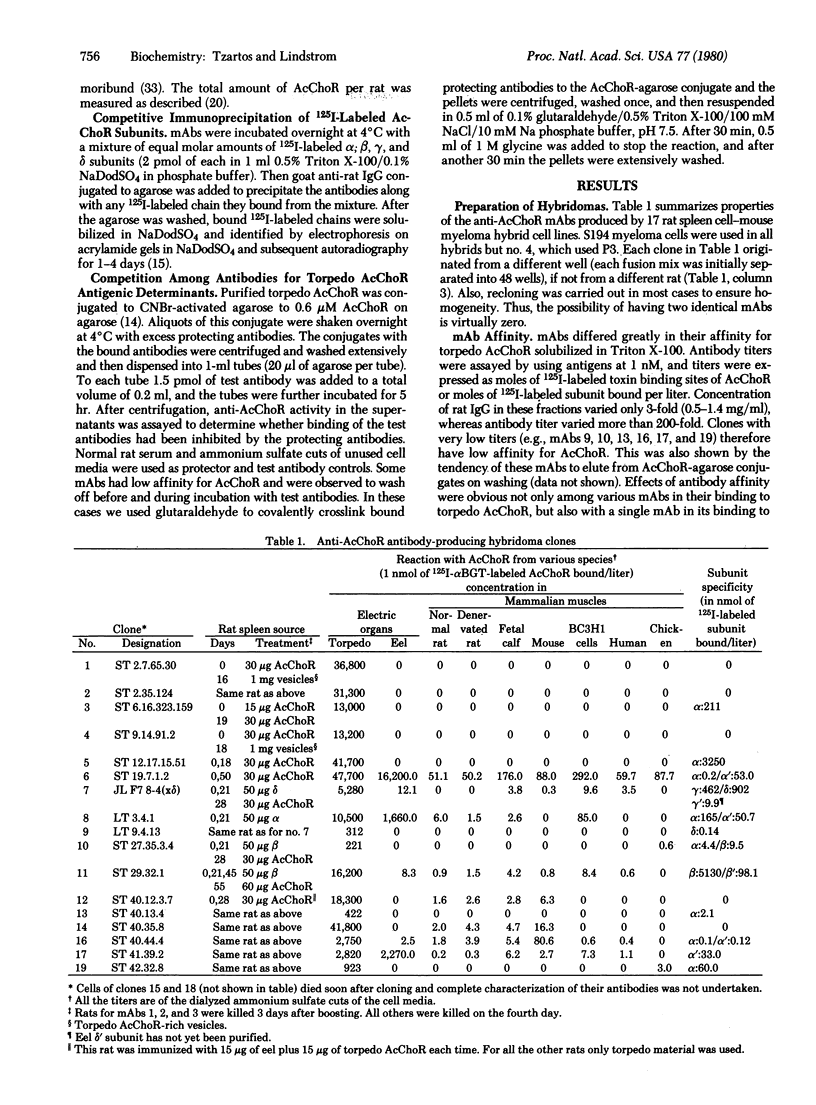
Seventeen cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies against Torpedo californica (torpedo) acetylcholine receptor (AcChoR) and its subunits were established. By using these antibodies as probes, we identified: (i) a similar antigenic determinant on alpha and beta torpedo subunits, (ii) a similar antigenic determinant on gamma and delta subunits, (iii) antigenic determinants unique for alpha or beta torpedo AcChoR subunits, (iv) a small region on the alpha subunit that dominates the immunogenicity of native torpedo AcChoR in rats (a monoclonal antibody directed at this region could bind to rat AcChoR in vivo and cause passive experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis), and (v) antigenic determinants on torpedo subunits recognized in AcChoR from other species. The unexpected similarities between alpha and beta and between gamma and delta subunits raise the possibility that the complex four-subunit structure of AcChoR was derived from a simpler precursor and suggests that these antigenic similarities might reflect some structural and functional homologies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanchard S. G., Raftery M. A. Identification of the polypeptide chains in Torpedo californica electroplax membranes that interact with a local anesthetic analog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):81–85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Benedetti L., Bourgeois J. P., Brisson A., Cartaud J., Devaux P., Grünhagen H., Moreau M., Popot J. L., Sobel A. Some structural properties of the cholinergic receptor protein in its membrane environmental relevant to its function as a pharmacological receptor. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:211–230. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Raftery M. A. Immunological comparison of acetylcholine receptors and their subunits from species of electric ray. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., Karlin A. Affinity labeling of one of two alpha-neurotoxin binding sites in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2039–2045. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi A. T., Eldefrawi M. E., Albuquerque E. X., Oliveira A. C., Mansour N., Adler M., Daly J. W., Brown G. B., Burgermeister W., Witkop B. Perhydrohistrionicotoxin: a potential ligand for the ion conductance modulator of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2172–2176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J., Dunn S. M., Blanchard S. G., Raftery M. A. Specific binding of perhydrohistrionicotoxin to Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2576–2579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Lindstrom J. M., Lambert E. H., Lennon V. A. Ultrastructural localization of the acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis and in its experimental autoimmune model. Neurology. 1977 Apr;27(4):307–315. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.4.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Sakakibara H., Sahashi K., Lindstrom J. M., Lambert E. H., Lennon V. A. Passively transferred experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Sequential and quantitative study of the motor end-plate fine structure and ultrastructural localization of immune complexes (IgG and C3), and of the acetylcholine receptor. Neurology. 1979 Feb;29(2):179–188. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Karlin A., Hall Z. W. Affinity alkylation labels two subunits of the reduced acetylcholine receptor from mammalian muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4685–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Rafto S. Comparison of the subunits of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor by peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):301–307. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez C. M., Richman D. P., Berman P. W., Burres S. A., Arnason B. G., Fitch F. W. Monoclonal antibodies against purified nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. L., McLaughlin M., Karlin A. Formation of disulfide-linked oligomers of acetylcholine receptor in membrane from torpedo electric tissue. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):155–163. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Changeux J. P. Structural and functional properties of the acetylcholine receptor protein in its purified and membrane-bound states. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:317–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S., Bevan S., Kullberg R., Lindstrom J., Rice J. Modulation of acetylcholine receptor by antibody against the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3090–3094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao I., Drachman D. B. Myasthenic immunoglobulin accelerates acetylcholine receptor degradation. Science. 1977 Apr 29;196(4289):527–529. doi: 10.1126/science.850793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Holtzman E., Valderrama R., Damle V., Hsu K., Reyes F. Binding of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors in Electrophorus and Torpedo electroplax membranes. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):577–592. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Weill C. L., McNamee M. G., Valderrama R. Facets of the structures of acetylcholine receptors from Electrophorus and Torpedo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:203–210. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Lindstrom J. M., Seybold M. E. Experimental autoimmune myasthenia: A model of myasthenia gravis in rats and guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1365–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Seybold M. E., Lindstrom J. M., Cochrane C., Ulevitch R. Role of complement in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):973–983. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Einarson B. L., Lennon V. A., Seybold M. E. Pathological mechanisms in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. I. Immunogenicity of syngeneic muscle acetylcholine receptor and quantitative extraction of receptor and antibody-receptor complexes from muscles of rats with experimental automimmune myasthenia gravis. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):726–738. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Engel A. G., Seybold M. E., Lennon V. A., Lambert E. H. Pathological mechanisms in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. II. Passive transfer of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis in rats with anti-acetylcholine recepotr antibodies. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):739–753. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Lennon V. A., Seybold M. E., Whittingham S. Experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis and myasthenia gravis: biochemical and immunochemical aspects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:254–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. Autoimmune response to acetylcholine receptors in myasthenia gravis and its animal model. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Campbell M., Nave B. Specificities of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. Muscle Nerve. 1978 Mar-Apr;1(2):140–145. doi: 10.1002/mus.880010206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Einarson B., Merlie J. Immunization of rats with polypeptide chains from torpedo acetylcholine receptor causes an autoimmune response to receptors in rat muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):769–773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Walter B., Einarson B. Immunochemical similarities between subunits of acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo, Electrophorus, and mammalian muscle. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4470–4480. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N. M., Hall Z. W. Subunit structure and peptide mapping of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors from rat muscle. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3392–3401. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Lindstrom J. Autoimmune response to acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1973 May 25;180(4088):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4088.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Vandlen R. L., Reed K. L., Lee T. Characterization of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor: its subunit composition and ligand-binding properties. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:193–202. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfrè G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Monoclonal xenogeneic antibodies to murine cell surface antigens: identification of novel leukocyte differentiation antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):539–551. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S. Interspecies spleen-myeloma hybrid producing monoclonal antibodies against mouse lymphocyte surface glycoprotein, T200. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):313–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weill C. L., McNamee M. G., Karlin A. Affinity-labeling of purified acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 11;61(3):997–1003. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Galfrè G., Milstein C. Analysis of cell surfaces by xenogeneic myeloma-hybrid antibodies: differentiation antigens of rat lymphocytes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]