Abstract
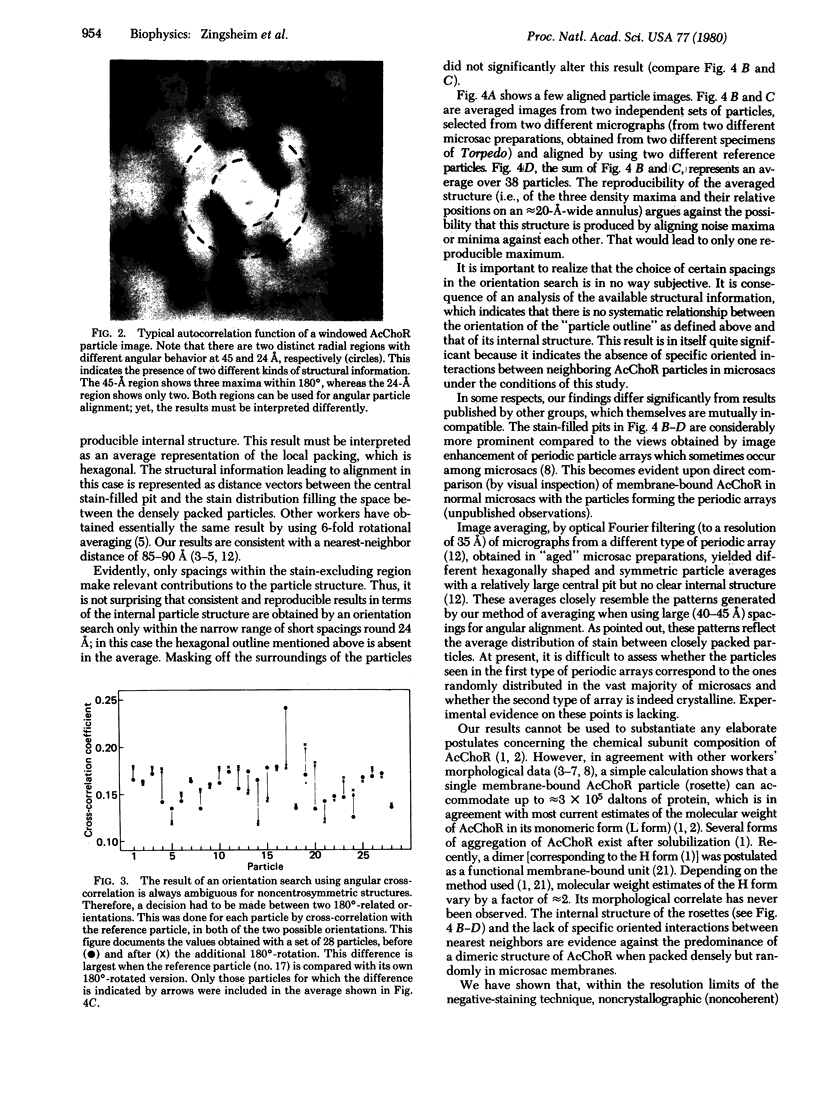
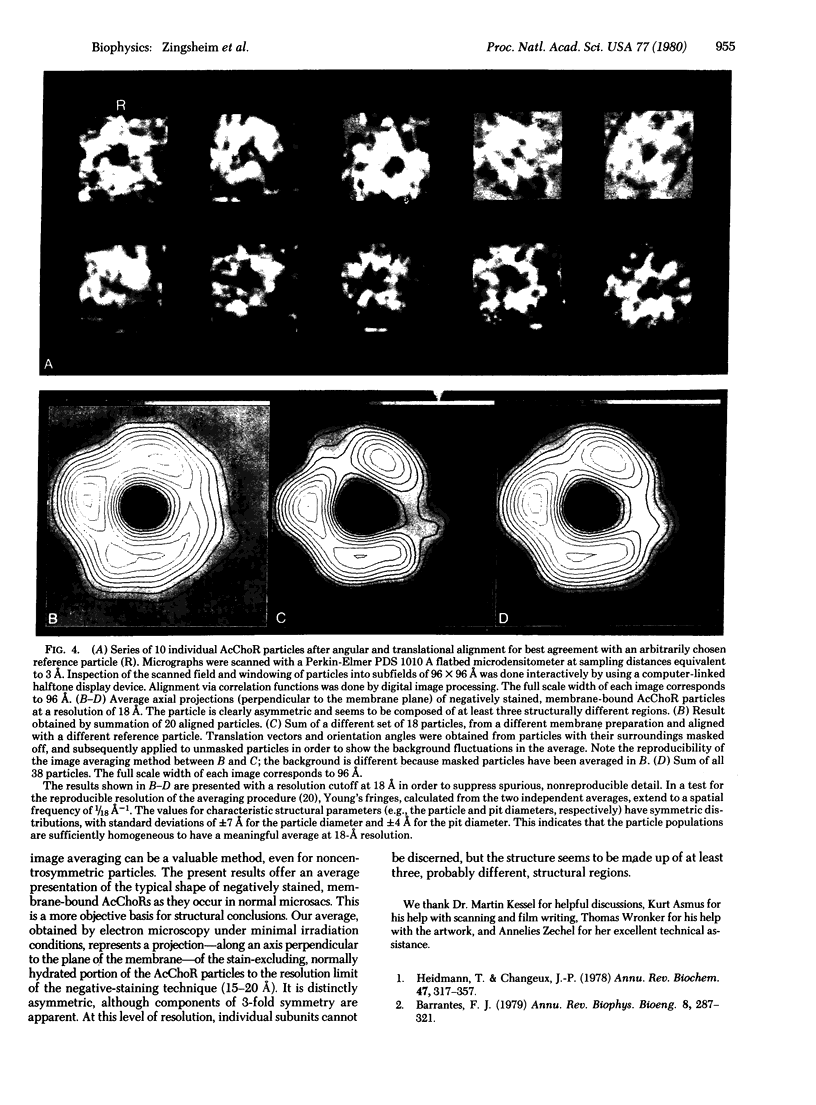
A projection, at 15- to 20-A resolution, is presented of the structure of the membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata. The projection has its axis perpendicular to the membrane plane; its main contribution originates from a hydrated portion of the protein, which extends from the membrane into the aqueous medium. The structure is distinctly asymmetric, with individual morphological subunits barely resolvable. These results have been obtained by noncrystallographic averaging, using correlation functions, applied to electron micrographs of receptor-rich membrane fragments. The micrographs had been taken with minimal beam exposure in a scanning transmission electron microscope.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrantes F. J. Endogenous chemical receptors: some physical aspects. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:287–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Benedetti E. L. A morphological study of the cholinergic receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata in its membrane environment and in its detergent-extracted purified form. J Cell Sci. 1978 Feb;29:313–337. doi: 10.1242/jcs.29.1.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Benedetti E. L., Cohen J. B., Meunier J. C., Changeux J. P. Presence of a lattice structure in membrane fragments rich in nicotinic receptor protein from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 15;33(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Bock E. Molecular forms of acetylcholine receptor. Effects of calcium ions and a sulfhydryl reagent on the occurrence of oligomers. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4513–4520. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Amos L. A. Harmonic analysis of electron microscope images with rotational symmetry. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank J., Goldfarb W., Eisenberg D., Baker T. S. Reconstruction of glutamine synthetase using computer averaging. Ultramicroscopy. 1978;3(3):283–290. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3991(78)80038-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Changeux J. P. Structural and functional properties of the acetylcholine receptor protein in its purified and membrane-bound states. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:317–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel E., Potter L. T. Ultrastructure of isolated membranes of Torpedo electric tissue. Brain Res. 1973 Jul 27;57(2):508–517. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottensmeyer F. P., Andrew J. W., Bazett-Jones D. P., Chan A. S., Hewitt J. Signal to noise enhancement in dark field electron micrographs of vasopressin: filtering of arrays of images in reciprocal space. J Microsc. 1977 Apr;109(3):259–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1977.tb01139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. J., Klymkowsky M. W., Agard D. A., Stroud R. M. Structural studies of a membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):635–659. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebler W., Hucho F. Membranes rich in acetylcholine receptor: characterization and reconstitution to excitable membranes from exogenous lipids. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A., Changeux J. P. Purification and characterization of the cholinergic receptor protein in its membrane-bound and detergent-soluble forms from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(2):511–514. doi: 10.1042/bst0050511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N. Electron microscopy of the stacked disk aggregate of tobacco mosaic virus protein. II. The influence of electron irradiation of the stain distribution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):657–670. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








