Abstract
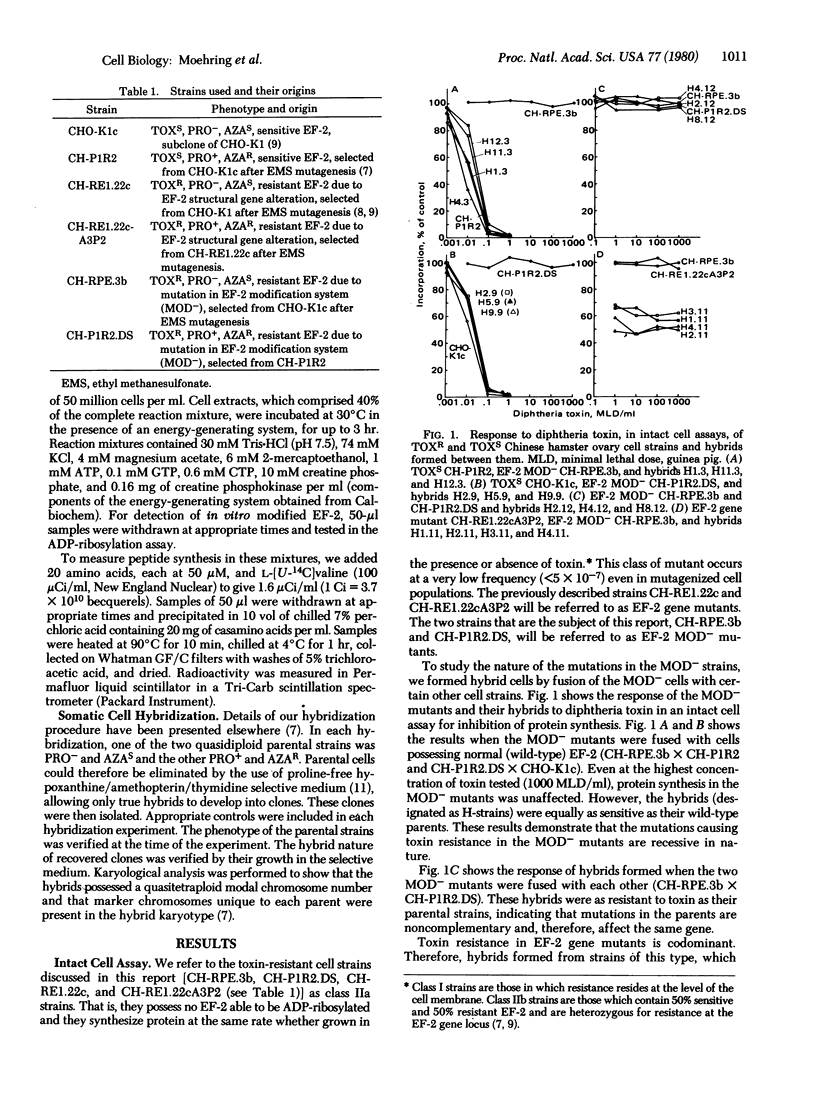
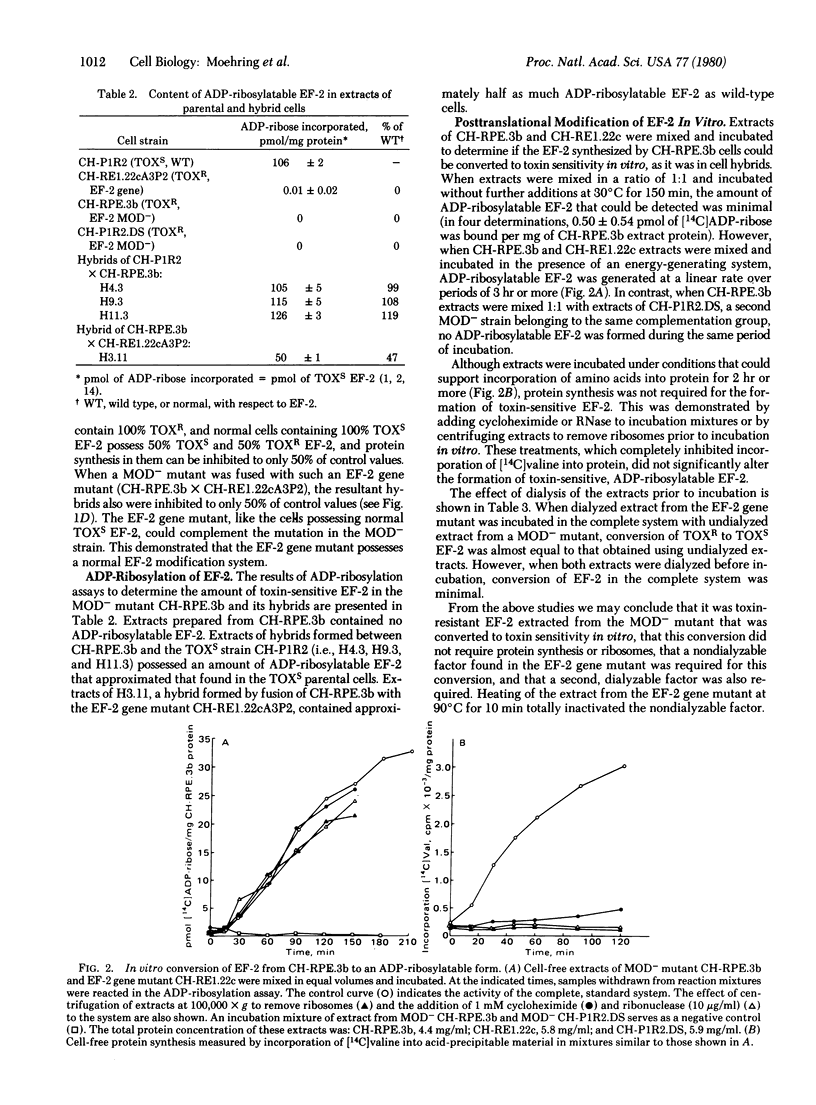
We have identified two types of mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells in which the unique ADP-ribose attachment site in elongation factor 2 (EF-2) is altered, thereby rendering them resistant to diphtheria and Pseudomonas toxins (TOXR). The first is mutant in the gene for EF-2 and possesses a permanently altered, TOXR gene product. The second lacks a component of a posttranslational modification system that converts TOXR EF-2 to the toxin-sensitive (TOXS) state. We postulate that this modification system is involved in the conversion of a single histidine residue in EF-2 to the specific target of toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation, the novel amino acid X. We have designated the second type MOD- mutants. The missing of nonfunctional component in the MOD- mutants can be restored by hybridizing them with either normal TOXS cells or with EF-2 structural gene mutants. The TOXR EF-2 from MOD- mutants is also converted to toxin sensitivity in vitro by incubation with extracts of TOXS or EF-2 gene mutant cells in the presence of an energy-generating system. Our results demonstrate that EF-2 can be synthesized and released from ribosomes in a toxin-resistant form and then converted to toxin sensitivity by posttranslational modification.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown B. A., Bodley J. W. Primary structure at the site in beef and wheat elongation factor 2 of ADP-ribosylation by diphtheria toxin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):253–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. Diphtheria-toxin-resistant mutants of CHO cells affected in protein synthesis: a novel phenotype. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 Sep;4(5):553–571. doi: 10.1007/BF01542926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Characterization of the diphtheria toxin-resistance system in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Jul;5(4):453–468. doi: 10.1007/BF01538880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. The response of cultured mammalian cells to diphtheria toxin. II. The resistant cell: enhancement of toxin action by poly-L-ornithine. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):541–554. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Danley D. E., Moehring J. M. Codominant translational mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells selected with diphtheria toxin. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Jul;5(4):469–480. doi: 10.1007/BF01538881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Selection and characterization of cells resistant to diphtheria toxin and pseudomonas exotoxin A: presumptive translational mutants. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Henriksen O., Maxwell E. S. Elongation factor 2. Amino acid sequence at the site of adenosine diphosphate ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5088–5093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch L. On the nature of hereditable variation in cultured somatic cells. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uy R., Wold F. Posttranslational covalent modification of proteins. Science. 1977 Dec 2;198(4320):890–896. doi: 10.1126/science.337487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Howard J. B., Bodley J. W. Isolation and properties of the trypsin-derived ADP-ribosyl peptide from diphtheria toxin-modified yeast elongation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8687–8690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


