Abstract
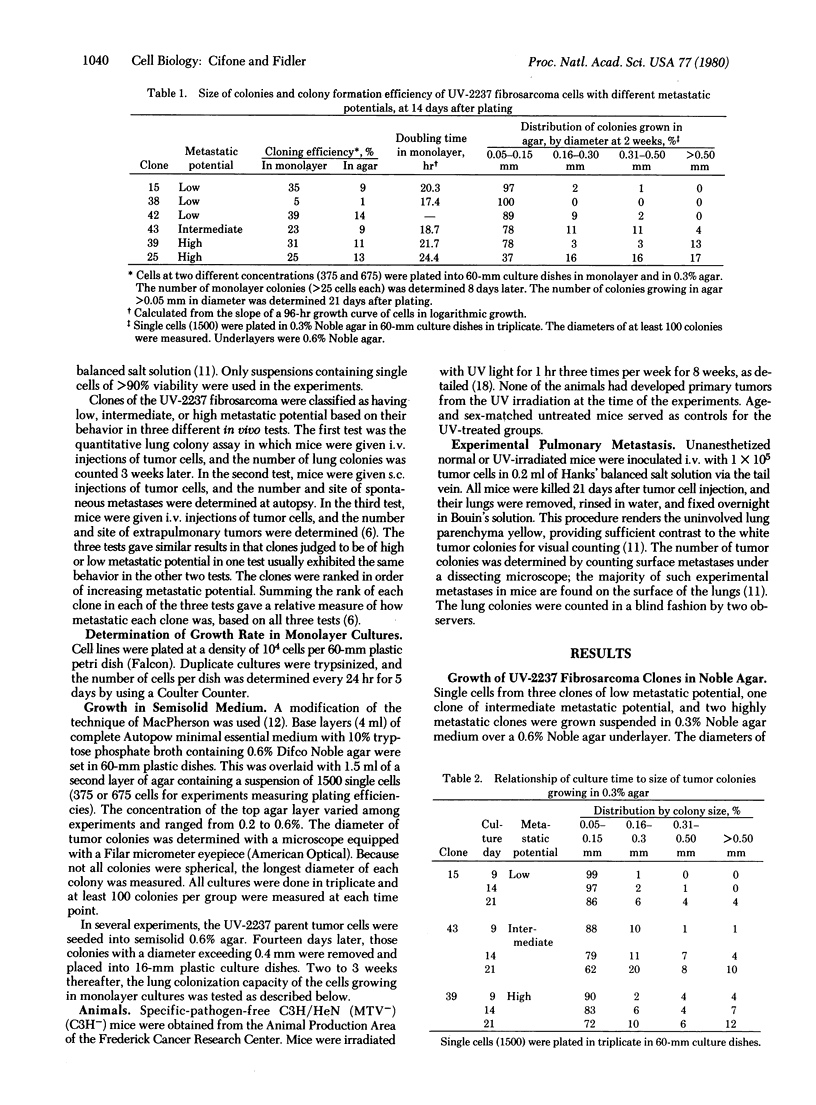
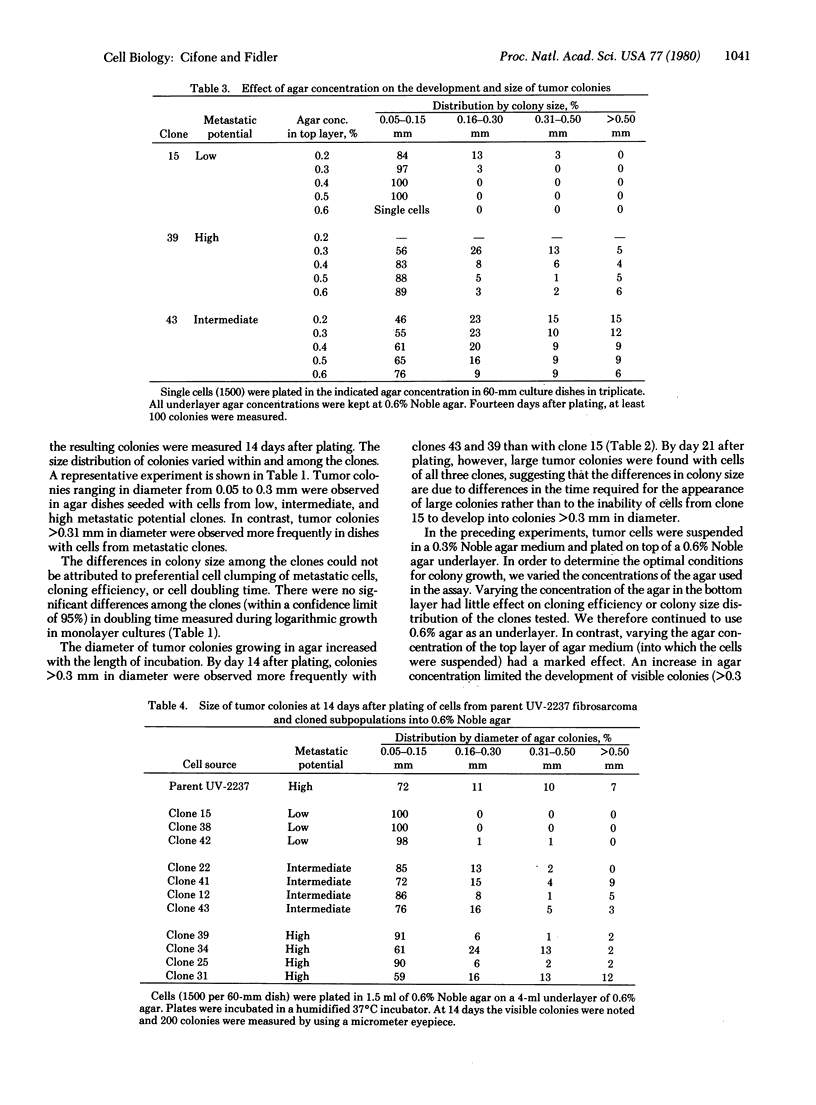
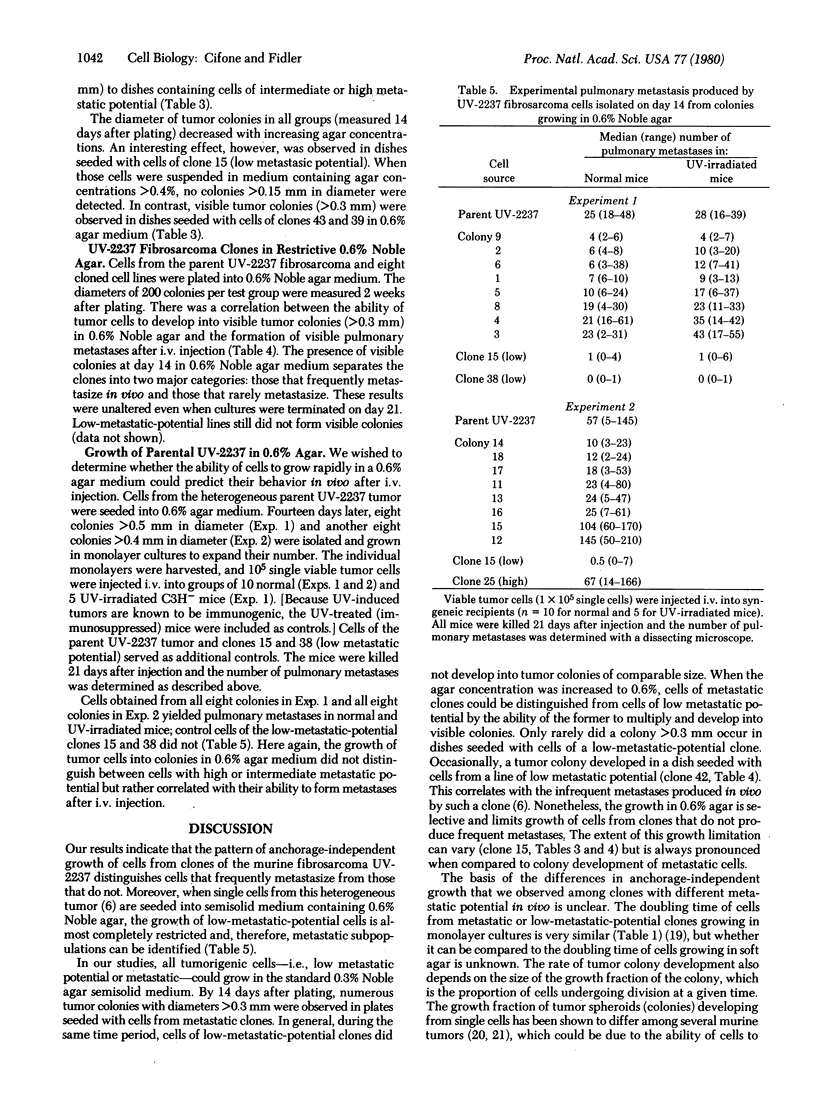
The pattern of in vitro anchorage-independent growth of tumor cells from the murine UV-2237 fibrosarcoma correlated with their ability to produce experimental metastasis in vivo. When seeded into 0.3% Noble agar semisolid medium, cells of metastatic clones developed into larger tumor colonies at a faster rate than did cells of clones with low metastatic potential. Furthermore, when tumor cells were plated into 0.6% Noble agar, colony development by cells of low metastatic potential clones was almost completely restricted. Tumor cells from the heterogeneous parent UV-2237 fibrosarcoma were plated into dishes containing 0.6% agar semisolid medium. In separate experiments, 16 colonies were isolated 2 weeks thereafter and were established as individual cell lines in monolayer cultures. All of these cell lines produced experimental metastases as determined by in vivo lung colony assay. The data suggest that anchorage-independent growth of UV-2237 tumor cells in 0.6% Noble agar semisolid medium is selective and permits the isolation of metastatic subpopulations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aidells B. D., Konrad M. W., Glaser D. A. Growth and morphology of colonies of Chinese hamster ovary cells growing on agar is affected by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1863–1867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. C., Ts'o P. O. Evidence for the progressive nature of neoplastic transformation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3761–3765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colburn N. H., Bruegge W. F., Bates J. R., Gray R. H., Rossen J. D., Kelsey W. H., Shimada T. Correlation of anchorage-independent growth with tumorigenicity of chemically transformed mouse epidermal cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):624–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Kripke M. L. Metastasis results from preexisting variant cells within a malignant tumor. Science. 1977 Aug 26;197(4306):893–895. doi: 10.1126/science.887927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Greenspan H. P. Influence of geometry on control of cell growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 31;417(3-4):211–236. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(75)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M., Penman S. The messenger-like properties of the poly(A)plus RNA in mammalian mitochondria. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Klein E. Immune surveillance against virus-induced tumors and nonrejectability of spontaneous tumors: contrasting consequences of host versus tumor evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2121–2125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L., Fisher M. S. Immunologic parameters of ultraviolet carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Jul;57(1):211–215. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L., Gruys E., Fidler I. J. Metastatic heterogeneity of cells from an ultraviolet light-induced murine fibrosarcoma of recent origin. Cancer Res. 1978 Sep;38(9):2962–2967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L. Latency, histology, and antigenicity of tumors induced by ultraviolet light in three inbred mouse strains. Cancer Res. 1977 May;37(5):1395–1400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Brunson K. W., Fidler I. J. Specificity of arrest, survival, and growth of selected metastatic variant cell lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4105–4111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science. 1976 Oct 1;194(4260):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.959840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin S. I., Freedman V. H., Risser R., Pollack R. Tumorigenicity of virus-transformed cells in nude mice is correlated specifically with anchorage independent growth in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4435–4439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Withers H. R. Isolation from a murine fibrosarcoma of cell lines with enhanced plating efficiency in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Jan;60(1):179–183. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuhas J. M., Li A. P. Growth fraction as the major determinant of multicellular tumor spheroid growth rates. Cancer Res. 1978 Jun;38(6):1528–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


