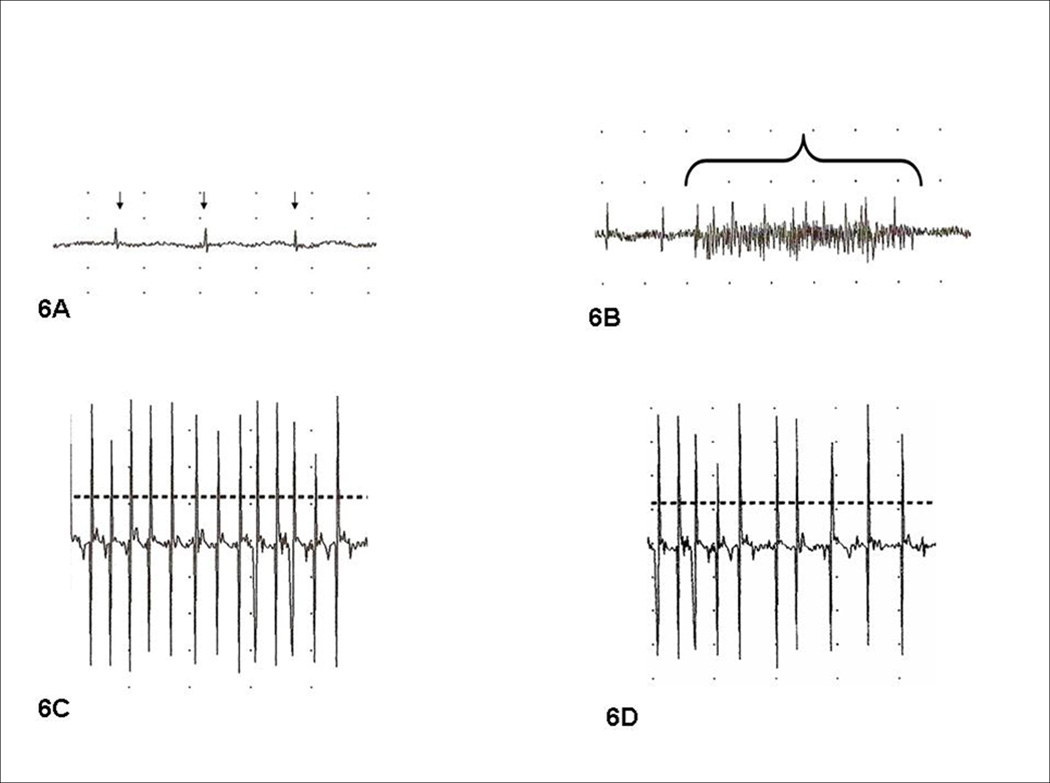
Figure 6. LEMG Findings after RLN injury & VNC PCA injection.
Figure 6A. Denervated, VNC-treated PCA 8 weeks after RLN injury shows severe denervation with fibrillations and fasciculations (small arrows), suggesting the VNC injection had effectively impaired reinnervation. Figure 6B. Denervated PCA with saline injection demonstrates spontaneous reinnervation based on inspiratory recruitment of small motor units. Figure 6C. Denervated TA with spontaneous reinnervation after the ipsilateral PCA had been treated with VNC. Note the reinnervation of C is similar to the TA reinnervation of 6D (control), suggesting that the VNC treatment did not affect TA reinnervation. Figure 6D. Control denervated TA with spontaneous reinnervation after ipsilateral PCA received saline alone.