Abstract
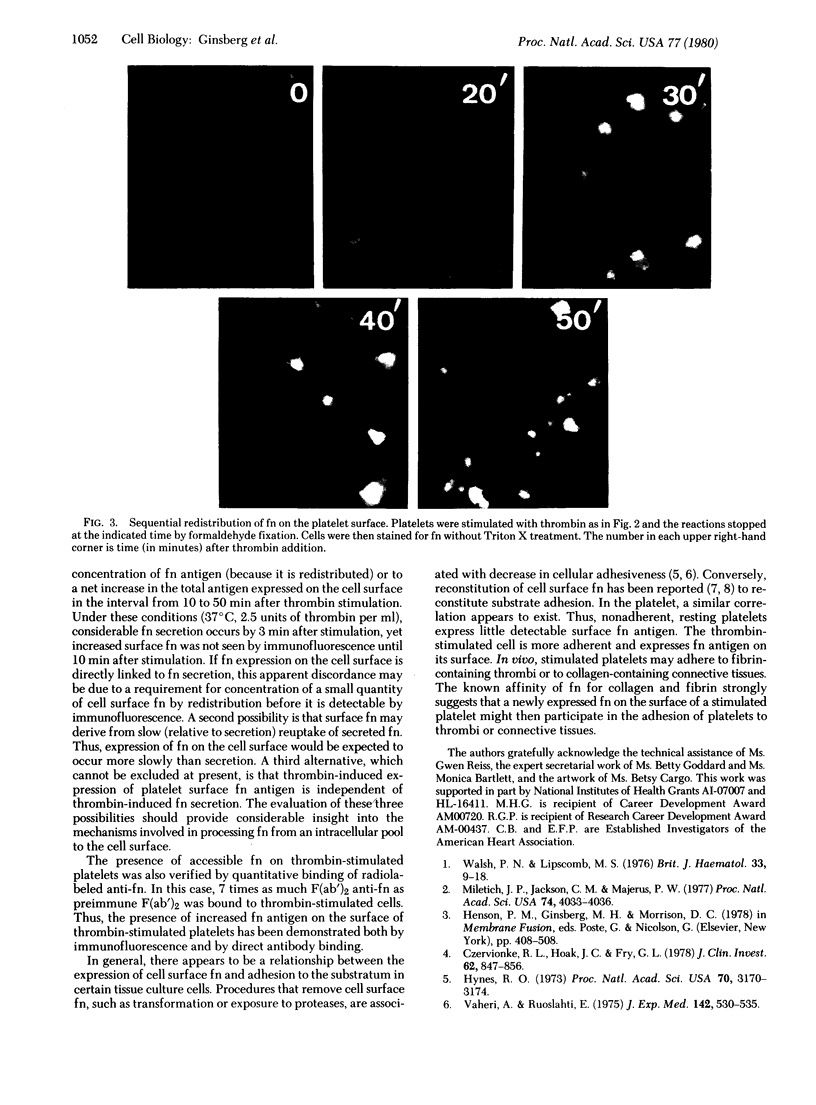
Fibronectins (fn) are adhesive glycoproteins which bind to collagen and to fibrin and appear to be important in cellular adhesion to other cells or surfaces. Fn-related antigen is present in human platelets, suggesting a possible role for fn in the adhesive properties of platelets. We have studied the localization of fn in resting and thrombin-stimulated platelets by immunofluorescence and quantitative binding of radiolabeled antibody. In resting fixed platelets, variable light surface staining for fn was observed. When these cells were made permeable to antibody with detergent, staining for fn was markedly enhanced and was present in a punctate distribution, suggesting intracellular localization. Stimulation with thrombin, which is associated with increased platelet adhesiveness, resulted in increased staining for fn antigen on intact platelets. These stimulated cells did not leak 51Cr nor did they stain for F-actin, thus documenting that the increased fn staining was not due to loss of plasma membrane integrity. The thrombin-induced increase in accessible platelet fn antigen was confirmed by quantitative antibody binding studies in which thrombin-stimulated platelets specifically bound 15 times as much radiolabeled F(ab')2 anti-fn as did resting cells. Thus, thrombin stimulation results in increased expression of fn antigen on the platelet surface. Here it may participate in interactions with fibrin, connective tissue, or other cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali I. U., Mautner V., Lanza R., Hynes R. O. Restoration of normal morphology, adhesion and cytoskeleton in transformed cells by addition of a transformation-sensitive surface protein. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90322-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensusan H. B., Koh T. L., Henry K. G., Murray B. A., Culp L. A. Evidence that fibronectin is the collagen receptor on platelet membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5864–5868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czervionke R. L., Hoak J. C., Fry G. L. Effect of aspirin on thrombin-induced adherence of platelets to cultured cells from the blood vessel wall. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):847–856. doi: 10.1172/JCI109197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E., Miller E. J. Affinity of fibronectin to collagens of different genetic types and to fibrinogen. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1584–1595. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Kozin F., O'Malley M., McCarty D. J. Release of platelet constituents by monosodium urate crystals. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):999–1007. doi: 10.1172/JCI108880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Ash J. F. Use of the avidin-biotin complex for the localization of actin and myosin with fluorescence microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):783–788. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Ali I. U., Destree A. T., Mautner V., Perkins M. E., Senger D. R., Wagner D. D., Smith K. K. A large glycoprotein lost from the surfaces of transformed cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:317–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. Human platelets possess an inducible and saturable receptor specific for fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5357–5363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Interaction of coagulation factor Xa with human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Umfleet R. A. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma. I. Purification, primary characterization, and relationship to fibrinogen and other cold-insoluble fraction components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5728–5736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Cross-linking of cold-insoluble globulin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6614–6621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Schad P. E. Cross-linking of fibronectin to collagen by blood coagulation Factor XIIIa. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):781–787. doi: 10.1172/JCI109524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S. Proteins secreted by the platelet. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Dec 15;38(4):924–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Thrombin substrates and the proteolytic site of thrombin action on human-platelet plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):218–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Birdwell C., Ginsberg M. H. Identification and quantitation of platelet-associated fibronectin antigen. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):540–543. doi: 10.1172/JCI109334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Ruoslahti E. Fibroblast surface antigen produced but not retained by virus-transformed human cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):530–535. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N., Lipscomb M. S. Comparison of the coagulant activities of platelets and phospholipids. Br J Haematol. 1976 May;33(1):9–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. Cell surface protein partially restores morphology, adhesiveness, and contact inhibition of movement to transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Mosesson M. W., Broekman M. J., Kaplan K. L. Release of platelet fibronectin (cold-insoluble globulin) from alpha granules induced by thrombin or collagen; lack of requirement for plasma fibronectin in ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Blood. 1979 Jul;54(1):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]