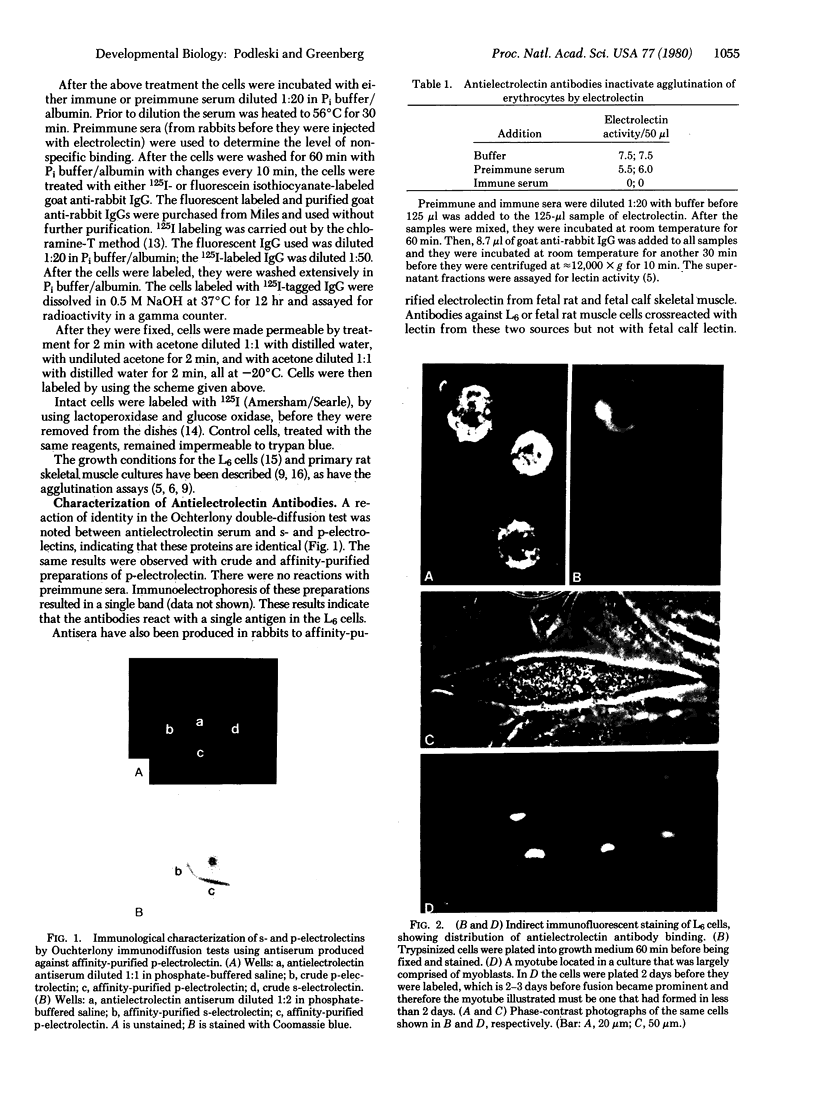
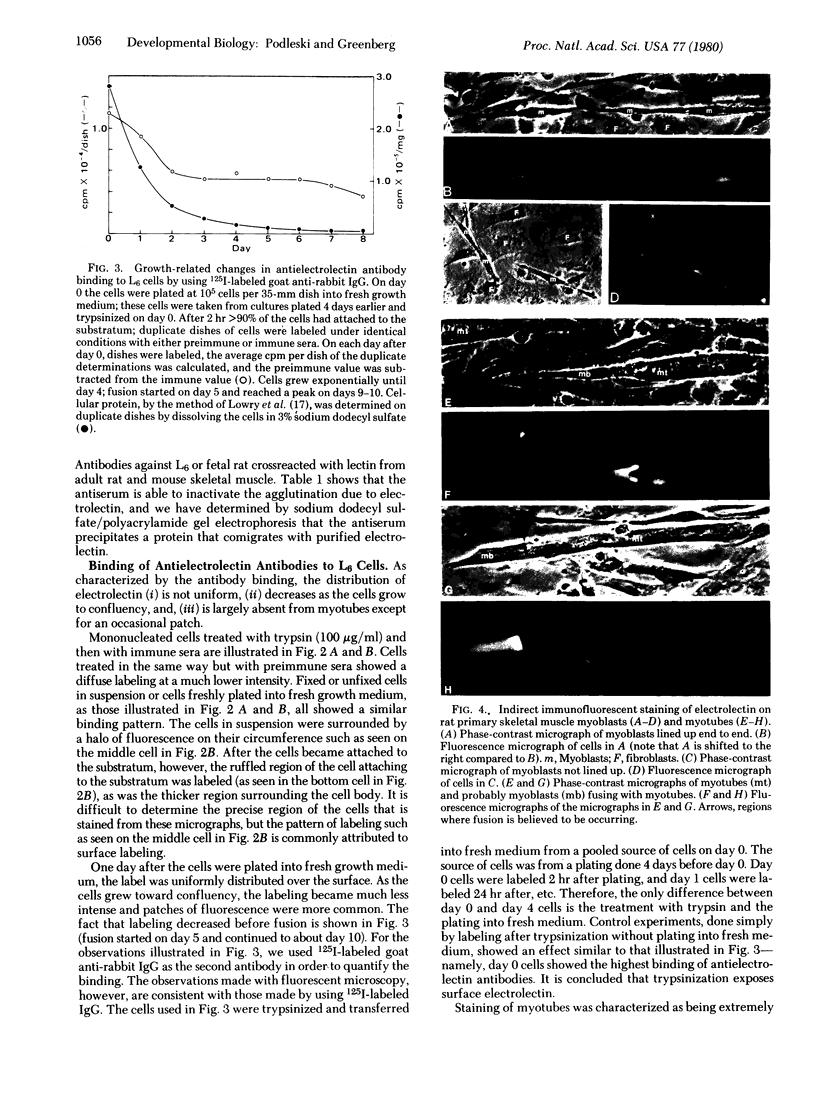
Abstract
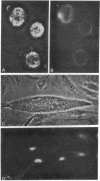
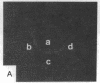
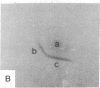
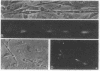
Antibodies to electrolectin, a lectin endogenous to embryonic skeletal muscle, have been used to study the distribution of electrolectin during myogenesis in L6 cells and rat primary muscle cultures. Antibody binding is highest to mononucleated cells and is low to myotubes in both systems. Binding is much lower to fibroblasts in the primary cultures. Binding appears to be on the surface of these cells, although evidence is presented for there being binding on the inside of cells as well. When observed on myotubes, binding is generally associated with highly stained patches and in some instances is near regions where fusion may be occurring, In L6 cells, binding sites can be exposed by treating mononucleated cells with trypsin. These results are discussed in terms of their possible role in myogenesis and synaptogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Den H., Malinzak D. A. Isolation and properties of beta-D-galactoside-specific lectin from chick embryo thigh muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5444–5448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den H., Malinzak D. A., Rosenberg A. Lack of evidence for the involvement of a beta-D-galactosyl-specific lectin in the fusion of chick myoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 5;69(3):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90921-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Walsh F. S., Nirenberg M. Lactose sensitive lectin of chick retina and spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1246–1252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Podleski T. R. Evidence that a membrane bound lectin mediates fusion of L6 myoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):972–978. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90770-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Podleski T. R. Evidence that the types and specific activity of lectins control fusion of L6 myoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 21;70(4):1142–1149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gremo F., Kobiler D., Barondes S. H. Distribution of an endogenous lectin in the developing chick optic tectum. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):491–499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. Externally disposed plasma membrane proteins. I. Enzymatic iodination of mouse L cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):438–460. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobiler D., Barondes S. H. Lectin activity from embryonic chick brain, heart, and liver: changes with development. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):326–330. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak T. P., Haywood P. L., Barondes S. H. Developmentally regulated lectin in embryonic chick muscle and a myogenic cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):650–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak T. P., Kobiler D., Roel L. E., Barondes S. H. Developmentally regulated lectin from embryonic chick pectoral muscle. Purification by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6026–6030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podleski T. R., Greenberg I., Nichols S. C. Studies on lectin activity during myogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Sep;122(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podleski T. R., Nichols S., Ravdin P., Salpeter M. M. Cloned myogenic cells during differentiation: membrane biochemistry and fine structural observations. Dev Biol. 1979 Jan;68(1):239–258. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. A. Development of normal and genetically dystrophic mouse muscle in tissue culture. I. Prefusion and fusion activities of muscle cells: phase contrast and time lapse study. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Aug;80(2):251–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Silman I., Beitsch D. D., Resheff G. A beta-D-galactoside binding protein from electric organ tissue of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Daniels M. P. Ultrastructure of acetylcholine receptor clusters on cultured muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1976 May;69(2):501–507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waard A., Hickman S., Kornfeld S. Isolation and properties of beta-galactoside binding lectins of calf heart and lung. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7581–7587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]