Abstract
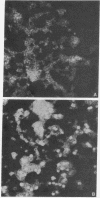
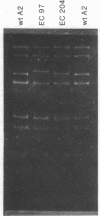
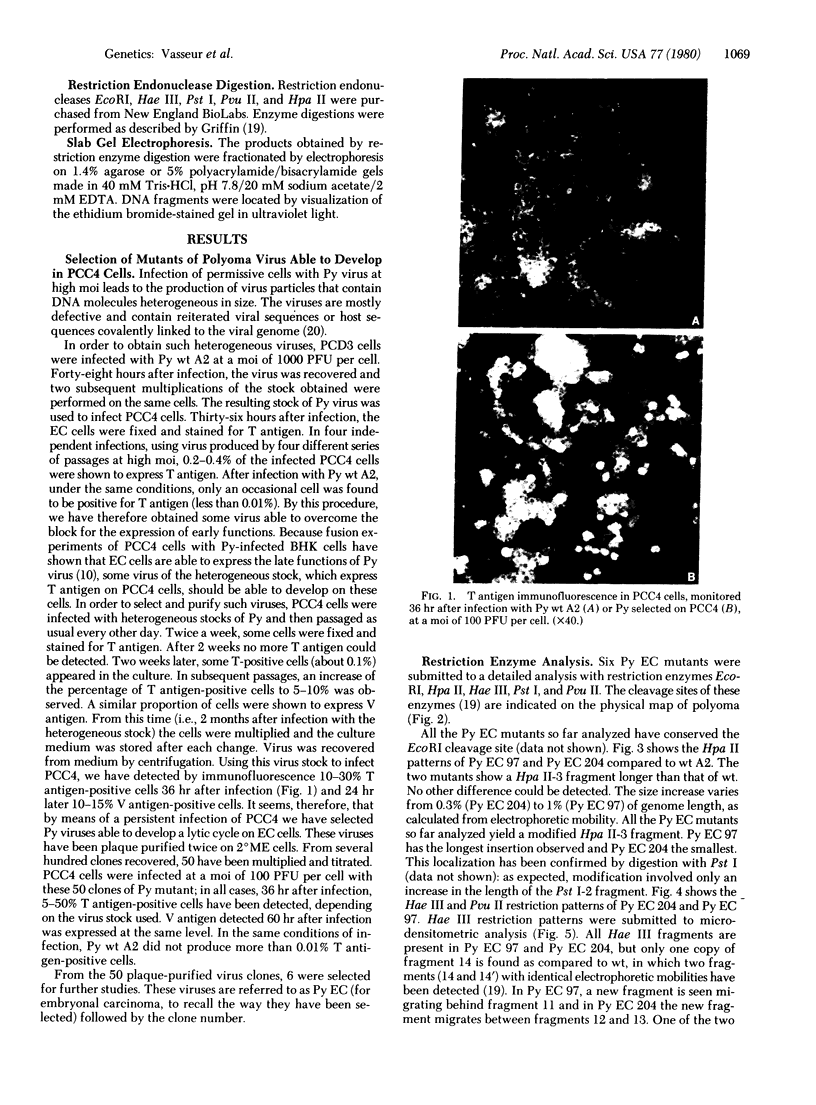
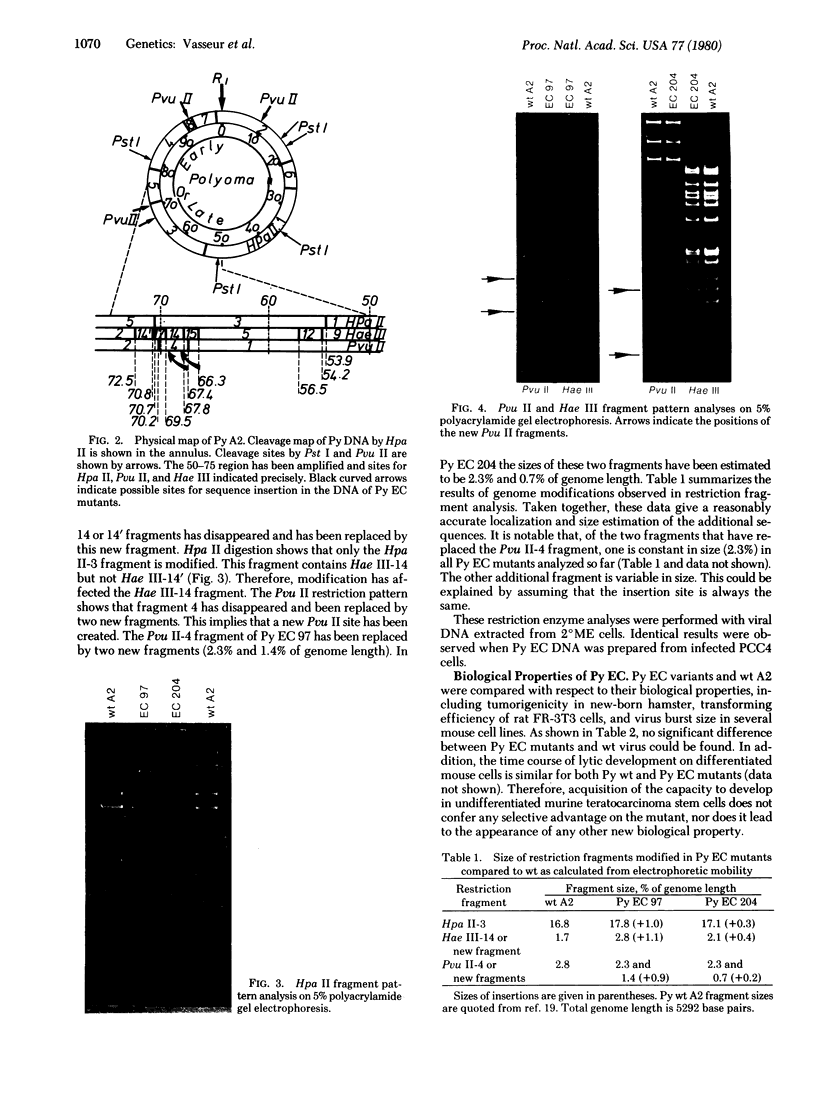
Embryonal carcinoma (EC) mouse cells have been shown to be resistant to infection by retroviruses and small oncogenic DNA viruses, including simian virus 40 and polyoma. When allowed to differentiate, in vitro or in vivo, EC cells become as susceptible to these viruses as differentiated mouse cell lines are. In order to study the relationships between differentiation of EC cells and viral expression, we have isolated and characterized several polyoma mutants that can express early and late functions in undifferentiated EC cells. These mutants, which arose spontaneously during high-multiplicity infection of PCD3 cells (a differentiated fibroblast-like cell line derived from PCC3 EC cells), were selected on PCC4 cells (undifferentiated EC cells) and twice plaque purified. Restriction enzyme analysis of the DNA from several mutants has shown that they all exhibit an additional sequence located in the Pvu II endonuclease fragment 4, close to the junction between Hpa II endonuclease fragments 3 and 5. The size of the insertion varies from 10 to 50 base pairs. The biological properties, including oncogenicity, transforming ability, host range, and burst size of the mutants so far analyzed are similar to those of wild-type virus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boccara M., Kelly F. Etude de la sensibilité au virus du polyome et à SV40 de plusieurs lignées cellulaires de tératocarcinome. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Feb-Mar;129(2):227–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boccara M., Kelly F. Expression of polyoma virus in heterokaryons between embryonal carcinoma cells and differentiated cells. Virology. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogen B. Virus-specific early RNA in 3T6 cells infected by a tsA mutant of polyoma virus. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90426-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Robbins A. K., Nicklin P. M. Location of the origin and terminus of replication in polyoma virus DNA. J Gen Virol. 1974 Oct;25(1):133–142. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feunteun J., Sompayrac L., Fluck M., Benjamin T. Localization of gene functions in polyoma virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Legon S., Kamen R. Multiple 5' terminal cap structures in late polyoma virus RNA. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):357–371. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Griffin B. E. Organization of the genomes of polyoma virus and SV40. Adv Cancer Res. 1977;24:67–113. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)61013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E. Fine structure of polyoma virus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 5;117(2):447–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett A. J., Sylvester S. S. Cell line derived from Balb-3T3 that is transformed by murine leukaemia virus: a focus assay for leukaemia virus. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 11;239(93):164–166. doi: 10.1038/newbio239164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob F. Mouse teratocarcinoma and embryonic antigens. Immunol Rev. 1977 Jan;33:3–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob F. The Leeuwenhoek Lecture, 1977. Mouse teratocarcinoma and mouse embryo. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 May 16;201(1144):249–270. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jainchill J. L., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses: assay using clonal lines of contact-inhibited mouse cells. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):549–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.549-553.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakob H., Boon T., Gaillard J., Nicolas J., Jacob F. Tératocarcinome de la spuris: isolement, culture et propriétés de cellules a potentialités multiples. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1973 Oct;124(3):269–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Shure H. Topography of polyoma virus messenger RNA molecules. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):361–371. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescure B., Dauguet C., Yaniv M. Transcription of polyoma virus DNA in vitro. III. Localization of calf thymus RNA polymerase II binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Griffin B. E., Fried M. Polyoma virus defective DNAs. II. Physical map of a molecule with rearranged and reiterated sequences (D74). J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 5;117(2):497–513. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson G., Nilsson M. G. Multiple free viral DNA copies in polyoma virus-transformed mouse cells surviving productive infection. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):646–653. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.646-653.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Teratocarcinomas as a model system for the study of embryogenesis and neoplasia. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Ward D. C., Ruddle F. H. Embryonal carcinoma cells (and their somatic cell hybrids) are resistant to infection by the murine parvovirus MVM, which does infect other teratocarcinoma-derived cell lines. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):393–401. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. F., Avner P., Gaillard J., Guenet J. L., Jakob H., Jacob F. Cell lines derived from teratocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4224–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIGEN IN SV40-TRANSFORMED CELLS BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:121–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal S., Levine A. J., Khoury G. Evidence for non-spliced SV40 RNA in undifferentiated murine teratocarcinoma stem cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):335–338. doi: 10.1038/280335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif R., Cuzin F. Temperature-sensitive growth regulation in one type of transformed rat cells induced by the tsa mutant of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):721–728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.721-728.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzendruber D. E., Friedrich T. D., Lehman J. M. Resistance of teratocarcinoma stem cells to infection with simian virus 40: early events. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Oct;93(1):25–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040930105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzendruber D. E., Lehman J. M. Neoplastic differentiation: interaction of simian virus 40 and polyoma virus with murine teratocarcinoma cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Apr;85(2 Pt 1):179–187. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teich N. M., Weiss R. A., Martin G. R., Lowy D. R. Virus infection of murine teratocarcinoma stem cell lines. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]