Abstract
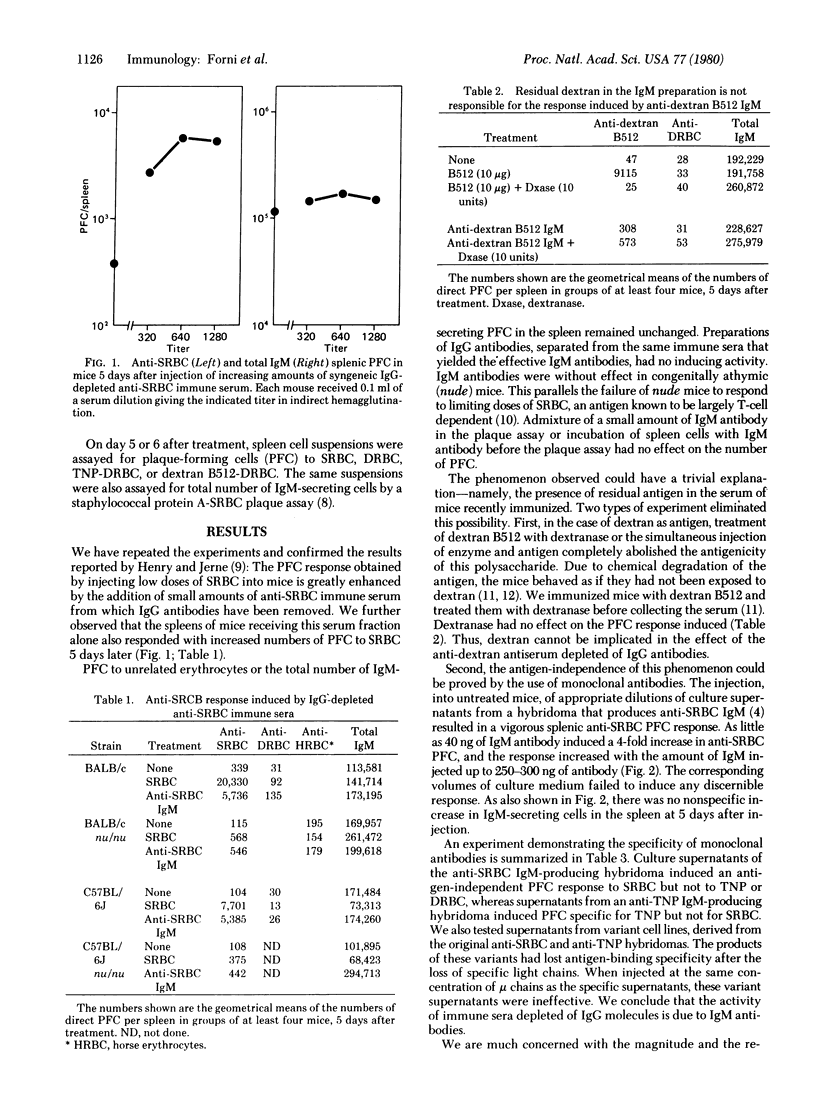
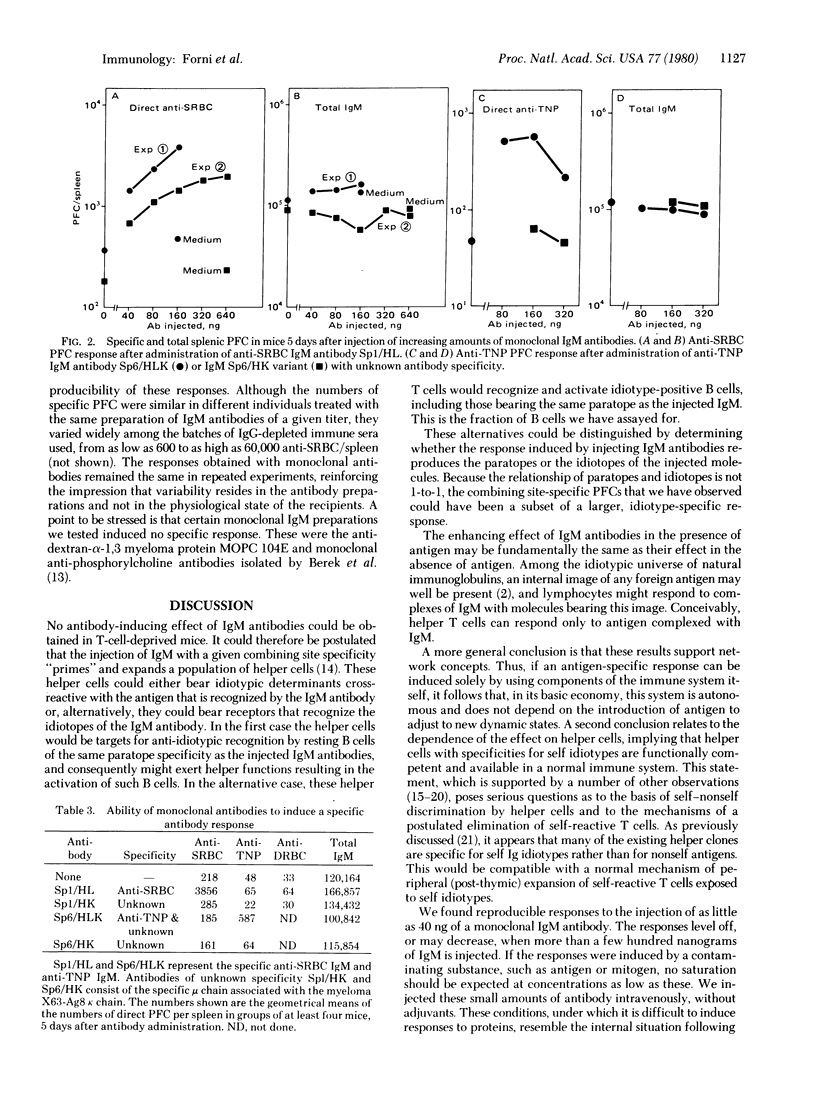
Injection in normal mice of IgM antibodies against sheep erythrocytes or dextran, in the form of an immune serum depleted og IgG, induces direct plaque-forming cells of the same specificity as the injected antibodies. The response is 10--70 times higher than the background plaque-forming cell titer of untreated control mice. Nanogram amounts of IgM induce a detectable response, and a ceiling is reached with a few hundred nanograms of monoclonal IgM. The inducing agent is not residual antigen: (i) treatment of the injected material and the recipients with dextranase abolishes the immunogenicity of dextran, but not the response to anti-dextran IgM; (ii) monoclonal IgM specific for sheep erythrocytes or trinitrophenyl likewise induces plaque-forming cells of the respective specificity, but variant hybridoma products (in which the light chain is that of the myeloma parent) are inactive. In normal mice, IgM-induced antibody responses were observed with antibodies to both thymus-dependent and thymus-independent antigens, but such could not be induced in athymic (nude) mice. Because the mechanism underlying this phenomenon would operate also in a normal immune response and, presumably, in the normal dynamic state of the immune system of unstimulated animals, a network regulation among the elements of the immune system itself is implied.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernabe R. R., Martinez-Alonso C., Coutinho A. The specificity of nonspecific concanavalin A-induced helper factors. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jul;9(7):546–552. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Falk I., Rajewsky K. Recognition of idiotypes in lymphocyte interactions. II. Antigen-independent cooperation between T and B lymphocytes that possess similar and complementary idiotypes. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Dec;8(12):853–857. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Rajewsky K. Induction of T and B cell immunity by anti-idiotypic antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Oct;5(10):661–666. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830051002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Howard J. G., Desaymard C. Role of antigen structure in the discrimination between tolerance and immunity by b cells. Transplant Rev. 1975;23:78–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez C., Hammarström L., Möller G., Primi D., Smith C. J. Immunological tolerance affects only a subpopulation of the antigen-specific B lymphocytes: evidence against clonal deletion as the mechanism of tolerance induction. Immunol Rev. 1979;43:3–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry C., Jerne N. K. Competition of 19S and 7S antigen receptors in the regulation of the primary immune response. J Exp Med. 1968 Jul 1;128(1):133–152. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Vicari G., Courtenay B. M. Influence of molecular structure on the tolerogenicity of bacterial dextrans. I. The alpha1--6-linked epitope of dextran B512. Immunology. 1975 Oct;29(4):585–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Murgita R. A., Weinbaum F. I., Asofsky R., Wigzell H. Evidence for an immunoglobulin-dependent antigen-specific helper T cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4582–4586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Sakato N., Eisen H. N. Recognition of immunoglobulin idiotypes by thymus-derived lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2357–2360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. THE NATURAL-SELECTION THEORY OF ANTIBODY FORMATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Nov 15;41(11):849–857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.11.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. F., Miller J. F. Immunological activity of thymus and thoracic-duct lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):296–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasanen V. J., Mäkelä O. Effect of the number of haptens coupled to each erythrocyte on haemolytic plaque formation. Immunology. 1969 Mar;16(3):399–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. M., Waldmann H. Monogamous T helper cell. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):641–642. doi: 10.1038/268641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullman S. F., Feinstein A. The relative distribution of foci forming antibodies to two different haptens in repopulated mouse spleens. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Jul;7(7):421–425. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz N. M., Varela F. J. Self and non-sense: an organism-centered approach to immunology. Med Hypotheses. 1978 May-Jun;4(3):231–267. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(78)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland R., Cantor H. Idiotype-specific T helper cells are required to induce idiotype-positive B memory cells to secrete antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):600–606. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


