Abstract
Epidemiological studies show that vascular risk factors (e.g. atherosclerosis, diabetes, homocysteine, hypertension or cholesterol) may play a role in the development of Alzheimer's disease. Animal models may help to discover the role of vascular risk factors on cognition. In the present project we treated male Sprague Dawley rats with a diet containing homocysteine (hyperhomocysteinemia) or cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia) for 5 months or exposed the rats to ethanol (20% in drinking water) or a combination of cholesterol + ethanol (mix) for 12 months. Our experiments show that all 3 treatments (homocysteine, cholesterol, ethanol) declined spatial memory in the 8-arm radial maze, reduced the number of cholinergic neurons and induced blood–brain barrier leakage in the cortex. Rats treated with cholesterol also displayed markedly enhanced inflammation in the cortex. Levels of amyloid precursor protein, beta-amyloid(1–42), as well as tau and phospho-tau 181 were significantly enhanced in the cortex of cholesterol-fed rats. A combination of ethanol and cholesterol did not further potentiate the effects on spatial memory, cholinergic neurons and blood–brain barrier leakage. The data suggest that chronic mild vascular risk factors over months induce small lesions of the brain capillaries in the cortex, which may contribute to the development of vascular dementia or also Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Vascular risk factors, Blood–brain barrier leakage, Alzheimer's disease, Vascular dementia
1. Introduction
1.1. Alzheimer's disease (AD)
AD is characterized by cerebrovascular damage and neuronal dysfunction leading to progressive cognitive decline. The hallmark pathologies include beta-amyloid (Aβ) deposition in brain (plaques) and vessels (Aβ-angiopathy), neurofibrillary tangles containing hyperphosphorylated tau, blood–brain barrier leakage and increased microglial reactivity as well as inflammatory processes. Blood–brain barrier dysfunction is associated with a reduction of cerebral blood flow, hypoxia and accumulation of neurotoxic molecules in brain parenchyma [1,2]. The amyloid hypothesis suggests that the accumulation of Aβ is the most important cascade for the development of AD [3]. Aβ-peptides (40, 42 or 43 amino acids) originate from the membrane-associated amyloid precursor protein (APP) by cleavage with α-, β- and γ-secretases and a dysbalance in Aβ-production and clearance may trigger neurodegeneration [3]. Vascular risk factors (e.g. cholesterol, homocysteine or ethanol) over long periods may cause such a dysfunctional Aβ-clearance as well as blood–brain barrier impairment and possibly initiate cerebrovascular dysfunction or inflammatory processes leading to the development of AD [4–8].
1.2. Vascular dementia (vaD)
AD and vaD share many risk factors suggesting a related pathogenesis [9]. The differentiation of AD from vaD is very difficult, because many symptoms of both diseases are overlapping. Thus, the differentiation is based on evidence of cerebrovascular dysfunction in vaD [8]. Indeed, cerebral vessel pathology results in blood–brain barrier leakage and such multiple cortical infarcts (silent strokes) may play a major role in development of vaD. This is accompanied by ischemic changes with cerebral hypoperfusion and oxidative stress. Clinical symptoms are multifaceted depending on location and size of the stroke lesions which are often asymptomatic for a long period. Vascular risk factors, such as cholesterol, homocysteine and ethanol may play an important role in the development of vaD [10] which is suggested by the fact that vaD is potentially preventable by life style modification and counteracting vascular risk factors [11].
1.2.1. The cerebrovascular system
In contrast to leaky vessels in peripheral organs [12], the blood–brain barrier restricts entry of polar molecules into the brain. Nutrients such as vitamins, glucose, and amino acids cross the blood–brain barrier by using specific transporters [13]. Peptides in general poorly cross the blood–brain barrier [14,15], but they can be transported into the brain via specific receptors expressed in brain endothelium under physiological or pathological conditions [16,17]. Intact neurovascular functions are necessary for proper neuronal structure and function. Thus, pericyte deficiency leads to microvascular degeneration and brain accumulation of toxic substances (e.g. Aβ) preceding neuronal degenerative changes, learning and memory impairment and neuroinflammatory response [18,19].
1.3. Methodological aspects
1.3.1. Treatment of rats
Male Sprague Dawley rats (aged 6 months) were housed at the Animal Department of the Medical University Innsbruck and had free access to food and tap water with a 12/12 h light–dark circle. All animal experiments were approved by the Austrian Ministry of Science. The diet of the control animals contained following ingredients: 450 g/kg cornstarch, 140 g/kg casein, 155 g/kg maltodextrin, 100 g/kg sucrose, 40 g/kg soybean oil, 50 g/kg fiber, 35 g/kg mineral mix, 1.8 g/kg L-cystine, 1.4 g/kg choline chloride, 0.008 g/kg butylhydroxytoluol, 10 g/kg vitamin mix (without folic acid), 1 g/kg chocolate aroma and 0.002 g/kg folic acid (Ssniff special diet GmbH; Soest Germany). The animals of the cholesterol group were fed for 5 months (n = 10) or 12 months (n = 12) with additional 50 g/kg cholesterol [20]. The animals of the homocysteine group were fed with additional 3 g / kg dl-homocysteine for 5 months (n = 9) or 15 months (n = 10) [21]. The animals of the ethanol group were treated with 20% ethanol in drinking water ad libitum for 12 months (n = 12) [22]. The animals of the cholesterol-homocysteine mix group were treated with a combined diet of 3 g ⁄ kg dl-homocysteine and 5% cholesterol for 5 months and the animals of the cholesterol ethanol mix group (n = 12) were fed with a diet containing 5% cholesterol and 20% ethanol in drinking water [21,22].
1.3.2. Cognition in the partially baited eight-arm radial maze
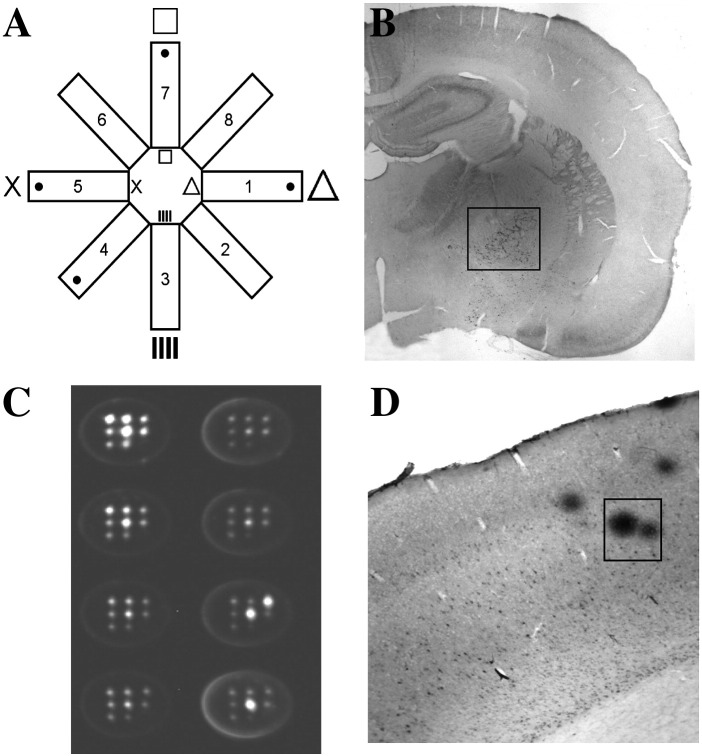
Spatial learning and long-term memory performance was assessed in the partially baited eight-arm radial maze (Fig. 1A), a well-established method to explore learning and memory in a controlled environment, as recently described by us in detail [21]. The maze consists of eight identical arms with side panels and sunk-in-food cups at the end radiating from a circular platform. For spatial navigation small high contrast visual cues (triangle, vertical bars, cross and squares) were placed above the doors of four arms and on the corresponding walls. Four arms were baited with food pellets (chocolate cereals) and the trial ended when all baits were found or after 10 min exceeded. The task for the animals was to find all baits in respective arms without visiting unbaited arms. The animals were restricted to food before the learning sessions were started to increase motivation. In a shaping session the rats were habituated to the testing procedures to decrease stress. In five training sessions (with each five trials) the animals had to learn the task. After three weeks of the last session the retention (five trials) was performed to investigate long-term memory performance. Memory errors were quantified according to Jarrard et al.'s definition [23]. The whole experiments was automatically controlled and monitored by a computer with MAZESOFT Software (Version 8.1.9).
Fig. 1.
(A) Spatial learning and long-term memory performance was assessed in the partially baited eight-arm radial maze. For spatial navigation small high contrast visual cues (triangle, vertical bars, cross and squares) were placed above the doors of four arms and on the corresponding walls. Four arms were baited with food pellets and the trial ended when all baits were found or after 10 min exceeded. (B) Rat brains were sectioned into 60 μm slices which were stained for the enzyme choline-acetyltransferase (ChAT). The number of ChAT-positive neurons located in the nucleus basalis of Meynert (small insert) was counted under the microscope. (C) Inflammatory markers were measured by multiplex ELISA. For the ELISA cortex extracts were added to pre-spotted plates, immune-detection was performed and the luminescent signal was evaluated by the Searchlight imaging and analysis system. (D) Blood–brain barrier leakage was assessed by using immunohistochemistry against rat immunoglobulin G (IgG). Rat IgG-positive spots (small insert) in the cortex were counted under the microscope at a 40 × magnification.
B, adapted from Pirchl et al. [21]); D, adapted from Ehrlich et al. [22].
1.3.3. Cholinergic neurons
The cholinergic neurons located in the septum and nucleus basalis of Meynert (nbM; Fig. 1B) play an important role in cognition and memory and are severely impaired in AD [24]. For immunohistochemistry brains were removed and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. Then brains were frozen under CO2 snow and sectioned into 60-μm slices with a cryostate (Leica Jung CM3000). Slices were immunohistochemically stained for the enzyme choline-acetyltransferase (ChAT) that serves as markers for cholinergic neurons. ChAT-positive neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynert (nbM) between Bregma − 0.7 to − 3.1 were counted at a 40 × magnification under the microscope.
1.3.4. Inflammation
Inflammation plays a role in both AD as well as in vaD [25]. In our studies levels of inflammatory markers (e.g. interleukine-1β, tumor-necrosis-factor-α, monocytochemotactic-protein-1, macrophage-inflammatory-protein-2) in the cortex were explored by multiplex ELISA (Fig. 1C) (Searchlight, Aushon Biosystems), as described recently by us [21]. Briefly, the brains were removed, the frontal cortex dissected and immediately frozen. Cortex tissue was homogenized in ice-cold sodium phosphate buffer with a protease inhibitor, centrifuged and subsequently the supernatant was added to the prespotted plates and incubated for 3 h. After washing the biotinylated antibody was added and incubated for 30 min. After being washed streptavidin-horseradish peroxidise reagent was added and the luminescent signal was detected by the Searchlight CCD imaging and analysis system. Sample values were calculated from the standard curve in a liner range.
1.3.5. Vascular disruptions
Vascular risk factors may induce leakage of the blood–brain barrier allowing certain substances to migrate into the brain. For immunohistochemistry brains were removed and were frozen under CO2 snow and sectioned into 20-μm sections with a cryostate (Leica Jung CM3000). Blood–brain barrier integrity was assessed by immunohistochemical staining against rat immunoglobulin G (IgG), as described in detail by us [21]. IgG-positive spots in the cortex were counted under the microscope at a 40 × magnification.
1.4. Effects of long-term moderate vascular risk factors in vivo in rats
Treatment with the vascular risk factors cholesterol, homocysteine and ethanol over months resulted in memory impairment, dysfunction of the cholinergic system, blood–brain barrier leakage and inflammation in adult Sprague Dawley rats.
1.5. Effects of hypercholesterolemia
Cholesterol may play a role in development of AD possibly by influencing APP processing which leads to enhanced levels of Aβ [26]. Indeed, inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis (statins) may have a protective effect against AD [27] and the C-terminal transmembrane domain C99 of APP specifically binds cholesterol and favors the amyloidogenic pathway in cells by promoting localization of C99 in lipid rafts [28,29]. We have shown that treatment of rats with a 5% cholesterol-rich diet for 5 months caused spatial memory deficits, a dysfunction of the cholinergic system, blood–brain barrier leakage and inflammation [20]. In the cortex of cholesterol-fed rats levels of APP, Aβ(1–42), as well as tau and phospho-tau 181 were significantly enhanced [10]. Thus, hypercholesterolemia in rats resembled some AD-like pathology and has been suggested to provide a good model to study AD development as well as cerebrovascular dysfunction [10].
1.6. Effects of hyperhomocysteinaemia
Elevated homocysteine plasma levels may enhance the risk for developing AD or vaD [30]. It is well established that hyperhomocysteinaemia induces memory and learning disabilities in several animal models [21,31]. We have shown that in adult Sprague Dawley rats hyperhomocysteinaemia for 5 months markedly affected spatial memory performance and the number of cholinergic neurons in the nbM [21]. In the cortex blood–brain barrier leakage was enhanced after 12 months homocysteine treatment, but inflammation was not induced [21]. Interestingly, hyperhomocysteinaemia in rats did not show an AD-like pathology, such as Aβ-plaques, tau-pathology or inflammation, but resulted in spatial memory impairment and dysfunction of the cholinergic system which might be initiated by blood–brain barrier impairment [21].
1.7. Effects of ethanol
Ethanol consumption might cause cerebrovascular diseases, such as stroke and vaD, and may induce cognitive decline and cholinergic dysfunction [10] and AD [32–34]. However, there is increasing evidence that moderate chronic ethanol has protective effects on AD development [35]. We have shown that long-term treatment (12 months) of adult Sprague Dawley rats with 20% ethanol in drinking water ad libitum resulted in cognitive decline, cholinergic dysfunction and blood–brain barrier leakage, but did not dramatically induce cortical inflammation [22]. In the cortex of ethanol treated rats only monocyte chemotactic-protein-1 (MCP-1) was enhanced suggesting that MCP-1 may take part in a signaling cascade deviating from its role as a pro-inflammatory cytokine [22]. MCP-1 is also secreted by activated microglia cells [36] and indeed, after moderate long-term ethanol treatment cortical microglia reactivity was enhanced in rats [22]. Interestingly, ethanol did not resemble an AD-like pathology, but rather suggested a protective effect against AD development [22]. In summary, the cerebrovascular risk factor ethanol may markedly contribute to some pathology of vaD, but did not resemble an AD-like neuropathology [22].
1.8. Combination of vascular risk factors
The combination of ethanol and cholesterol did not dramatically affect the changes in spatial memory, cholinergic neurons, blood–brain barrier impairment and inflammation [22]. However, ethanol counteracted some of the cholesterol-induced effects: it reduced weight, plasma cholesterol levels and cortical Aβ(1–40) and Aβ(1–42) content, suggesting a protective role of ethanol in the development of AD [22]. In contrast, cholesterol did not markedly affect the ethanol-induced changes showing only a prominent reduction of plasma ethanol levels [22]. Cholesterol may modulate the absorption of ethanol into the blood, possibly due to a prolonged retention of ethanol in the stomach after cholesterol-rich nutrition [37]. Taken together, a combined treatment of ethanol and cholesterol did not potentiate the effects of a single treatment but rather counteracted some of the ethanol- or cholesterol-induced effects [22]. A combined cholesterol and homocysteine diet for 5 months resulted in spatial impairment and reduced cholinergic neurons similar to a single treatment, but homocysteine counteracted the cholesterol-induced inflammation and reduced slightly cortical blood–brain barrier leakage.
1.9. Long-term versus short-term effects: differences
Short-term (5 months) 5% cholesterol diet markedly reduced spatial memory performance, the number of cholinergic neurons in the nbM, induced inflammation as well as blood–brain barrier leakage in the cortex [20]. Interestingly, chronic ethanol or cholesterol treatment for 12 months had similar effects in vivo, although they were not as pronounced as the 5-month cholesterol effects. Long-term treatment of cholesterol did not result in inflammation and the changes were not as pronounced, most likely due to adaptive and compensatory mechanisms. This is in line with Pirchl et al. [21], who reported that short-term (5 months) treatment with the vascular risk factor homocysteine had more severe effects than long-term (15 months) homocysteine treatment. The cholinergic impairment after prolonged exposure to homocysteine was possibly counteracted by the upregulation of nerve growth factor [21], which is the most potent trophic molecule to support survival of cholinergic neurons [38].
2. Conclusion
Moderate chronic vascular risk factors, such as cholesterol, homocysteine or ethanol impair spatial memory, decline cholinergic neurons and induce blood–brain barrier leakage in rats in vivo which may contribute to the development of vascular dementia or Alzheimer's disease (Table 1).
Table 1.
Effects of vascular risk factors in Sprague Dawley rats in vivo.
| Risk factor | Spatial memory | Cholinergic neurons | Inflammation | Blood–brain barrier leakage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Homocysteine | ↓ | ↓ | – | ↑ |
| Ethanol | ↓ | ↓ | – | ↑ |
| Ethanol + cholesterol | ↓ | ↓ | – | ↑ |
| Homocysteine + cholesterol | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
Spatial memory was tested on the eight arm radial maze. The number of cholinergic neurons was measured by immunohistochemistry. Inflammatory markers were analyzed by multiplex Searchlight ELISA. Blood–brain barrier leakage was indirectly shown by anti-rat immunoglobulin G histochemistry. (↓ decreased, ↑ increased, – no change).
Conflict of interest
None.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Austrian Science Funds (P191220-B05 and L429-B05). We thank Ursula Kirzenberger–Winkler for her excellent technical help.
References
- 1.Zlokovic B.V. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and other disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12:723–738. doi: 10.1038/nrn3114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kalaria R.N. Vascular basis for brain degeneration: faltering controls and risk factors for dementia. Nutr Rev. 2010;68(Suppl. 2):74–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00352.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hardy J., Selkoe D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. doi: 10.1126/science.1072994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shepardson N.E., Shankar G.M., Selkoe D.J. Cholesterol level and statin use in Alzheimer disease: II. Review of human trials and recommendations. Arch Neurol. 2011;68:1385–1392. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brust J.C. Ethanol and cognition: indirect effects, neurotoxicity and neuroprotection: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2010;7:1540–1557. doi: 10.3390/ijerph7041540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhuo J.M., Wang H., Praticò D. Is hyperhomocysteinemia an Alzheimer's disease (AD) risk factor, an AD marker, or neither? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011;32:562–571. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2011.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dickstein D.L., Walsh J., Brautigam H., Stockton S.D., Jr., Gandy S., Hof P.R. Role of vascular risk factors and vascular dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Mt Sinai J Med. 2010;77:82–102. doi: 10.1002/msj.20155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Humpel C. Chronic mild cerebrovascular dysfunction as a cause for Alzheimer's disease? Exp Gerontol. 2011;46:225–232. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2010.11.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.De la Torre J.C. Alzheimer's disease as a vascular disorder. Stroke. 2002;33:1152–1162. doi: 10.1161/01.str.0000014421.15948.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mostofsky E., Burger M.R., Schlaug G., Mukamal K.J., Rosamond W.D., Mittleman M.A. Alcohol and acute ischemic stroke onset: the stroke onset study. Stroke. 2010;41:1845–1849. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.580092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee A.Y. Vascular dementia. Chonnam Med J. 2011;47:66–71. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2011.47.2.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mann G.E., Zlokovic B.V., Yudilevich D.L. Evidence for a lactate transport system in the sarcolemmal membrane of the perfused rabbit heart: kinetics of unidirectional influx, carrier specificity and effects of glucagon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;819:241–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zlokovic B.V., Apuzzo M.L. Cellular and molecular neurosurgery: pathways from concept to reality—part I: target disorders and concept approaches to gene therapy of the central nervous system. Neurosurgery. 1997;40:789–803. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199704000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zlokovic B.V., Segal M.B., Begley D.J., Davson H., Rakić L. Permeability of the blood–cerebrospinal fluid and blood–brain barriers to thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Brain Res. 1985;358:191–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90963-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zlokovic B.V., Begley D.J., Chain-Eliash D.G. Blood–brain barrier permeability to leucine-enkephalin, D-alanine2-D-leucine5-enkephalin and their N-terminal amino acid (tyrosine) Brain Res. 1985;336:125–132. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zlokovic B.V., Mackic J.B., Djuricic B., Davson H. Kinetic analysis of leucine-enkephalin cellular uptake at the luminal side of the blood–brain barrier of an in situ perfused guinea-pig brain. J Neurochem. 1989;53:1333–1340. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb08522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zlokovic B.V., Hyman S., McComb J.G., Lipovac M.N., Tang G., Davson H. Kinetics of arginine-vasopressin uptake at the blood–brain barrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990;1025:191–198. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bell R.D., Winkler E.A., Singh I., Sagare A.P., Deane R., Wu Z. Apolipoprotein E controls cerebrovascular integrity via cyclophilin A. Nature. 2012;485:512–516. doi: 10.1038/nature11087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bell R.D., Winkler E.A., Sagare A.P., Singh I., LaRue B., Deane R. Pericytes control key neurovascular functions and neuronal phenotype in the adult brain and during brain aging. Neuron. 2010;68:409–427. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ullrich C., Pirchl M., Humpel C. Hypercholesterolemia in rats impairs the cholinergic system and leads to memory deficits. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010;45:408–417. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2010.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pirchl M., Ullrich C., Humpel C. Differential effects of short- and long-term hyperhomocysteinemia on cholinergic neurons, spatial memory and microbleedings in vivo in rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;32:1516–1527. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Daniela Ehrlich, Michael Pirchl, Humpel Christian. Effects of long-term moderate ethanol and cholesterol on cognition, cholinergic neurons, inflammation and vascular impairment in rats. Neuroscience. 2012;205:154–166. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.12.054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jarrard L.E., Okaichi H., Steward O., Goldschmidt R.B. On the role of hippocampal connections in the performance of place and cue tasks: comparisons with damage to hippocampus. Behav Neurosci. 1984;98:946–954. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.98.6.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mufson E.J., Counts S.E., Perez S.E., Ginsberg S.D. Cholinergic system during the progression of Alzheimer's disease: therapeutic implications. Expert Rev Neuroether. 2008;8:1703–1718. doi: 10.1586/14737175.8.11.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Helmy A.A., Abdel Naseer M.M., El Shafie S., Nada M.A. Role of interleukin 6 and alpha-globulins in differentiating Alzheimer and vascular dementias. Neurodegener Dis. 2012;9(2):81–86. doi: 10.1159/000329568. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ehehalt R., Keller P., Haass C., Thiele C., Simons K. Amyloidogenic processing of the Alzheimer beta-amyloid precursor protein depends on lipid rafts. J Cell Biol. 2003;160:113–123. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200207113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tong X.K., Nicolakakis N., Fernandes P., Ongali B., Brouillette J., Quirion R. Simvastatin improves cerebrovascular function and counters soluble amyloid-beta, inflammation and oxidativestress in aged APP mice. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;35:406–414. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Beel A.J., Sakakura M., Barrett P.J., Sanders C.R. Direct binding of cholesterol to the amyloid precursor protein: an important interaction in lipid–Alzheimer's disease relationships? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1801:975–982. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Barrett P.J., Song Y., Van Horn W.D., Hustedt E.J., Schafer J.M., Hadziselimovic A. The amyloid precursor protein has a flexible transmembrane domain and binds cholesterol. Science. 2012;336:1168–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.1219988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ravaglia G., Forti P., Maioli F., Martelli M., Servadei L., Brunetti N. Homocysteine and folate as risk factors for dementia and Alzheimer disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;82:636–643. doi: 10.1093/ajcn.82.3.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Stefanello F.M., Monteiro S.C., Matte' C., Scherer E.B., Netto C.A., Wyse A.T. Hypermethioninemia increases cerebral acetylcholinesterase activity and impairs memory in rats. Neurochem Res. 2007;32:1868–1874. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9464-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Floyd E.A., Young-Seigler A.C., Ford B.D., Reasor J.D., Moore E.L., Townsel J.G. Chronic ethanol ingestion produces cholinergic hypofunction in rat brain. Alcohol. 1997;14:93–98. doi: 10.1016/s0741-8329(97)86147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Arendt T. Impairment in memory function and neurodegenerative changes in the cholinergic basal forebrain system induced by chronic intake of ethanol. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1994;44:173–187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9350-1_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Arendt T., Brückner M.K., Krell T., Pagliusi S., Kruska L., Heumann R. Degeneration of rat cholinergic basal forebrain neurons and reactive changes in nerve growth factor expression after chronic neurotoxic injury—II. Reactive expression of the nerve growth factor gene in astrocytes. Neuroscience. 1995;65:647–659. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00523-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Anstey K.J., Mack H.A., Cherubin N. Alcohol consumption as a risk factor for dementia and cognitive decline: meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2009;17:542–555. doi: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e3181a2fd07. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kaul M., Garden G.A., Lipoton S.A. Pathways to neuronal injury and apoptosis in HIV-associated dementia. Nature. 2001;410:988–994. doi: 10.1038/35073667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gentry T.R. Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of alcohol absorption. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000;24:403–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Levi-Montalcini R., Skaper S.D., Dal Toso R., Petrelli L., Leon A. Nerve growth factor: from neurotrophin to neurokine. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19:514–520. doi: 10.1016/S0166-2236(96)10058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]