Abstract
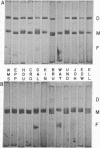
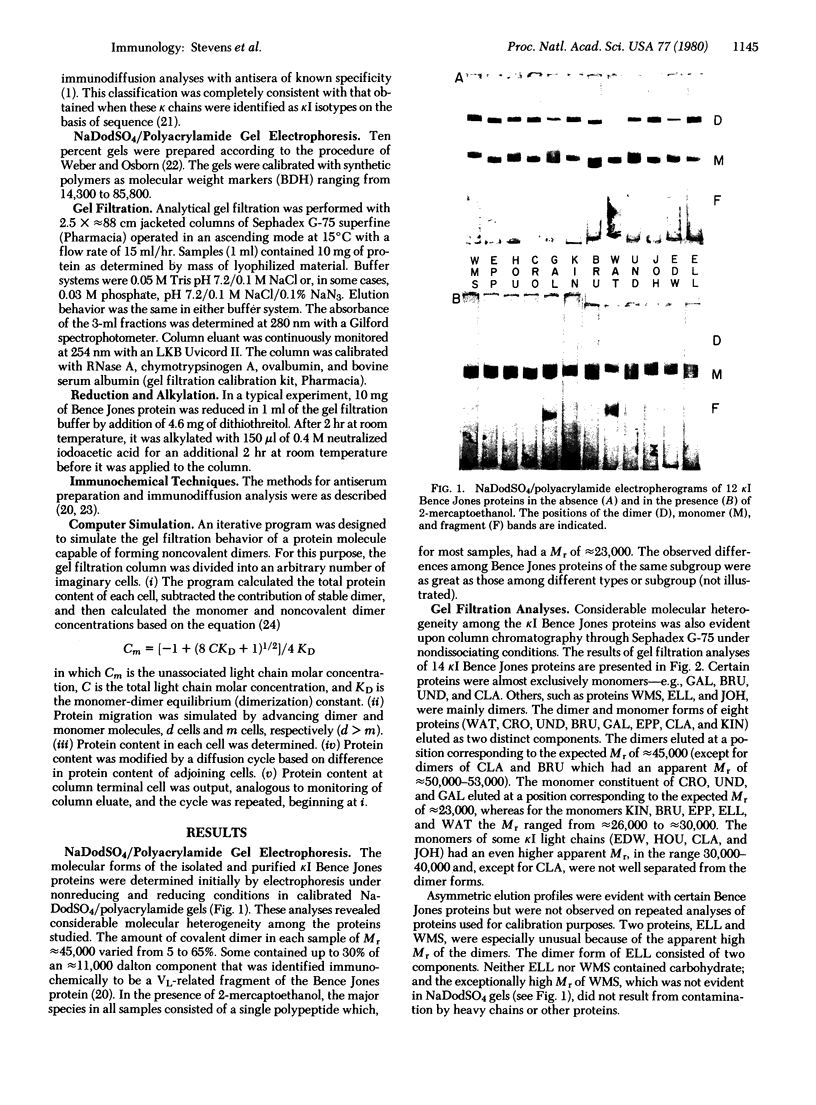
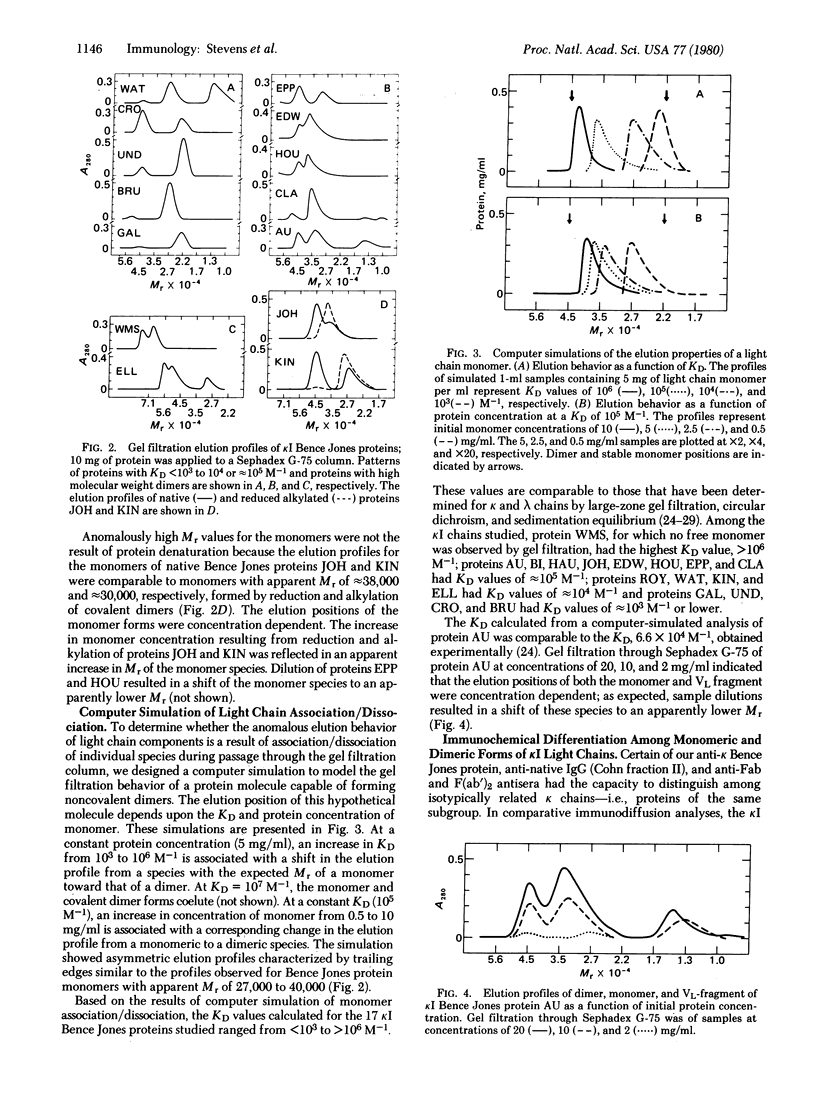
Gel electrophoresis and molecular sieve chromatography were used to compare 17 different human kappa I type Bence Jones proteins including 5 for which the amino acid sequence is known. Although electrophoresis in the presence of NaDodSO4 showed uniformity of covalent dimer and monomer molecular weights, Sephadex chromatography under nondissociating conditions showed that monomers eluted with different apparent molecular weights. These differences were attributed to heterogeneity in light chain self-association; dimerization constants of the 17 proteins, calculated from a computer simulation of their behavior upon gel filtration, ranged from less than 10(3) to greater than 10(6) M-1. The variable region, more specifically the third hypervariable region, appears to be responsible for the variation in the dimerization constant. Association properties of light chains of known sequence suggest that the presence of an aromatic or hydrophobic residue at position 96 enhances dimer formation whereas a charged residue at that position results in light chains remaining stable monomers. The location of hypervariable residue 96 within the amino-terminal portion of the joining segment of the variable region suggests that the joining region may account for the variability of self-association of light chains and, moreover, that it has a function in determining the selective association of immunoglobulin polypeptide chains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma T., Hamaguchi K., Migita S. Interactions between immunoglobulin polypeptide chains. J Biochem. 1974 Oct;76(4):685–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma T., Hamaguchi K. The mechanism of reassembly of immunoglobulin G. J Biochem. 1976 Nov;80(5):1023–1038. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma T., Kobayashi O., Goto Y., Hamaguchi K. Monomer-dimer equilibria of a Bence Jones protein and its variable fragment. J Biochem. 1978 May;83(5):1485–1492. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNIER G. M., PUTNAM F. W. POLYMERISM, POLYMORPHISM, AND IMPURITIES IN BENCE-JONES PROTEINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 11;86:295–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggård I., Peterson P. A. Polymeric forms of free normal kappa and lambda chains of human immunoglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4299–4307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Schramm H. J., Guss J. M. Crystal and molecular structure of the dimer of variable domains of the Bence-Jones protein ROY. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Préval C., Fougereau M. Specific interaction between VH and VL regions of human monoclonal immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):657–678. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epp O., Lattman E. E., Schiffer M., Huber R., Palm W. The molecular structure of a dimer composed of the variable portions of the Bence-Jones protein REI refined at 2.0-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 4;14(22):4943–4952. doi: 10.1021/bi00693a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlhammer H., Schiffer M., Epp O., Colman P. M., Lattman E. E., Schwager P., Steigemann W., Schramm H. J. The structure determination of the variable portion of the Bence-Jones protein Au. Biophys Struct Mech. 1975 Feb 19;1(2):139–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00539775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLY J. A., EDELMAN G. M. PROTEIN-PROTEIN INTERACTIONS AMONG L POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS OF BENCE-JONES PROTEINS AND HUMAN GAMMA-GLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1964 May 1;119:817–836. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.5.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. W. Conformation and association of the light chain from a homogeneous human immunoglobulin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3225–3231. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Mannik M. Specificity of recombination of H and L chains from human gamma-G-myeloma proteins. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):619–632. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazin A. R., Beychok S. Covalent immunoglobulin assembly in vitro: reactivity of light chain covalent dimers (L2) and blocked light chain monomers. Science. 1978 Feb 10;199(4329):688–690. doi: 10.1126/science.415360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishida F., Azuma T., Hamaguchi K. A type kappa Bence Jones protein containing a cysteinyl residue in the variable region. J Biochem. 1975 Mar;77(3):481–491. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Kells D. I., Tinker D. O., Dorrington K. J. Thermodynamic and conformational studies on an immunoglobulin light chain which reversibly precipitates at low temperatures. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 8;16(3):552–560. doi: 10.1021/bi00622a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Engel J., Schramm H. J. Kinetics of dimerization of the variable fragment of the Bence-Jones protein Au. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):133–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Steffen E., Engel J. Kinetics of dimerization of the Bence-Jones protein Au. Biophys Chem. 1978 Nov;9(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(78)87015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima M., Marquart M., Jones T. A., Colman P. M., Bartels K., Huber R. Crystal structure of the human Fab fragment Kol and its comparison with the intact Kol molecule. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jun 5;121(4):441–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin C. L., Solomon A. Bence-Jones proteins and light chains of immunoglobulins. VII. Localization of antigenic sites responsible for immunochemical heterogeneity of kappa chains. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5017–5025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROHOLT O., ONOUE K., PRESSMAN D. SPECIFIC COMBINATION OF H AND L CHAINS OF RABBIT GAMMA-GLOBULINS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:173–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. N., Rudikoff S., Krutzsch H., Potter M. Structural evidence for independent joining region gene in immunoglobulin heavy chains from anti-galactan myeloma proteins and its potential role in generating diversity in complementarity-determining regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2890–2894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Hüppi K., Heinrich G., Tonegawa S. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):288–294. doi: 10.1038/280288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul F. A., Amzel L. M., Poljak R. J. Preliminary refinement and structural analysis of the Fab fragment from human immunoglobulin new at 2.0 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):585–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Girling R. L., Ely K. R., Edmundson A. B. Structure of a lambda-type Bence-Jones protein at 3.5-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4620–4631. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H., Rudikoff S., Potter M., Davies D. R. The three-dimensional structure of a phosphorylcholine-binding mouse immunoglobulin Fab and the nature of the antigen binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. Bence-Jones proteins and light chains of immunoglobulins (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 1;294(1):17–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601012940105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A., McLaughlin C. L. Bence-Jones proteins and light chains of immunoglobulins. I. Formation and characterization of amino-terminal (variant) and carboxyl-terminal (constant) halves. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3393–3404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Dorrington K. J. The recombination of dimers of immunoglobulin peptide chains. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;118(5):703–712. doi: 10.1042/bj1180703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Mole L. E. The specificity of chain interactions among immunoglobulins. Combinations of gamma chains with kappa chains of the same subgroup as in the parent immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1974 May;139(2):369–374. doi: 10.1042/bj1390369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M., Gatmaitan L., Loh E., Schilling J., Hood L. Rearrangement of genetic information may produce immunoglobulin diversity. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):785–790. doi: 10.1038/276785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]