Abstract
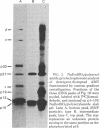
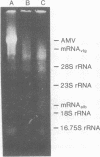
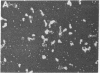
A native ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex of avian myeloblastosis virus was prepared under conditions that gave optimal cDNA synthesis. The complex was an autonomous transcriptional unit capable of synthesizing DNA complementary to the RNA virus genome in the absence of exogenous reverse transcriptase (RNA-dependent DNA nucleotidyltransferase), genomic RNA, and primer. The RNA of the RNP complex cannot be translated in an in vitro cell-free translational system. The RNP contains intact viral RNA, the two subunits of the reverse transcriptase (beta and alpha), the p32 polypeptide resulting from the cleavage of the beta subunit into the alpha subunit, and p12. The principal polypeptide constituent of the RNP complex is the highly basic protein p12, which occurs at a molar ratio of 40:1 in relation to the beta subunit of the polymerase. When examined by the electron microscope, the RNP complex appears similar to the beaded structure of chromatin fiber. A significant portion of these molecules are circular, with headlike structures attached. The circular nature of the proviral DNA and the ability of the RNP complex to generate large intact cDNA copies from the natural primer end suggest that the 5' and 3' ends of the viral RNA are in proximity when in the RNP complex.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. M. Retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:35–88. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi D. P., Montelaro R. C., Frank H., Schäfer W. Assembly of type C oncornaviruses: a model. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):183–186. doi: 10.1126/science.202022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen G., Griffith J. Salt and divalent cations affect the flexible nature of the natural beaded chromatin structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):1837–1851. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Temin H. M. Comparison of Rous sarcoma virus-specific deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases in virions of Rous sarcoma virus and in Rous sarcoma virus-infected chicken cells. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):625–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.625-634.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Rueckert R. R. Properties of a ribonucleoprotein particle isolated from Nonidet P-40-treated Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1010–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1010-1020.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of avian sarcoma virus polypeptide p19. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90390-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleissner E., Tress E. Isolation of a ribonucleoprotein structure from oncornaviruses. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1612–1615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1612-1615.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Marciani D. J., Papas T. S. Cell-free synthesis of the precursor polypeptide for avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4951–4954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Means G. E. Radioactive labeling of proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):831–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N. H., Nowinski R. C., Moore D. H. Helical nucleocapsid structure of the oncogenic ribonucleic acid viruses (oncornaviruses). J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):564–572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.564-572.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M., Garon C. F., Salzman N. P. The relationship of SV40 replicating chromosomes to two forms of the non-replicating SV40. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2877–2893. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Phosphorylation of murine type C viral p12 proteins regulates their extent of binding to the homologous viral RNA. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Specific binding of the type C viral core protein p12 with purified viral RNA. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]