Abstract
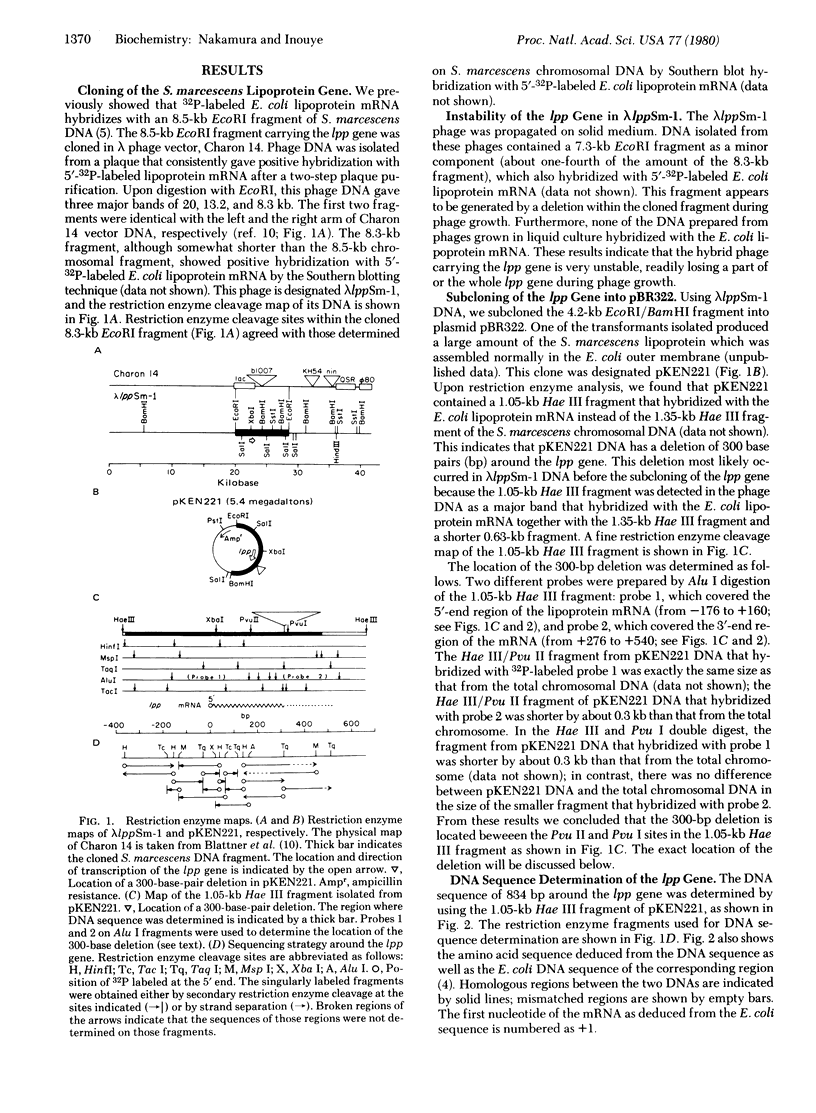
The Serratia marcescens gene for the outer membrane lipoprotein (lpp) was cloned in λ phage vector Charon 14. The recombinant phage was very unstable, and the lpp gene with a 300-base-pair deletion at the transcription termination site was further cloned in pBR322. The DNA sequence of 834 base pairs encompassing the lpp gene was determined and compared with that of the Escherichia coli lpp gene. The sequence comparisons exhibit several unique features. (i) The promoter region is highly conserved (84% homology) and has an extremely high A+T content (78%) as in E. coli (80%). (ii) The 5′ nontranslated region of the lipoprotein mRNA is also highly conserved (95% homology). (iii) In the DNA sequence corresponding to the signal peptide of this secretory protein, there are three drastic changes, including addition of one base pair and deletion of four base pairs in S. marcescens as compared to E. coli. The resultant alterations in the amino acid sequence, however, do not change the basic properties of the signal peptide, which are assumed to be essential for its function in the secretory mechanism. (iv) The DNA sequence from the amino terminus to the 51st residue of the mature lipoprotein is highly conserved (95% homology) and there is no amino acid substitution. (v) The DNA sequence corresponding to the seven amino acid residues at the carboxyl terminus has only 42% homology, resulting in four amino acid substitutions. (vi) Within the section of 40 base pairs beginning with the termination codon (UAA) and ending immediately before the oligo(T) transcription termination site in the E. coli lpp gene, there is about 60% homology. However, after this section, there is no obvious homology between the two sequences, probably because of a deletion of 300 base pairs at this region. (vii) Seven stable stem-and-loop structures could be formed in the mRNA region. (viii) Alterations in the third position of codons used in the lpp gene suggest that the gene has evolved somewhat differently from other genes in S. marcescens.
Keywords: promoter, A-T base pairs, secretion, signal peptide, loop model, gene evolution
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer P. N., Dengler B., Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C. Stability of ribonucleic acid double-stranded helices. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Stern R. H., Wensink P. C. Filter replicas and permanent collections of recombinant DNA plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2115–2136. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M. Lipoprotein of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Biomembranes. 1979;10:141–208. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-6564-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Wang S., Sekizawa J., Halegoua S., Inouye M. Amino acid sequence for the peptide extension on the prolipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G. F., Yanofsky C. Gene fusion during the evolution of the tryptophan operon in enterobacteriaceae. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):486–489. doi: 10.1038/277486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G. F., Yanofsky C. The regulatory region of the trp operon of Serratia marcescens. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):684–689. doi: 10.1038/276684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Inouye M. DNA sequence of the gene for the outer membrane lipoprotein of E. coli: an extremely AT-rich promoter. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1109–1117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Katz-Wurtzel E. T., Pirtle R. M., Inouye M. Restriction enzyme cleavage sites surrounding the structural gene for the lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):715–720. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.715-720.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Pirtle R. M., Inouye M. Homology of the gene coding for outer membrane lipoprotein within various Gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):595–604. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.595-604.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Pirtle R. M., Pirtle I. L., Takeishi K., Inouye M. Messenger ribonucleic acid of the lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. II. The complete nucleotide sequence. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):210–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirtle R. M., Pirtle I. L., Inouye M. Homologous nucleotide sequences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic mRNAs: the 5'-end sequence of the mRNA of the lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2190–2194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirtle R. M., Pirtle I. L., Inouye M. Messenger ribonucleic acid of the lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. I. Nucleotide sequence at the 3' terminus and sequences of oligonucleotides derived from complete digests of the mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):199–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E. Genetic relatedness in the family Enterobacteriaceae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:327–349. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.001551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider H. J., Fiandt M., Szybalski W. A relationship between DNA helix stability and recognition sites for RNA polymerase. Science. 1979 Aug 3;205(4405):508–511. doi: 10.1126/science.377494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



