Abstract
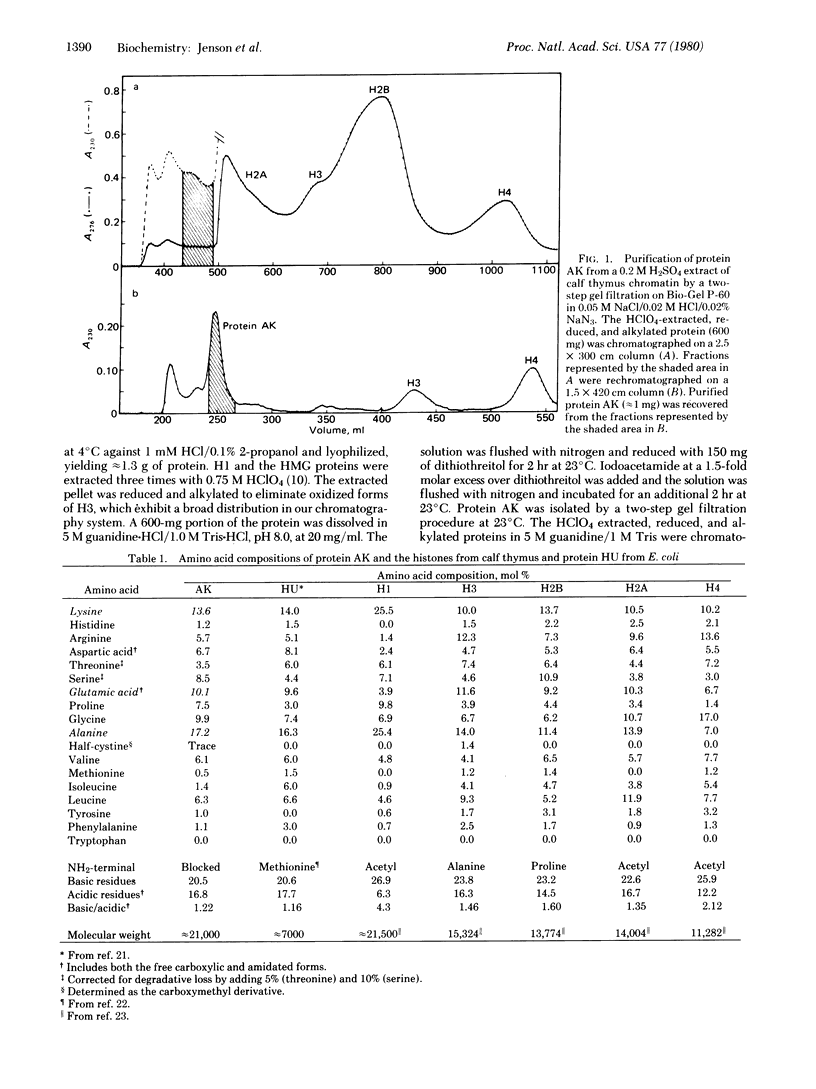
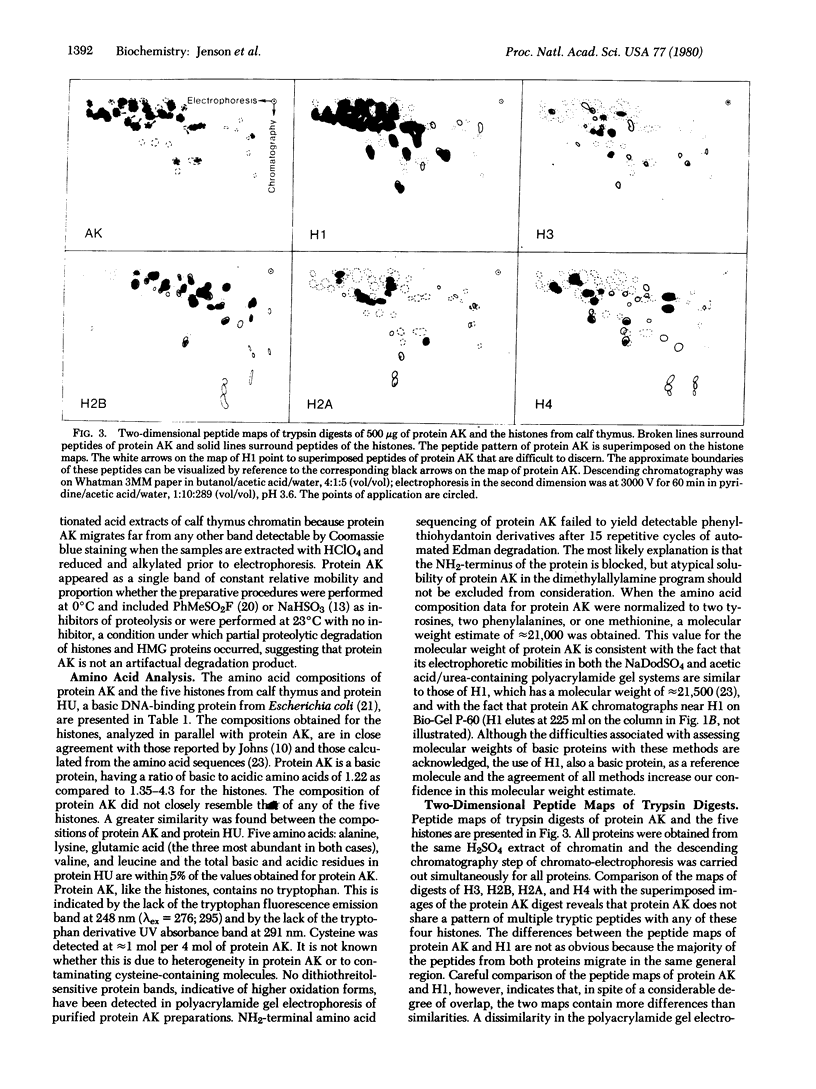
A histone-like protein that is rich in alanine and lysine (protein AK) has been obtained in homogeneous form by high-resolution gel filtration of H2SO4 extracts of calf thymus chromatin. Protein AK: (i) migrates as a single band in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in both acetic acid/urea and sodium dodecyl sulfate; (ii) is a basic protein; (iii) lacks tryptophan; (iv) is not extracted from chromatin with 0.35 M NaCl; and (v) is not soluble in 0.75 M HClO4. Protein AK is distinguished from the high-mobility group (HMG) proteins on the basis of these latter solubility characteristics and from the histones and protein A24 on the basis of amino acid composition and distribution of tryptic peptides in two-dimensional chromato-electrophoresis. In addition, protein AK is distinguished from the HMG proteins, the histones, and protein A24 on the basis of its mobility in two polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis systems. The amino acid composition of protein AK resembles that of HU, a basic DNA-binding protein found in Escherichia coli.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balhorn R., Rieke W. O., Chalkley R. Rapid electrophoretic analysis for histone phosphorylation. A reinvestigation of phosphorylation of lysine-rich histone during rat liver regeneration. Biochemistry. 1971 Oct 12;10(21):3952–3959. doi: 10.1021/bi00797a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm E. L., Strickland W. N., Strickland M., Thwaits B. H., van der Westhuizen D. R., von Holt C. Purification of the five main calf thymus histone fractions by gel exclusion chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C., Weintraub H. Chromosomal proteins and chromatin structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:725–774. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):115–122. doi: 10.1038/271115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin S. G., Zweidler A. Non-allelic variants of histones 2a, 2b and 3 in mammals. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):273–275. doi: 10.1038/266273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldknopf I. L., French M. F., Daskal Y., Busch H. A reciprocal relationship between contents of free ubiquitin and protein A24, its conjugate with histone 2A, in chromatin fractions obtained by the DNase II, Mg++ procedure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):786–793. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldknopf I. L., Taylor C. W., Baum R. M., Yeoman L. C., Olson M. O., Prestayko A. W., Busch H. Isolation and characterization of protein A24, a "histone-like" non-histone chromosomal protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7182–7187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. The isolation and purification of the high mobility group (HMG) nonhistone chromosomal proteins. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:257–267. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Sanders C., Johns E. W. A new group of chromatin-associated proteins with a high content of acidic and basic amino acids. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 21;38(1):14–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O. Amino-terminal sequence identity of ubiquitin and the nonhistone component of nuclear protein A24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):650–655. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90352-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. W. The isolation and purification of histones. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:183–203. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Hadden J. W., Inoue A., Allfrey V. G. DNA binding by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase from calf thymus nuclei. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3873–3884. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine B., Sautière P., Biserte G., Cohen-Solal M., Gros F., Rouvière-Yaniv J. The amino- and carboxy-terminal amino acid sequences of protein HU from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 1;89(1):116–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80535-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeStourgeon W. M., Beyer A. L. The rapid isolation, high-resolution electrophoretic characterization, and purification of nuclear proteins. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:387–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy B. W., Connor W., Dixon G. H. A subset of trout testis nucleosomes enriched in transcribed DNA sequences contains high mobility group proteins as major structural components. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):609–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson H. G., McCarthy B. J. Histone-histone associations within chromatin. Cross-linking studies using tetranitromethane. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 11;14(5):1073–1078. doi: 10.1021/bi00676a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nooden L. D., Van Den Broek H. W.J., Sevall J. S. Stabilization of histones from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1973 Feb 1;29(3):326–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrick L. R., Olson M. O., Busch H. Comparison of nucleolar proteins of normal rat liver and Novikoff hepatoma ascites cells by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1316–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Bilek D., Chalkley R. An electrophoretic comparison of vertebrate histones. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4206–4215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Gros F. Characterization of a novel, low-molecular-weight DNA-binding protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. A method for the fractionation of the high-mobility-group non-histome chromosomal proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 10;78(3):1034–1042. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90525-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherod D., Johnson G., Chalkley R. Studies on the hetrogeneity of lysine-rich histones in dividing cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3923–3931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. The isolation and identification of ubiquitin from the high mobility group (HMG) non-histone protein fraction. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 15;90(2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80397-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. The primary structure of the nucleosome-associated chromosomal protein HMG 14. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):394–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S., Weintraub H. Isolation of a subclass of nuclear proteins responsible for conferring a DNase I-sensitive structure on globin chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):630–634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]