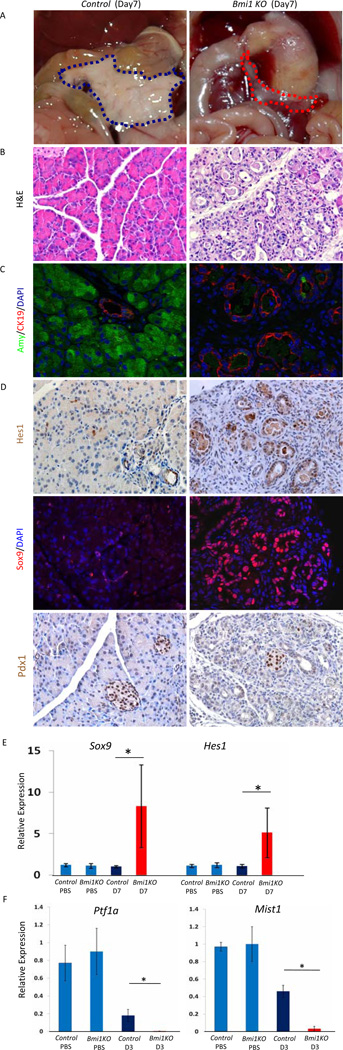
Figure 2. Impaired exocrine pancreas regeneration in Bmi1 KO mice after caerulein pancreatitis.
Control or Bmi1 KO mice were injected with caerulein and sacrificed 7 days post-injection.
(A) Macroscopic views of pancreas (outlined with dashed lines), showing hypoplastic pancreas in Bmi1 KO mice (red) compared to control mice (blue).
(B) H&E staining showing impaired exocrine pancreas regeneration with increased duct-like structures and reduced acinar area in Bmi1 KO pancreas compared to control mice.
(C) Co-staining for amylase/CK19/DAPI reveals reduced number of amylase-positive cells and increased number of CK19-positive duct-like epithelial cells in Bmi1 KO pancreas.
(D) Immunostaining for Hes1, Sox9, and Pdx1. Immunohistochemistry shows Hes1 expression in the duct-like epithelial cells in Bmi1 KO pancreas 7 days post-injection. Co-staining for Sox9/DAPI demonstrates Sox9 expression in the duct-like epithelial cells in Bmi1 KO pancreas 7 days post-injection. Immunohistochemistry shows absence of Pdx1 expression in the duct-like epithelial cells in Bmi1 KO pancreas 7 days post-injection. Pdx1 remains expressed in control and mutant islets.
(E) Relative expression levels of Sox9 and Hes1 in control and Bmi1 KO pancreata 7 days post-injection by q-PCR. N = 3 mice.
(F) Relative expression levels of Ptf1a and Mist1 in control and Bmi1 KO pancreata 3 days post-injection. N = 3 mice. Means ± SD. * p< 0.05.