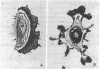
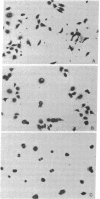
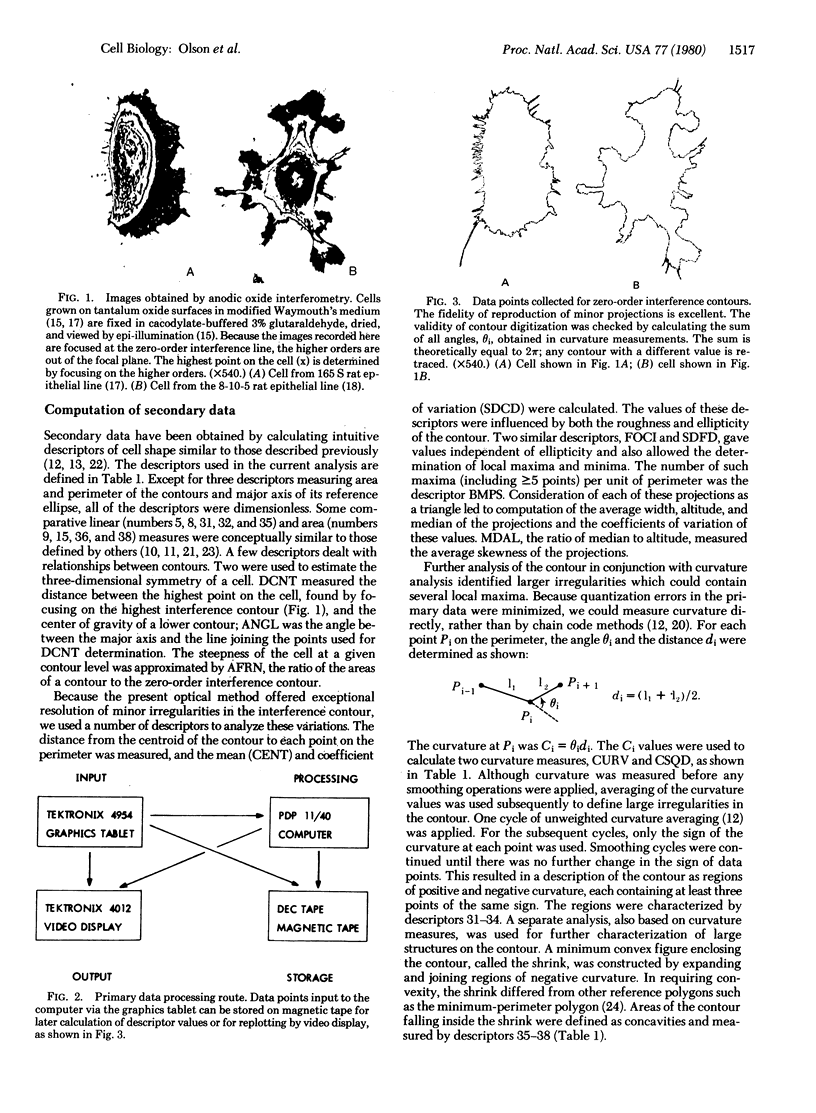
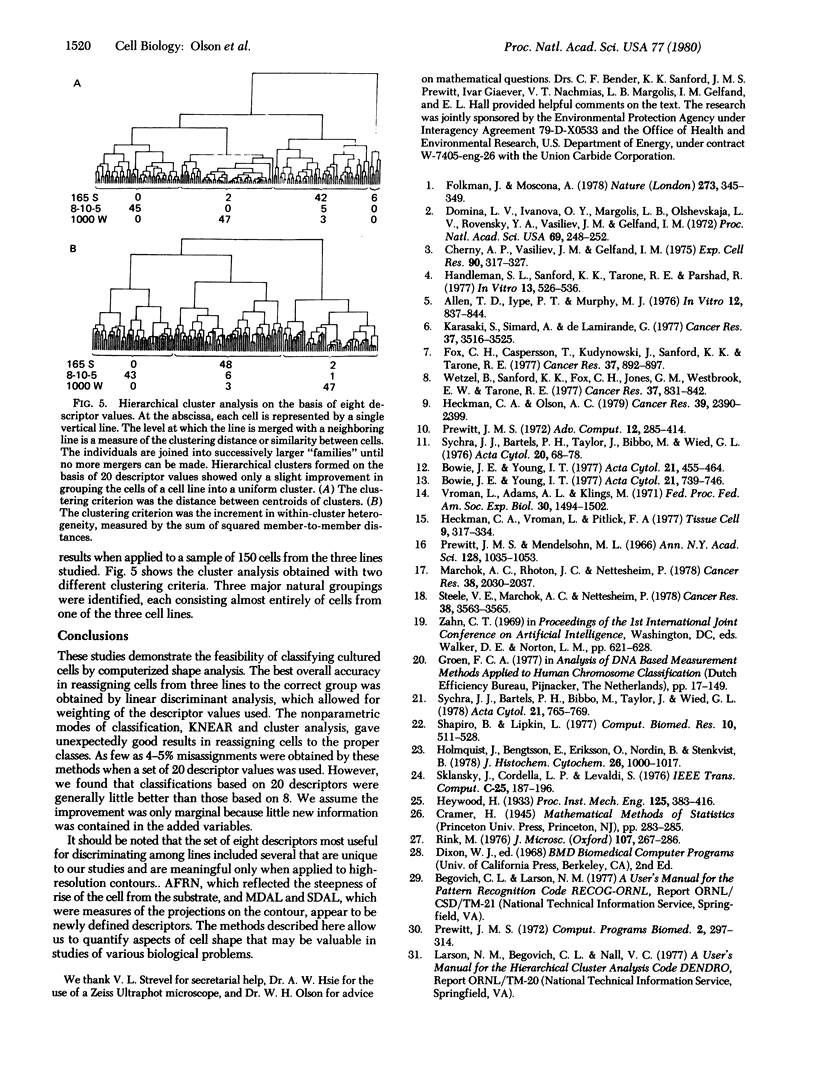
Abstract
We have developed a method for classifying cultured cells on the basis of shape characteristics. High-resolution optical information on three-dimensional shape was obtained by anodic oxide interferometry. Each interference order formed in a cell was considered as a closed figure; measurement of 37 mathematical descriptors was carried out for each figure. The individual cells were classified according to the values of their descriptors. We used standard principles of pattern recognition, such as hierarchical cluster analysis and nearest neighbor analysis, as a basis for ordering the cells into groups. Alternatively, linear discriminant functions could be used, but they provided only a slight improvement in correct classification of the cells. We anticipate that the method will be appropriate for classification of cultured cell lines and for determination of the magnitude and direction of cell shape changes implicated in various biological processes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T. D., Iype P. T. The surface morphology of normal and malignant rat liver epithelial cells in culture. In Vitro. 1976 Dec;12(12):837–844. doi: 10.1007/BF02796369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowie J. E., Young I. T. An analysis technique for biological shape-III. Acta Cytol. 1977 Nov-Dec;21(6):739–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherny A. P., Vasiliev J. M., Gelfand I. M. Spreading of normal and transformed fibroblasts in dense cultures. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Feb;90(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domnina L. V., Ivanova O. Y., Margolis L. B., Olshevskaja L. V., Rovensky Y. A., Vasiliev J. M., Gelfand I. M. Defective formation of the lamellar cytoplasm by neoplastic fibroblasts (L cells-transformed cells-cell attachment-contact inhibition-scanning electron microscopy-microcinematography). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):248–252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Moscona A. Role of cell shape in growth control. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):345–349. doi: 10.1038/273345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. H., Caspersson T., Kudynowski J., Sanford K. K., Tarone R. E. Morphometric analysis of neoplastic transformation in rodent fibroblast cell lines. Cancer Res. 1977 Mar;37(3):892–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handleman S. L., Sanford K. K., Tarone R. E., Parshad R. The cytology of spontaneous neoplastic transformation in culture. In Vitro. 1977 Sep;13(9):526–536. doi: 10.1007/BF02627848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckman C. A., Olson A. C. Morphological markers of oncogenic transformation in respiratory tract epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1979 Jul;39(7 Pt 1):2390–2399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckman C. A., Vroman L., Pitlick A. The nature of substrate-attached materials in human fibroblast cultures: localization of cell and fetal calf serum components. Tissue Cell. 1977;9(2):317–334. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(77)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist J., Bengtsson E., Eriksson O., Nordin B., Stenkvist B. Computer analysis of cervical cells. Automatic feature extraction and classification. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Nov;26(11):1000–1017. doi: 10.1177/26.11.569164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasaki S., Simard A., de Lamirande G. Surface morphology and nucleoside phosphatase activity of rat liver epithelial cells during oncogenic transformation in vitro. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3516–3525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchok A. C., Rhoton J. C., Nettesheim P. In vitro development of oncogenicity in cell lines established from tracheal epithelium preexposed in vivo to 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene. Cancer Res. 1978 Jul;38(7):2030–2037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prewitt J. M. A versatile clustering algorithm with objective function and objective measure. Comput Programs Biomed. 1972 Nov;2(4):297–314. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(72)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prewitt J. M., Mendelsohn M. L. The analysis of cell images. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jan 31;128(3):1035–1053. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B., Lipkin L. The circle transform, an articulable shape descriptor. Comput Biomed Res. 1977 Oct;10(5):511–528. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(77)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele V. E., Marchok A. C., Nettesheim P. Establishment of epithelial cell lines following exposure of cultured tracheal epithelium to 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1978 Oct;38(10):3563–3565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sychra J. J., Bartels P. H., Bibbo M., Taylor J., Wied G. L. Computer recognition of abnormal ectocervical cells. Comparison of the efficacy of contour and textural features. Acta Cytol. 1977 Nov-Dec;21(6):765–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sychra J. J., Bartels P. H., Taylor J., Bibbo M., Wied G. L. Cytoplasmic and nuclear shape analysis for computerized cell recognition. Acta Cytol. 1976 Jan-Feb;20(1):68–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vroman L., Adams A. L., Klings M. Interactions among human blood proteins at interfaces. Fed Proc. 1971 Sep-Oct;30(5):1494–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel B., Sanford K. K., Fox C. H., Jones G. M., Westbrook E. W., Tarone R. E. Topography of nonneoplastic and neoplastic cells of common origin. Cancer Res. 1977 Mar;37(3):831–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]