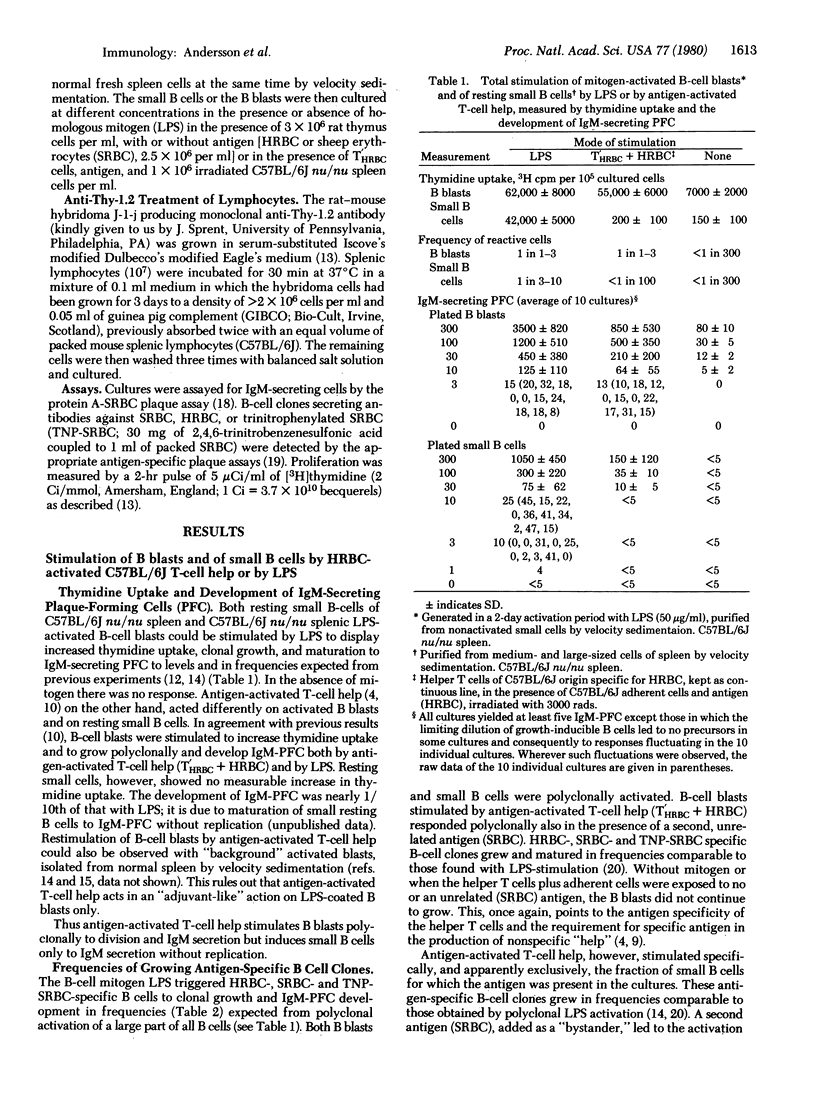
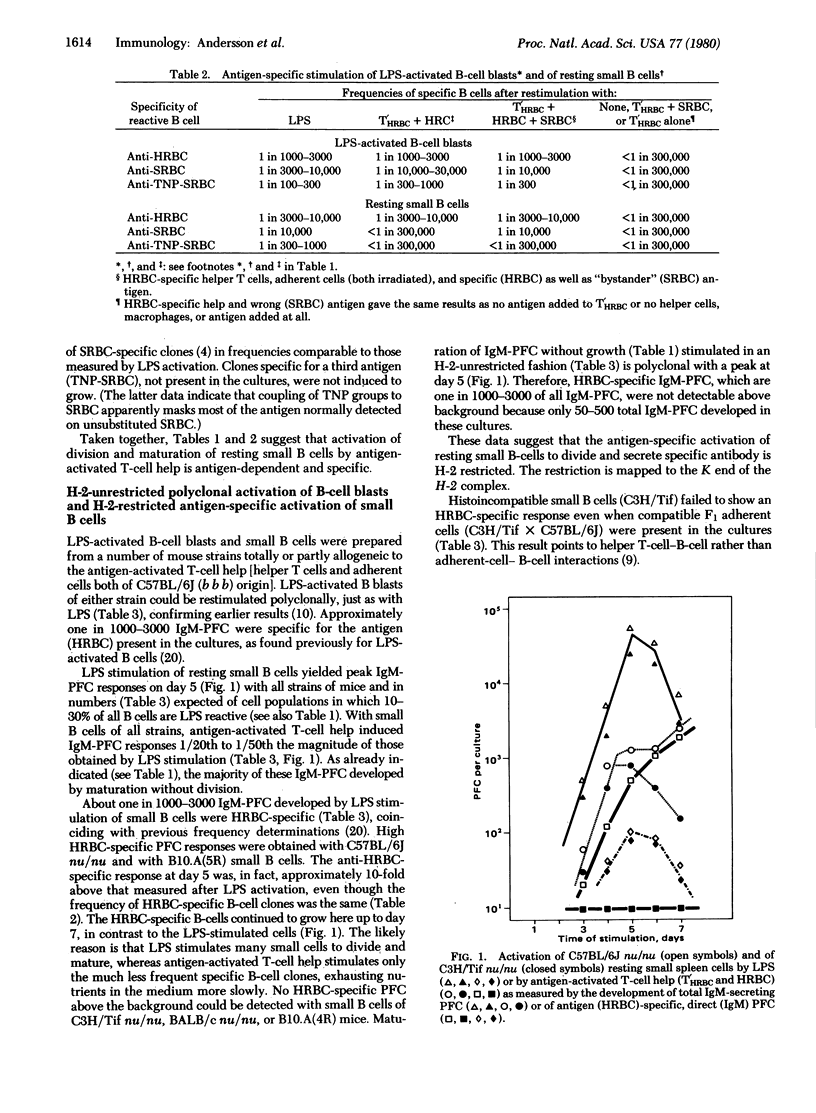
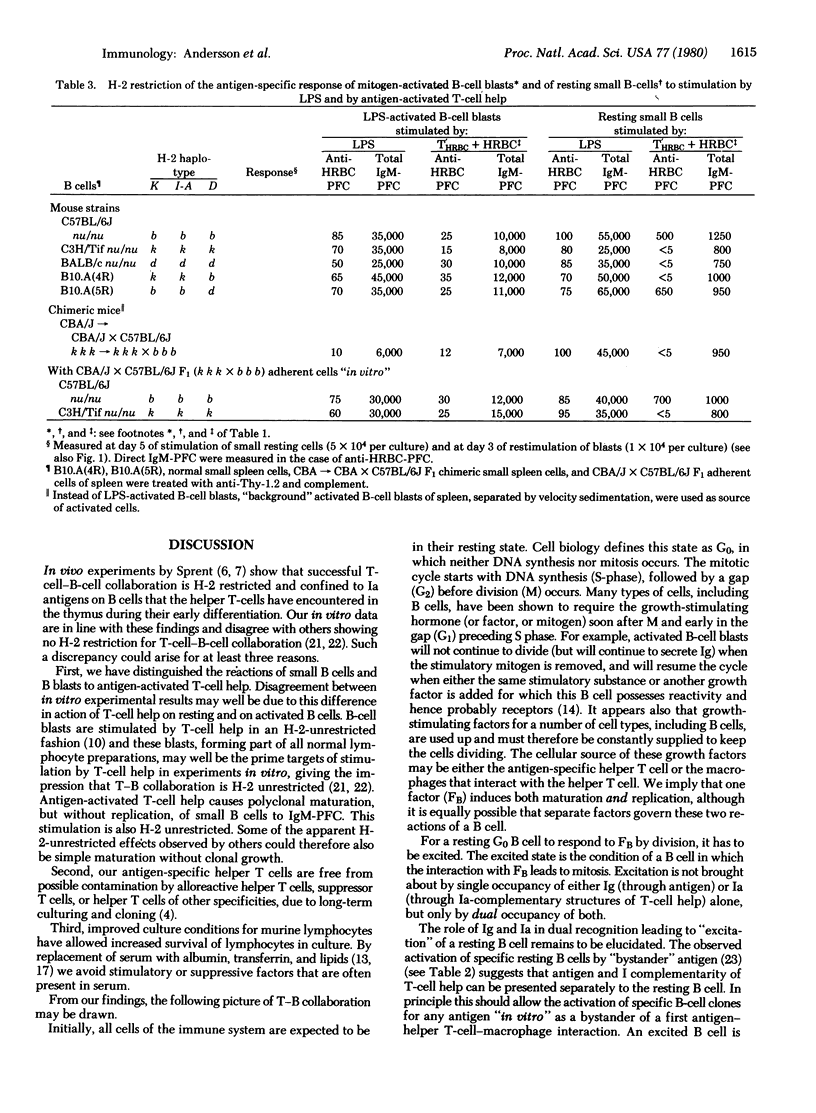
Abstract
Cloned lines of helper thymus-derived (T) cells produce help for bone marrow-derived (B) cell growth and Ig secretion in the presence of histocompatible adherent cells and of specific antigen. This help stimulates histocompatible as well as histoincompatible B-cell blasts polyclonally. Thus, neither antigen nor histocompatibility, but antigen-unspecific factor(s) for growth and Ig secretion are required to stimulate a B-cell blast through the next round of division. On the other hand, only histocompatible, resting, small B cells, and only those binding their specific antigen, can be stimulated by antigen-activated T-cell help to initiate growth and Ig secretion. The preference of the resting B cells for such collaboration with T-cell help is mapped to the K end of the H-2 histocompatibility locus, and probably constitutes the antigen expressed on B cells by the immune response (I) region. It appears that a resting B cell is excited by the binding of specific antigen to surface Ig and by the interaction of its surface Ia antigen with helper T cells. After this dual recognition the excited B cell can be stimulated by the antigen-unspecific factor(s) generated by the interaction of helper T-cells, adherent cells, and antigen to initiate replication.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Lernhardt W., Melchers F. Clonal growth and maturation to immunoglobulin secretion in vitro of every growth-inducible B lymphocyte. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Melchers F. Frequencies of mitogen-reactive B cells in the mouse. I. Distribution in different lymphoid organs from different inbred strains of mice at different ages. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1511–1519. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Melchers F. Frequencies of mitogen-reactive B cells in the mouse. II. Frequencies of B cells producing antibodies which lyse sheep or horse erythrocytes, and trinitrophenylated or nitroiodophenylated sheep erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1520–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Melchers F. Mitogen-activated B-cell blasts reactive to more than one mitogen. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):553–564. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armerding D., Katz D. H. Activation of T and B lymphocytes in vitro. II. Biological and biochemical properties of an allogeneic effect factor (AEF) active in triggering specific B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):19–37. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Coutinho A., Melchers F. Absolute frequencies of lipopolysaccharide-reactive B cells producing A5A idiotype in unprimed, streptococcal A carbohydrate-primed, anti-A5A idiotype-sensitized and anti-A5A idiotype-suppressed A/J mice. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1436–1449. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb P., Meier B., Matsunaga T., Feldmann M. Nature of T-cell macrophage interaction in helper-cell induction in vitro. II. Two stages of T-helper-cell differentiation analyzed in irradiation and allophenic chimeras. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):686–701. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann K. U. Induction of a hemolysin response in vitro. Interaction of cells of bone marrow origin and thymic origin. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1267–1278. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Melchers F. Complete replacement of serum by albumin, transferrin, and soybean lipid in cultures of lipopolysaccharide-reactive B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):923–933. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Hamaoka T., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B. Cell interactions between histoincompatible T and B lymphocytes. The H-2 gene complex determines successful physiologic lymphocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2624–2628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Phillips R. A. Separation of cells by velocity sedimentation. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Jun;73(3):191–201. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S., Shevach E. M. Function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. I. Requirement for histocompatible macrophages and lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1194–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Andersson J., Lernhardt W., Melchers F. Antigen-specific T-helper cells stimulate H-2-compatible and H-2-incompatible B-cell blasts polyclonally. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):194–203. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H. B-cell precursors specific to sheep erythrocytes. Estimation of frequency in a specific helper assay. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1612–1619. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer A., Hathcock K. S., Hodes R. J. Cellular and genetic control of antibody responses. V. Helper T-cell recognition of H-2 determinants on accessory cells but not B cells. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1208–1226. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J. Restricted helper function of F1 hybrid T cells positively selected to heterologous erythrocytes in irradiated parental strain mice. II. Evidence for restrictions affecting helper cell induction and T-B collaboration, both mapping to the K-end of the H-2 complex. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1159–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J. Role of H-2 gene products in the function of T helper cells from normal and chimeric mice in vivo. Immunol Rev. 1978;42:108–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann H., Munro A. Letter: T cell-dependent mediator in the immune response. Nature. 1973 Jun 8;243(5406):356–357. doi: 10.1038/243356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann H. The influence of the major histocompatibility complex on the function of T-helper cells in antibody formation. Immunol Rev. 1978;42:202–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Callahan G. N., Althage A., Cooper S., Klein P. A., Klein J. On the thymus in the differentiation of "H-2 self-recognition" by T cells: evidence for dual recognition? J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):882–896. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


