Abstract
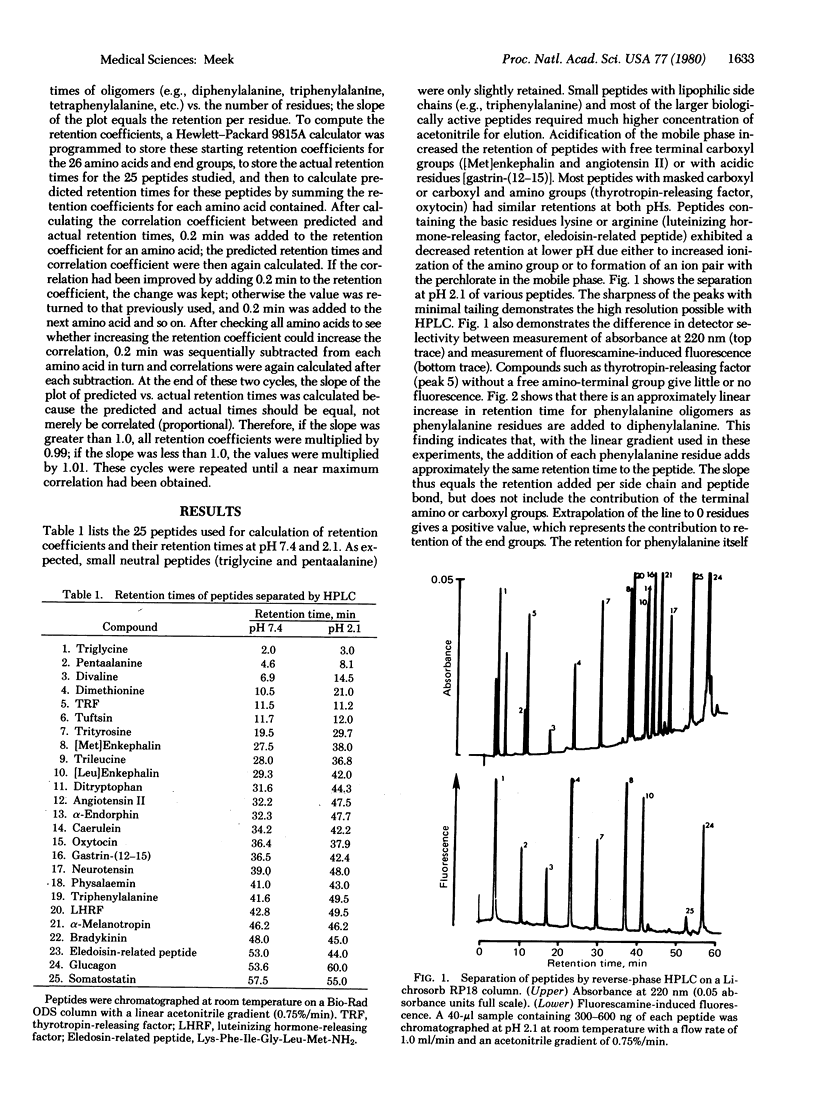
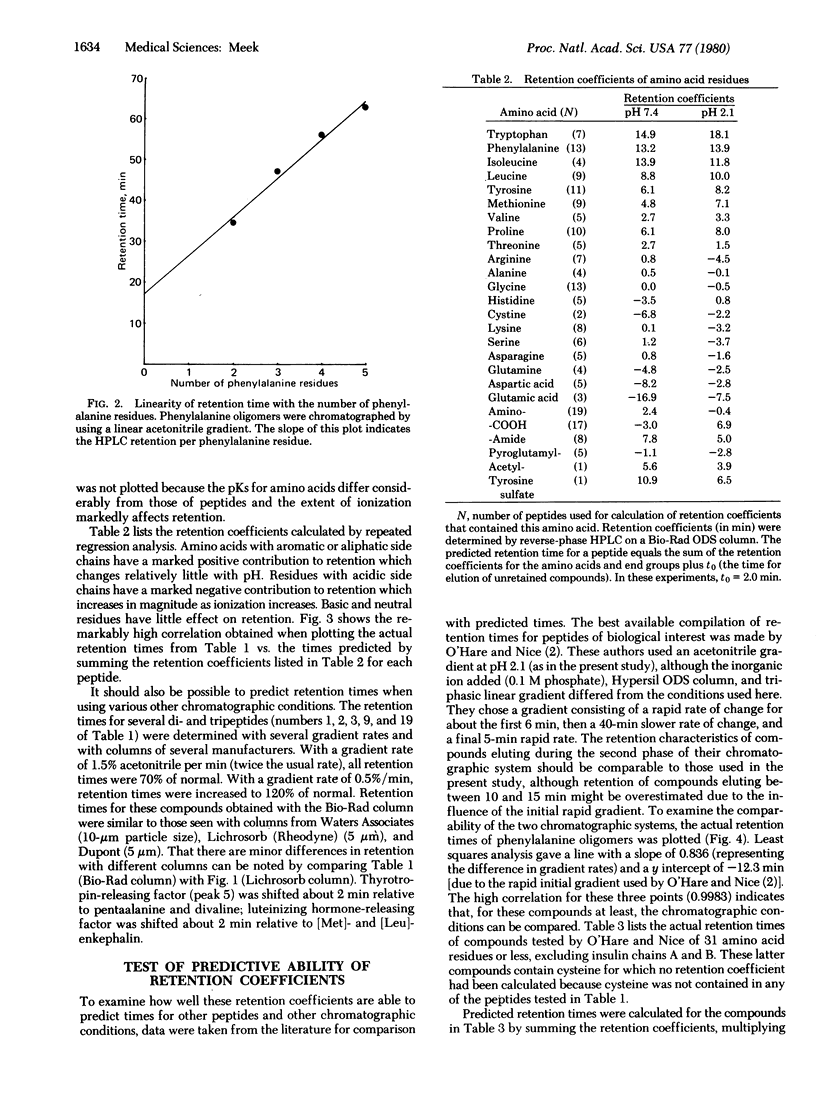
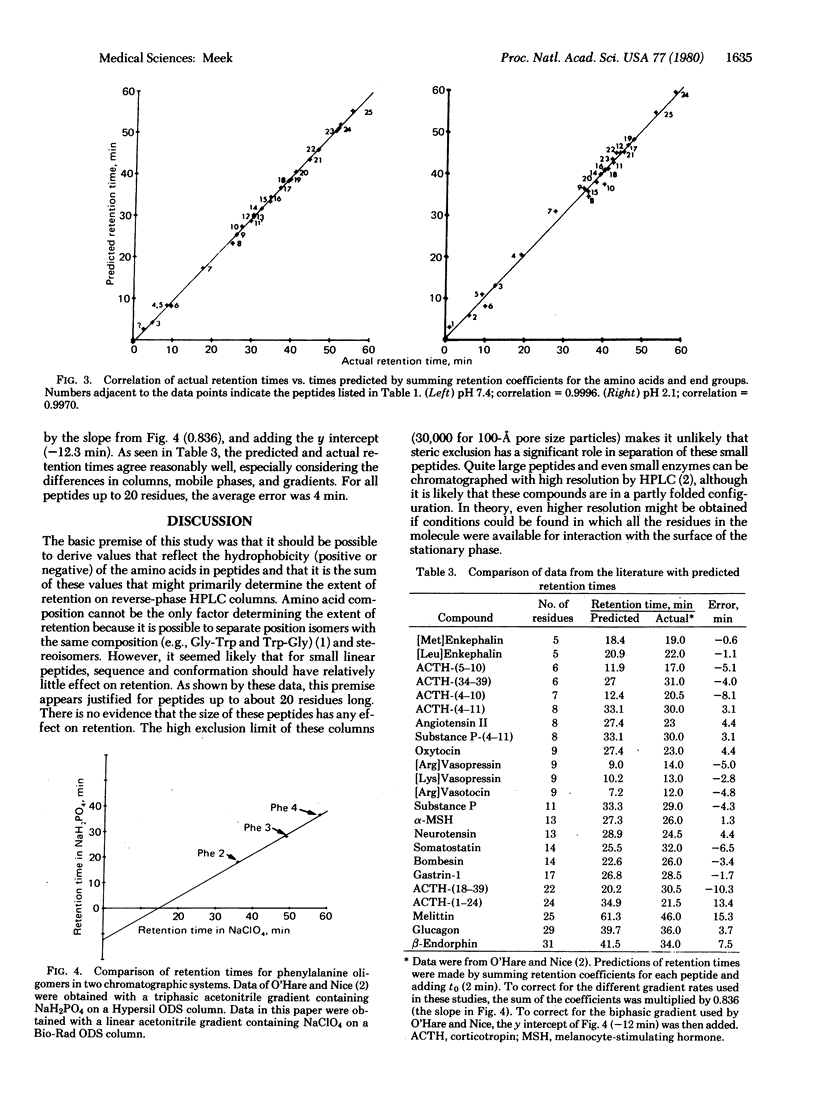
Analysis of peptides by reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography would be simplified if retention times could be predicted by summing the contribution to retention of each of the peptide's amino acid side chains. This paper describes the derivation of values (“retention coefficients”) that represent the contribution to retention of each of the common amino acids and end groups. Peptide retention times were determined on a Bio-Rad “ODS” column at room temperature with a linear gradient from 0.1 M NaclO4, pH 7.4 or 2.1, at 0 min to 60% acetonitrile/0.1 M NaclO4 at 80 min. The NaclO4, a chaotropic agent, was added to improve peak shape and to minimize conformational effects. Retention coefficients for the amino acids were computed by using a Hewlett-Packard 9815A calculator programmed to change the retention coefficients for all amino acids sequentially to obtain a maximum correlation between actual and predicted retention times. Correlations of 0.999 at pH 7.4 and 0.997 at pH 2.1 were obtained for 25 peptides including glucagon, oxytocin, [Met]enkephalin, neurotensin, and somatostatin. This high degree of correlation suggests that, for peptides containing up to 20 residues, retention is primarily due to partition processes that involve all the residues. Although steric or conformational factors do have some effect on retention, the data suggest that under the above chromatographic conditions the retention of peptides containing up to 20 residues can be predicted solely on the basis of their amino acid composition. This possibility was tested by using data taken from the literature.
Keywords: lipophilicity, separation techniques
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frei R. W., Michel L., Santi W. Post-column fluorescence derivatization of peptides. Problems and potential in high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1976 Nov 3;126:665–677. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)84110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. S., Bishop C. A., Prestidge R. L., Harding D. R., Hearn M. T. Reversed-phase, high-pressure liquid chromatography of peptides and proteins with ion-pairing reagents. Science. 1978 Jun 9;200(4346):1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.206966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatefi Y., Hanstein W. G. Solubilization of particulate proteins and nonelectrolytes by chaotropic agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKSHMANAN T. K., LIEBERMAN S. An improved method of gradient elution chromatography and its application to the separation of urinary ketosteroids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Nov;53(1):258–281. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnár I., Horváth C. Separation of amino acids and peptides on non-polar stationary phases by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1977 Nov 11;142:623–640. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)92073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare M. J., Nice E. C. Hydrophobic high-performance liquid chromatography of hormonal polypeptides and proteins on alkylsilane-bonded silica. J Chromatogr. 1979 Apr 1;171:209–226. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)95300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Stein S., Udenfriend S. Isolation and characterization of the opioid peptides from rat pituitary: beta-endorphin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4969–4972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



