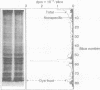
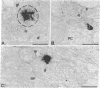
Abstract
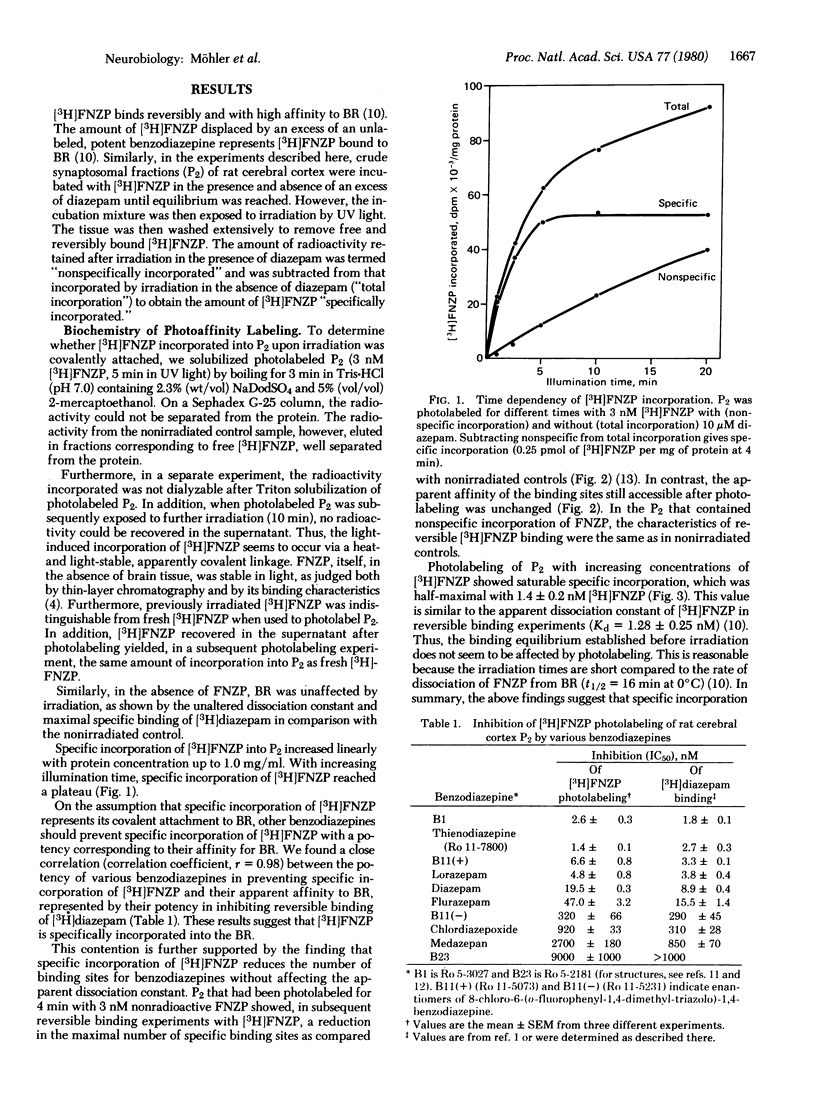
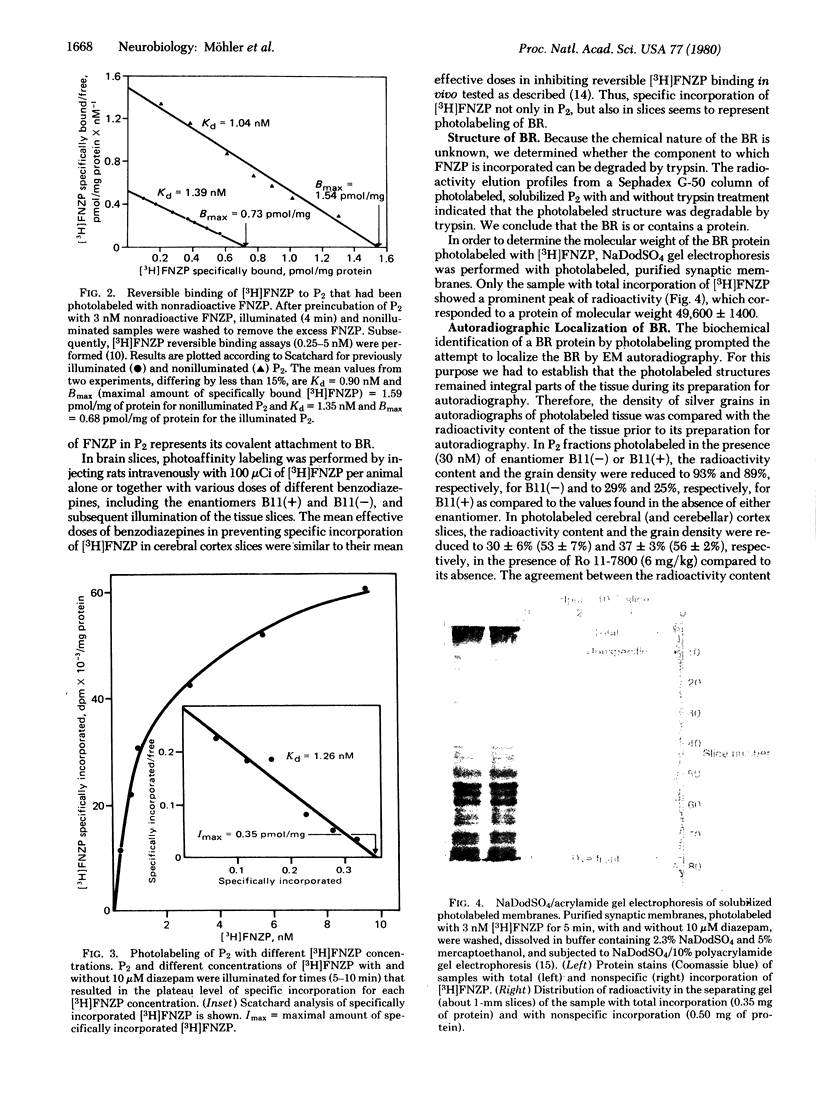
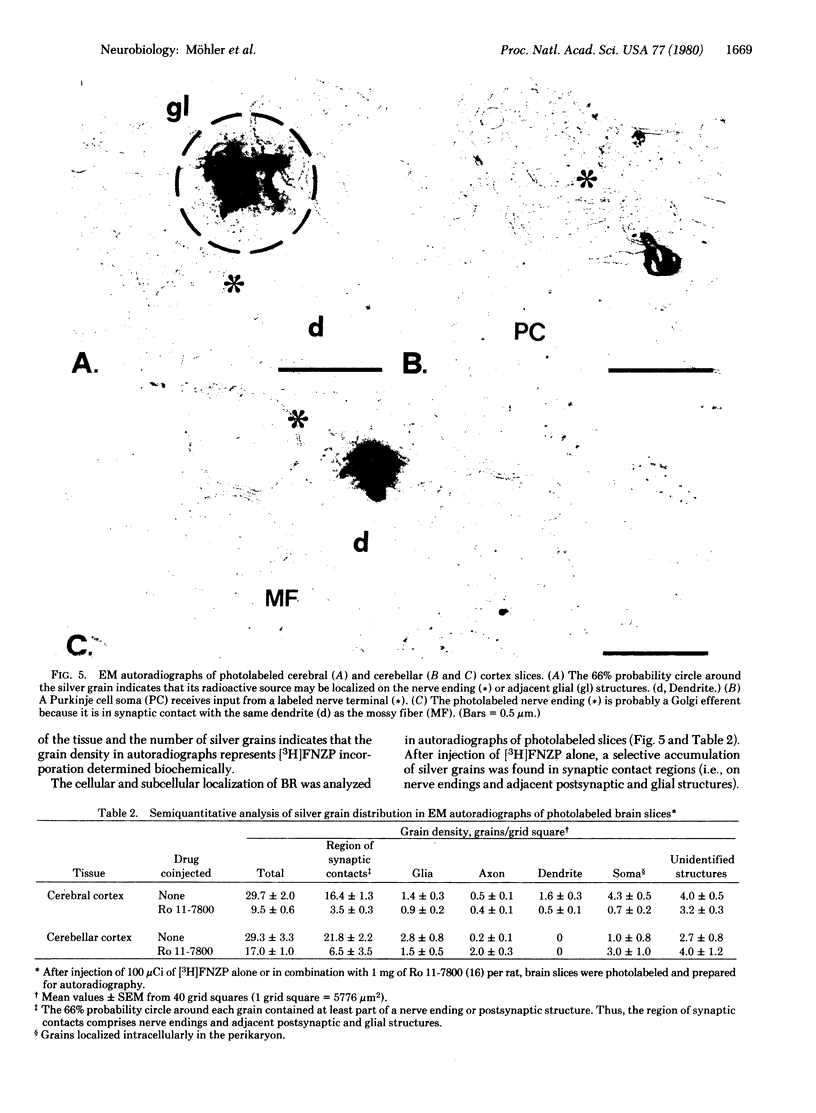
Flunitrazepam, a potent benzodiazepine, reversibly binds to the benzodiazepine receptor with high affinity. When irradiated with UV light, flunitrazepam was irreversibly linked to brain tissue. Incorporation of [3H]flunitrazepam was inhibited by other benzodiazepines with a potency corresponding to their affinity for the benzodiazepine receptor. Photolabeling with flunitrazepam reduced the number of benzodiazepine receptors determined by reversible binding of benzodiazepines, whereas the apparent affinity of the remaining receptors was unchanged. Half-maximal incorporation of flunitrazepam occurred at a concentration similar to the apparent dissociation constant of flunitrazepam. Thus, flunitrazepam appears to be a photoaffinity label for the benzodiazepine receptor. The receptor component photolabeled with flunitrazepam was a protein of molecular weight 50,000. Its location in cerebral and cerebellar cortex slices could be visualized by electron microscopic autoradiography. A predominant localization of benzodiazepine receptors in regions of synaptic constants, including those formed by GABAergic neurons (GABA is gamma-aminobutyric acid), was observed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battersby M. K., Richards J. G., Möhler H. Benzodiazepine receptor: photoaffinity labeling and localization. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug 1;57(2-3):277–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B., Case K. R., DiStefano P. Diazepam receptor characterization: specific binding of a benzodiazepine to macromolecules in various areas of rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80623-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G., VAN TUBERGEN R. P., KOLB J. A. High-resolution autoradiography. I. Methods. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:173–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Lodge D., Johnston G. A., Brand S. J. Central actions of benzodiazepines. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 17;118(2):344–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90723-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray E. G. Electron microscopy of excitatory and inhibitory synapses: a brief review. Prog Brain Res. 1969;31:141–155. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B., Barnard E. A., Chang L. R., Dolly J. O. Putative benzodiazepine receptor: a protein solubilised from brain. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laroche J., Laroche C. Nouvelles recherches sur la modification de la vision des couleurs sous l'action des médicaments à dose thérapeutique. Ann Pharm Fr. 1977 May-Jun;35(5-6):173–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin B. J., Wood J. G., Saito K., Barber R., Vaughn J. E., Roberts E., Wu J. Y. The fine structural localization of glutamate decarboxylase in synaptic terminals of rodent cerebellum. Brain Res. 1974 Aug 23;76(3):377–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90815-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Properties of 3H-diazepam binding to benzodiazepine receptors in rat cerebral cortex. Life Sci. 1977 Jun 15;20(12):2101–2110. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salpeter M. M., McHenry F. A., Salpeter E. E. Resolution of electron microscope autoradiography. IV. Application to analysis of autoradiographs. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jan;76(1):127–145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth R. C., Wastek G. J., Johnson P. C., Yamamura H. I. Benzodiazepine binding in human brain: characterization using [3H]flunitrazepam. Life Sci. 1978 Mar;22(10):859–866. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90610-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth R. C., Wastek G. J., Yamamura H. I. Benzodiazepine receptors: temperature dependence of [3H]flunitrazepam binding. Life Sci. 1979 Jan 22;24(4):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Brastrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):732–734. doi: 10.1038/266732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer O., Zürcher K., Krebs A. Hautnebenwirkungen interner Arzneimittel. IV. Teil einer Synopsis. 6./7. Medikamente mit Wirkung auf das Zentralnervensystem. C. Medikamentöse Lichtempfindlichkeit. D. Medikamentöse Veränderungen der Hautfarbe. Dermatologica. 1976;152(4):193–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin G., Wilson J. E., Balazs R., Schon F., Kelly J. S. How selective is high affinity uptake of GABA into inhibitory nerve terminals? Nature. 1974 Nov 29;252(5482):397–399. doi: 10.1038/252397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. J., Paul S. M., Skolnick P. Labelling of benzodiazepine receptors in vivo. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):551–553. doi: 10.1038/275551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zbinden G., Randall L. O. Pharmacology of benzodiazepines: laboratory and clinical correlations. Adv Pharmacol. 1967;5:213–291. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60658-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]