Abstract
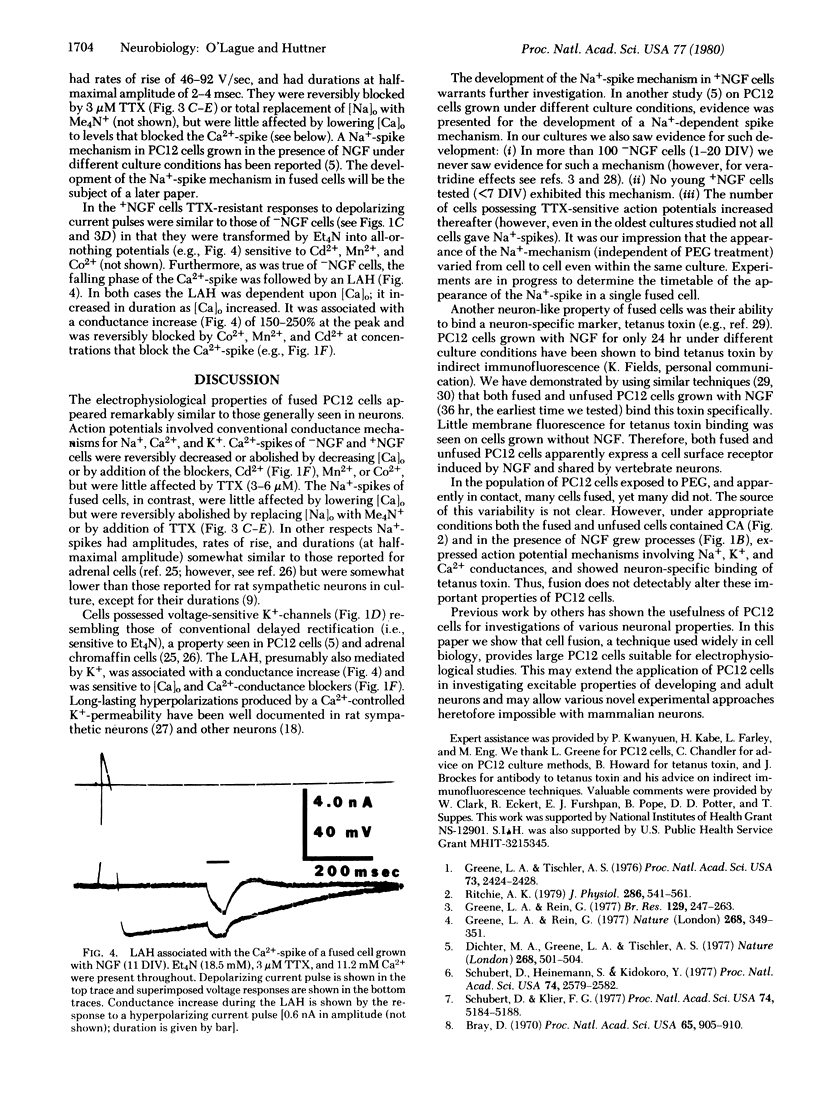
Cell fusion induced by polyethylene glycol has been used to produce in culture giant multinucleate PC12 cells (up to 300 micron in diameter compared to 10-20 micron for unfused cells). Fused cells, like their unfused counterparts, were found to express various neuronal properties. They contained catecholamines. In the presence of nerve growth factor they extended long processes and expressed Na+, Ca2+, and K+ conductances generally associated with excitable cells. In the absence of nerve growth factor these cells neither grew long processes nor generated Na+-spikes. Other neuronal properties were also observed.
Full text
PDF
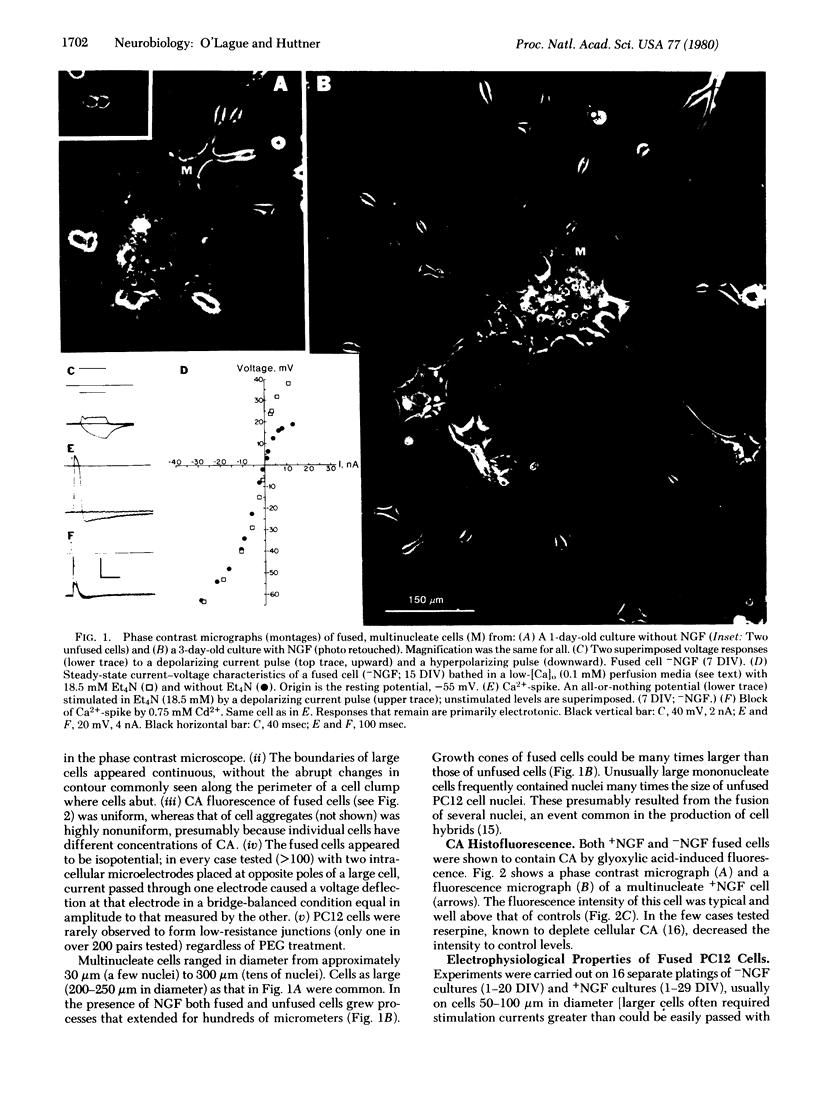
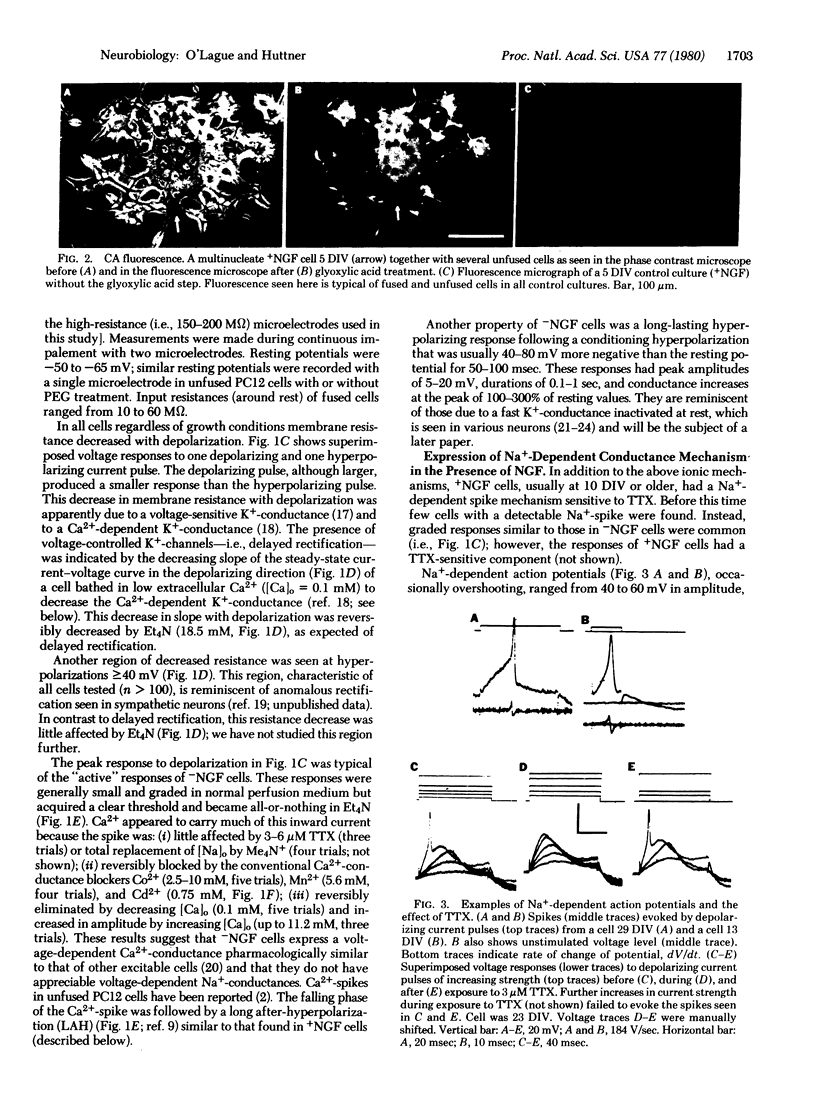

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biales B., Dichter M., Tischler A. Electrical excitability of cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):743–753. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt B. L., Hagiwara S., Kidokoro Y., Miyazaki S. Action potentials in the rat chromaffin cell and effects of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(3):417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D. Surface movements during the growth of single explanted neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):905–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christ D. D., Nishi S. Anomalous rectification of mammalian sympathetic ganglion cells. Exp Neurol. 1973 Sep;40(3):806–815. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(73)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., O'Malley K. A., Wheeler T. B. Polyethylene glycol-induced mammalian cell hybridization: effect of polyethylene glycol molecular weight and concentration. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 May;2(3):271–280. doi: 10.1007/BF01538965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Tischler A. S., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor-induced increase in electrical excitability and acetylcholine sensitivity of a rat pheochromocytoma cell line. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):501–504. doi: 10.1038/268501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Brockes J. P., Mirsky R., Wendon L. M. Cell surface markers for distinguishing different types of rat dorsal root ganglion cells in culture. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Rein G. Release, storage and uptake of catecholamines by a clonal cell line of nerve growth factor (NGF) responsive pheo-chromocytoma cells. Brain Res. 1977 Jul 1;129(2):247–263. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Rein G. Synthesis, storage and release of acetylcholine by a noradrenergic pheochromocytoma cell line. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):349–351. doi: 10.1038/268349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., SAITO N. Voltage-current relations in nerve cell membrane of Onchidium verruculatum. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:161–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca spike. Adv Biophys. 1973;4:71–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H., Watkins J. F., Ford C. E., Schoefl G. I. Artificial heterokaryons of animal cells from different species. J Cell Sci. 1966 Mar;1(1):1–30. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magherini P. C., Precht W. Electrical properties of frog motoneurons in the in situ spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1976 May;39(3):459–473. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAfee D. A., Yarowsky P. J. Calcium-dependent potentials in the mammalian sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):507–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirsky R., Wendon L. M., Black P., Stolkin C., Bray D. Tetanus toxin: a cell surface marker for neurones in culture. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 9;148(1):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90399-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Lague P. H., Potter D. D., Furshpan E. J. Studies on rat sympathetic neurons developing in cell culture. I. Growth characteristics and electrophysiological properties. Dev Biol. 1978 Dec;67(2):384–403. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. K. Catecholamine secretion in a rat pheochromocytoma cell line: two pathways for calcium entry. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:541–561. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Heinemann S., Kidokoro Y. Cholinergic metabolism and synapse formation by a rat nerve cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2579–2583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Klier F. G. Storage and release of acetylcholine by a clonal cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5184–5188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore P. A. The mechanism of norepinephrine depletion by reserpine, metaraminol and related agents. The role of monoamine oxidase. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Mar;18(1):561–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup W. B. Sodium and calcium fluxes in a clonal nerve cell line. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:525–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Nomura J., Shooter E. M. The isolation of the mouse nerve growth factor protein in a high molecular weight form. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):2202–2209. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]