Abstract
Purified acetylcholine receptor and total lipids, both extracted from Torpedo californica electroplax, were utilized to reconstitute chemically excitable membrane vesicles. Reconstitution was achieved by dialysis of the extraction detergent, octyl beta-D-glucoside from protein/lipid incubation mixtures. The reconstituted preparations could be fractionated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation and consisted of vesicular structures visible in electron micrographs. In addition, the reconstituted vesicles exhibited;the following properties characteristic of native receptor-enriched membranes: (i) an external distribution of alpha-bungarotoxin-binding sites, (ii) a time-dependent binding of alpha-bungarotoxin that is depressed by preincubation with the cholinergic agonist carbamoylcholine ("desensitization"), (iii) an ability to retain 22Na+ that is lost in the presence of detergents or gramicidin A, and (iv) a carbamoylcholine-induced acceleration of 22Na+ efflux that can be blocked by alpha-bungarotoxin. The purified acetylcholine receptor that was utilized in the reconstitution experiments apparently does not require other protein components for ligand recognition or ion translocation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen T. J., Doerge D. R., McNamee M. G. Effects of phospholipase A2 on the binding and ion permeability control properties of the acetylcholine receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 May;194(2):468–480. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90641-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briley M. S., Changeux J. P. Recovery of some functional properties of the detergent-extracted cholinergic receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata after reintegration into a membrane environment. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):429–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M., Racker E. Reconstitution of carbamylcholine-dependent sodium ion flux and desensitization of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6660–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Ros J. M., Sator V., Calvo-Fernandez P., Martinez-Carrion M. Pyrenesulfonyl azide: a covalent probe permitting in vitro desensitization of labeled acetylcholine-rich membrane fragments from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91668-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig P. R., Raftery M. A. Preparation of right-side-out, acetylcholine receptor enriched intact vesicles from Torpedo californica electroplaque membranes. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1146–1150. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Changeux J. P. Reconstitution of a chemically excitable membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1479–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Changeux J. P. Structural and functional properties of the acetylcholine receptor protein in its purified and membrane-bound states. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:317–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Fries E., Kartenbeck J. Reconstitution of Semliki forest virus membrane. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):866–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Carrion M., Sator V., Raftery M. A. The molecular weight of an acetylcholine receptor isolated from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Duguid J. R., Miller D. L., Raftery M. A. Reconstitution of a purified acetylcholine receptor. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(3):419–425. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Raftery M. A. Purified acetylcholine receptor: its reconstitution to a chemically excitable membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4768–4772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Reconstitution into liposomes of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus by detergent dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4313–4316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sator V., Gonzalez-Ros J. M., Calvo-Fernandez P., Martinez-Carrion M. Pyrenesulfonyl azide: a marker of acetylcholine receptor subunits in contact with membrane hydrophobic environment. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1200–1206. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
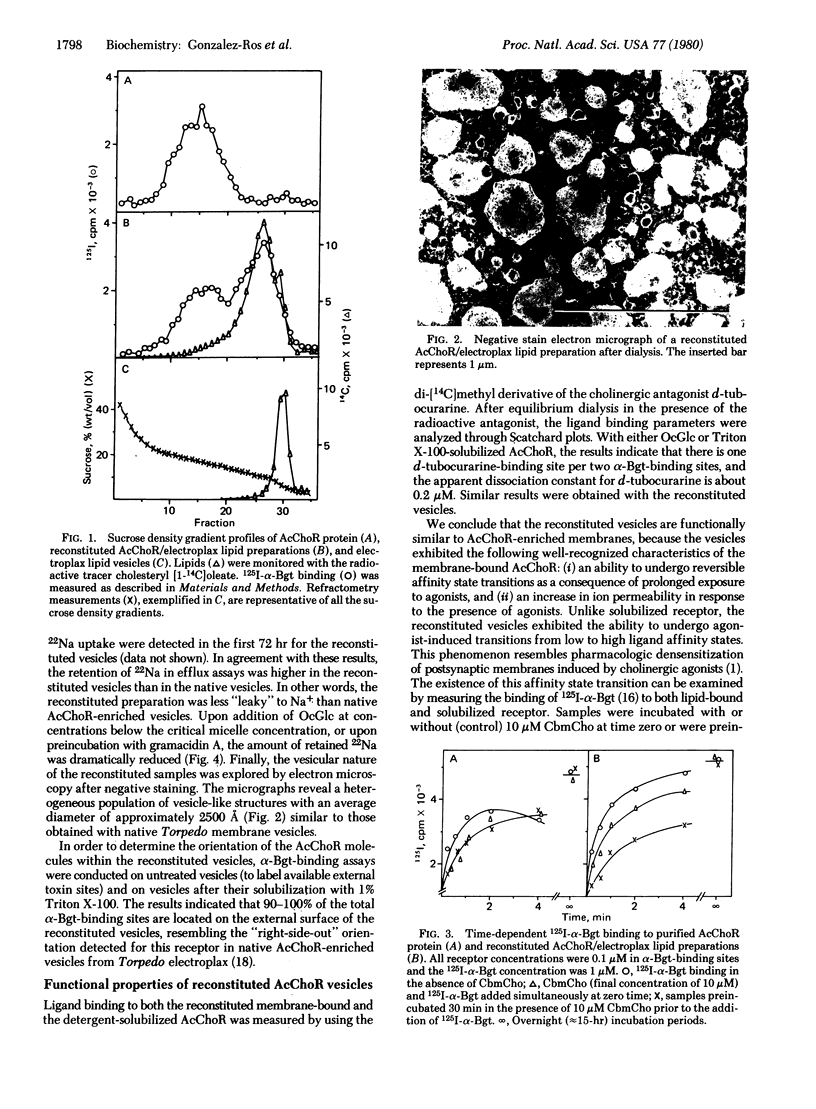
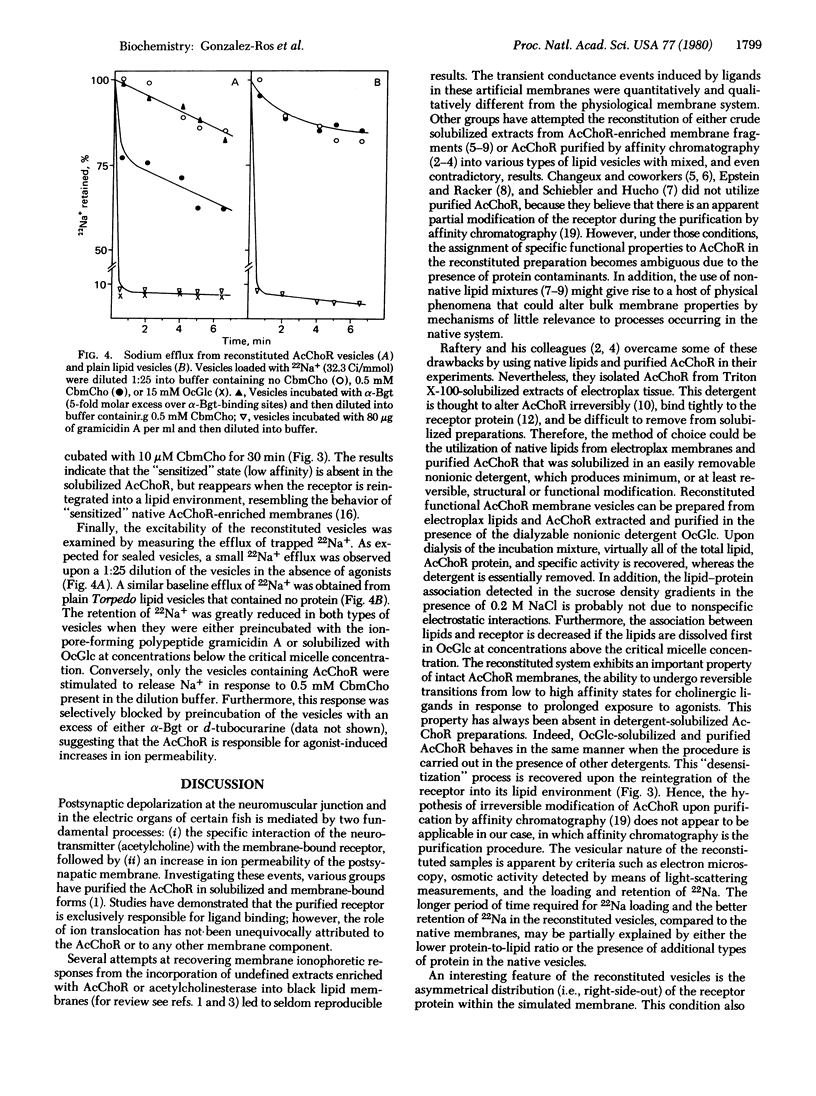
- Schiebler W., Hucho F. Membranes rich in acetylcholine receptor: characterization and reconstitution to excitable membranes from exogenous lipids. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. A simple assay for the study of solubilized acetylcholine receptors. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Isla B. A., Hucho F. Acetylcholine receptor: SH group reactivity as indicator of conformational changes and functional states. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Changeux J. P. Interconversion between different states of affinity for acetylcholine of the cholinergic receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 15;55(3):505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Raftery M. A. Carbamylcholine-induced rapid cation efflux from reconstituted membrane vesicles containing purified acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):26–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




