Abstract
Malaria and schistosomiasis are the world's two most important parasitic infections in terms of distribution, morbidity, and mortality. In areas where Plasmodium and Schistosoma species are both endemic, coinfections are commonplace. Mouse models demonstrate that schistosomiasis worsens a malaria infection; however, just as mice and humans differ greatly, the murine-infecting Plasmodium species differ as much from those that infect humans. Research into human coinfections (Schistosoma haematobium-Plasmodium falciparum versus Schistosoma mansoni-P. falciparum) has produced conflicting results. The rhesus macaque model provides a helpful tool for understanding the role of S. mansoni on malaria parasitemia and antimalarial immune responses using Plasmodium coatneyi, a malaria species that closely resembles P. falciparum infection in humans. Eight rhesus macaques were exposed to S. mansoni cercariae. Eight weeks later, these animals plus 8 additional macaques were exposed to malaria either through bites of infected mosquitos or intravenous inoculation. When malaria infection was initiated from mosquito bites, coinfected animals displayed increased malaria parasitemia, decreased hematocrit levels, and suppressed malaria-specific antibody responses compared to those of malaria infection alone. However, macaques infected by intravenous inoculation with erythrocytic-stage parasites did not display these same differences in parasitemia, hematocrit, or antibody responses between the two groups. Use of the macaque model provides information that begins to unravel differences in pathological and immunological outcomes observed between humans with P. falciparum that are coinfected with S. mansoni or S. haematobium. Our results suggest that migration of malaria parasites through livers harboring schistosome eggs may alter host immune responses and infection outcomes.
INTRODUCTION
Research on parasitic infections has typically been focused on a singular disease, but in recent years there has been a growing recognition that patients in tropical regions around the globe often experience concomitant infections (11). The interactions between diseases can cause altered immunologic and pathological outcomes compared to what usually occurs with single infections (26). These differential outcomes during coinfection may also negatively influence vaccine and chemotherapeutic efficacy (17, 19).
Much of the recent data on concomitant infections has focused on interactions between Plasmodium spp. and helminths, with a particular emphasis on malaria and schistosome infections. The shared geographical distribution of Plasmodium and Schistosoma parasites often leads to this type of coinfection (18, 21), as malaria and schistosomiasis are two of the most prevalent parasitic diseases. Annually there are an estimated 300 million to 500 million clinical cases of malaria (mostly Plasmodium falciparum malaria) (23) and 780,000 deaths, with the highest burden of mortality occurring in children under 5 years of age (28). Chronic schistosomiasis affects an estimated 200 million people each year, and approximately 780 million are at risk for a schistosome infection (25). Both infections cause significant morbidity in addition to detrimental socioeconomic effects.
There have been several studies in mice examining Plasmodium-Schistosoma coinfections. Mice infected with Plasmodium chabaudi and Schistosoma mansoni have severely altered immune responses, with reduced specific antibody responses to schistosome antigens and higher levels of malaria parasitemia in coinfected mice (10). A Plasmodium berghei-S. mansoni-coinfected mouse model displayed delayed clearance of parasitemia after malaria chemotherapy (14). Similarly, in a murine immunization model, concomitant infection with P. berghei and S. mansoni demonstrated increased mortality associated with malaria (13). However, these findings are limited, as the malaria species that infect mice do not adequately reflect the biology and pathogenesis of the species, particularly P. falciparum, that cause human malaria infections (8).
Research on human malaria and schistosome coinfections has been more difficult to interpret. Studies of Schistosoma haematobium and P. falciparum infections in Malian children demonstrated a protective effect of schistosomiasis on clinical malaria in young children (ages 4 to 8 years) but no effect in slightly older individuals (ages 9 to 14 years) (15). A protective effect of S. haematobium on malaria was also seen in Senegal, where children with light schistosome infections had significantly lower P. falciparum parasitemia than children without schistosomiasis (2). In contrast, Kenyan children with S. mansoni infections who were also chronically exposed to malaria had worse hepatosplenomegaly than children with schistosomiasis or malaria exposure alone (29, 30). Additionally, Senegalese children with S. mansoni infections demonstrated more clinical malaria compared to children not infected with schistosomes (24). In cross-sectional studies of Kenyan children living in communities close to Lake Victoria, those infected with S. mansoni had a significantly higher prevalence of malaria parasitemia than children who were negative for schistosomiasis (27). These seemingly contradictory results may be due to the differences in the schistosome species but may also be affected by the study design, presence of other infections, or infectious disease exposure history. To study coinfections in a more controlled setting, using a malaria species that mimics the biological features and pathogenic mechanisms of P. falciparum, we utilized a nonhuman primate model to explore the effects of concomitant S. mansoni infection on malaria (Plasmodium coatneyi) pathology and antimalarial immune responses.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Rhesus macaques.
Sixteen Chinese-origin rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) between the ages of 4 and 6 years were studied in two experiments. Macaques were used in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines on the care and use of laboratory animals at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), fully accredited by the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care International. Animal experiments were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of the CDC.
Parasitic infections.
To establish schistosome infections, four naïve rhesus macaques were percutaneously exposed to 500 S. mansoni cercariae. Infection was monitored by collecting stool samples weekly, beginning 5 to 6 weeks after exposure to cercariae, when eggs first appeared, and continued until egg counts returned to zero for at least two consecutive weeks. Stool was processed by formalin-ethyl acetate sedimentation and concentration. Egg counts were determined microscopically and recorded as eggs per gram of stool.
Eight weeks after exposure to cercariae, the group of four schistosome-infected rhesus macaques plus four additional naïve macaques were exposed to the bites of 5 Anopheles dirus mosquitoes infected with P. coatneyi for 10 min to establish a mosquito-borne malaria infection. These mosquitoes had previously fed on a donor monkey infected by intravenous inoculation with P. coatneyi blood-stage parasites. Malaria parasitemia was monitored daily by microscopic counting of parasites in Giemsa-stained thick and/or thin blood smears beginning on the tenth day after infection. The macaques were treated with subcurative doses of quinine when deemed necessary to prevent excessive life-threatening parasitemia and death (dosage ranged from 50 mg to 300 mg per day, dependent on level of parasitemia). Infection was cured at week eight after malaria exposure by administration of three 150-mg doses of chloroquine.
For the initiation of blood-stage malaria infections, a group of four rhesus macaques previously infected with schistosomes 8 weeks prior and four additional naïve macaques were intravenously inoculated with 50,000 P. coatneyi ring-stage-infected rhesus monkey erythrocytes. The blood-stage parasites were obtained from a donor monkey infected by intravenous inoculation with cryopreserved P. coatneyi blood-stage parasites. Malaria parasitemia was monitored daily as described above, beginning the day after parasite injection. The macaques were treated with subcurative doses of quinine when deemed necessary to prevent excessive parasitemia and death (dosage ranged from 150 mg to 450 mg per day, dependent on the level of parasitemia). Infection was cured at week seven after malaria exposure by administration of three 150-mg doses of chloroquine.
Complete blood count.
Blood was collected weekly following malaria exposure using EDTA microcontainer tubes. Complete blood cell counts, including hematocrit and hemoglobin levels, were determined using a Beckman Coulter hematology analyzer (Brea, CA).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Plates were coated with 40 μg/ml of P. coatneyi trophozoite and schizont-stage crude antigen in 0.5 M sodium carbonate buffer, pH 9.6, and incubated overnight at 4°C. Plates were blocked with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.3% Tween 20 and 5% nonfat dry milk and incubated overnight at 4°C. Plasma samples were diluted 1:100 in PBS containing 0.3% Tween 20 and 5% nonfat dry milk and incubated for 2 h at room temperature. Plates were washed five times in PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20. Antigen-specific IgG binding was measured by the addition of horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) diluted 1:20,000 in PBS containing 0.3% Tween 20 with incubation for 2 h. Antigen-specific IgM binding was measured by the addition of horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-monkey IgM (Rockland, Gilbertsville, PA) diluted 1:10,000 as described above. Plates were developed with TMB substrate (Kirkegaard & Perry Laboratories, Gaithersburg, MD) and stopped with 18% sulfuric acid. The plates were read on a Molecular Diagnostics Vmax microplate reader (Molecular Devices Corporation, Sunnyvale, CA) at 450 nm and analyzed with Softmax software (Molecular Devices). To ensure consistency between plates, a standard curve was developed and included on each plate. A 1:3 serial dilution curve was made from positive plasma collected from the P. coatneyi donor macaque. A four-parameter curve-fitting model was used to assign units to each unknown plasma sample.
Multiplex cytokine analysis.
Cytokines [granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), gamma interferon (IFN-γ), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), IL-1ra, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12/23(p40), IL-13, IL-15, IL-17, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), macrophage inflammatory protein 1α (MIP-1α), MIP-1β, sCD40L, transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-α), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), IL-18] were analyzed from plasma collected at different time points during the infections using a nonhuman primate cytokine assay (Millipore, Billerica, MA) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Statistics.
Parasitemia, anemia, antibody, and cytokine levels were compared between malaria-only-infected and coinfected groups over the course of infection by two-way analysis of variance using GraphPad Prism version 5.03 (GraphPad Software, Inc., LaJolla, CA).
RESULTS
Differential clinical outcomes in coinfected macaques infected by mosquito exposure.
Schistosome eggs first appeared in the stool between 6 and 8 weeks after exposure to cercariae, and infection was patent until spontaneous clearance at 12 to 13 weeks. At 8 weeks after infection with S. mansoni, groups of schistosomiasis-positive macaques and previously uninfected animals were exposed to the bites of 5 A. dirus mosquitos that had fed 11 days previously on a P. coatneyi-infected rhesus macaque. Although mosquitos for challenge bites were selected from fed batches with 90% to 100% infections, mosquito infections were also confirmed by subsequent dissection of the salivary glands after challenge feeds. All animals became patent for blood-stage parasites on day 12 or 13 following this sporozoite challenge. When infecting macaques by the bites of infected mosquitos, the number of sporozoites inoculated into each animal cannot be tightly controlled, although the very close prepatent periods of between 12 and 13 days noted above indicate that similar numbers of sporozoites were delivered. Additionally, because malaria parasites replicate within the host to several orders of magnitude beyond the infecting dose, the rate of replication has a greater impact on resulting parasitemia than do potential differences in numbers of sporozoites inoculated by the same number of mosquitos.
The parasitemia for both coinfected and malaria-only-infected macaques rapidly increased, and both groups of macaques were treated with subcurative doses of quinine when parasitemia reached very high levels around days 17 and 18. Coinfected macaques maintained significantly higher parasitemia levels for a longer time period than their malaria-only-infected counterparts (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 1A and B), even in the presence of antimalarial drug treatment. The average dosage of quinine for the coinfected macaques was 123 mg/day over a period of 6 days. For the malaria-only-infected macaques, the average was 75 mg/day over the same 6-day period. Thus, although the coinfected group received more quinine, they experienced higher parasitemia levels than the malaria-only-infected macaques.
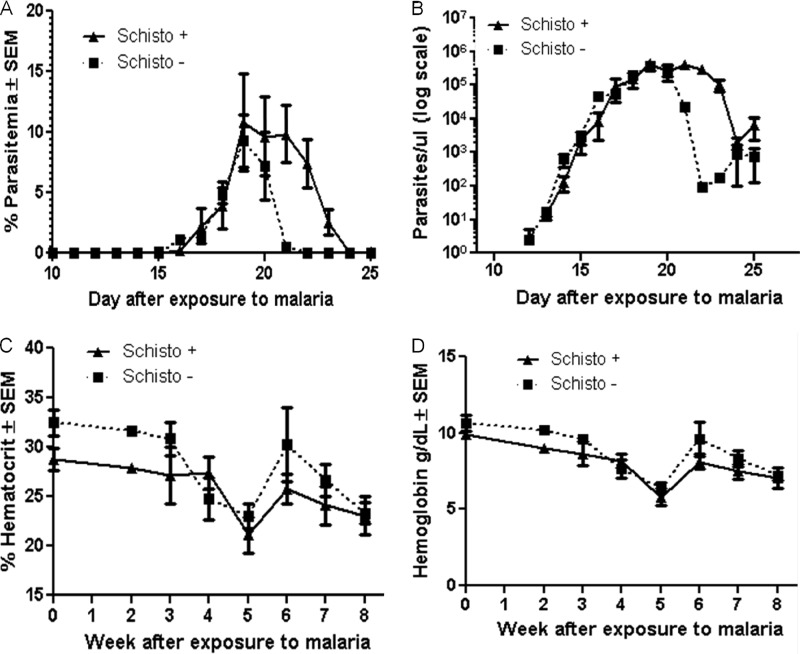
Fig 1.
Clinical responses in coinfected and malaria-only-infected macaques infected by sporozoite challenge. (A) Parasitemia was calculated as the number of P. coatneyi-infected red blood cells per the total number of uninfected red blood cells. Macaques were treated on days 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, and 22 with subcurative doses of quinine. Parasitemia is shown here from day 10 to day 25 after malaria exposure and is graphed on a linear scale. The difference between parasitemia of the coinfected and malaria-only-infected macaques was found to be significant (P < 0.0001; ■, malaria only or schistosomiasis negative; ▲, coinfected or schistosomiasis positive). (B) Parasites per microliter were defined as the total number of parasites present per microliter of blood, and these values from day 10 to day 25 after malaria exposure were graphed on a log scale. The difference between the curves was significant (P < 0.0001). (C) Hematocrit values were determined weekly after malaria exposure and graphed here on a linear scale. Hematocrit values between the coinfected and malaria-only-infected macaques were significantly different (P = 0.025). (D) Hemoglobin levels were also determined for the same time period as the hematocrit values, and these numbers are shown in grams per deciliter and graphed on a linear scale. The difference in hemoglobin levels was also determined to be significantly different (P = 0.027).
We defined severe anemia as a hematocrit value (or packed-cell volume) below 20%. Complete blood cell counts were obtained every week during the course of the infections, with the exception of the first week after malaria exposure. Over the course of the malaria infection, the average hematocrit value for the coinfected macaques was significantly lower than that for the malaria-only-infected macaques (P = 0.025; Fig. 1C). Although the average group hematocrit values did not fall below 20%, individual macaques did at times experience hematocrit values of <20%. Hemoglobin levels were also significantly lower in coinfected macaques (P = 0.027; Fig. 1D). These data indicate that S. mansoni infection exacerbates concomitant P. coatneyi-associated parasitemia and anemia of rhesus macaques infected by the bites of malaria-positive mosquitos.
P. coatneyi-specific antibody responses (IgG and IgM) are altered in concurrently infected macaques.
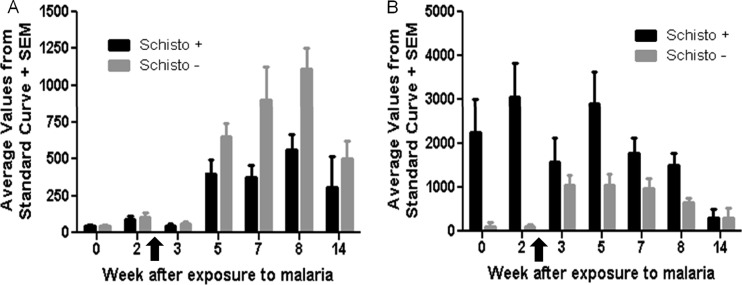
Malaria-specific antibody responses were analyzed over the course of the infection for both groups of macaques. At 8 weeks after malaria exposure, macaques were given curative doses of antimalarial drugs. A final blood sample was obtained at 14 weeks after exposure to malaria (i.e., 6 weeks after malaria cure). Plasma levels of IgG antibody against P. coatneyi crude antigen were significantly reduced in coinfected macaques in comparison to the malaria-only-infected macaques over the course of the infection (P = 0.01; Fig. 2A). Additionally, IgG antibody levels remained higher for malaria-only-infected macaques 6 weeks after malaria infection was cured. In contrast, plasma levels of IgM antibody against the same P. coatneyi crude antigen were significantly increased in coinfected macaques (P = 0.01; Fig. 2B); however, by 6 weeks after malaria cure, the IgM antibody levels were similar for both coinfected macaques and malaria-only-infected macaques.
Fig 2.
Antibody responses (IgG and IgM) to malaria antigen during a sporozoite infection. Plasma was collected at 0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, and 14 weeks after malaria exposure. Malaria was cured at week 8 after malaria exposure, and so week 14 corresponds to 6 weeks after malaria cure. The antibody values were determined from a standard curve using P. coatneyi immune plasma. The arrows indicate when drug treatment was started (day 17). (A) Malaria-specific IgG antibody responses were determined using P. coatneyi crude antigen. IgG responses for coinfected macaques are displayed by the black bars and those for malaria-only-infected macaques are displayed by the gray bars. The IgG responses for coinfected macaques are significantly lower than those of the malaria-only-infected macaques (P = 0.01). (B) Malaria-specific IgM responses were also determined using a P. coatneyi crude antigen, and IgM responses for coinfected macaques are displayed in black and those for malaria-only macaques are in gray. The IgM responses are significantly different, with malaria-only-infected macaques having significantly lower IgM responses (P = 0.01).
Malaria parasitemia and hematocrit levels are not significantly different for macaques infected by blood-stage inoculation.
We next evaluated if the route of infection with P. coatneyi influenced whether schistosomiasis affected malaria progression. Rather than exposing macaques to the bites of infected mosquitos, schistosome-positive and previously uninfected animals were intravenously injected with 50,000 blood-stage parasites. Similar to the parasitemia levels for macaques infected by sporozoite challenge, parasitemia increased rapidly 10 days after malaria infection. Macaques were treated with subcurative doses of quinine beginning on the following (11th) day. Unlike the difference that was observed in macaques infected by sporozoite challenge, macaques infected by blood-stage inoculation showed no statistically significant differences in parasitemia between the malaria-only-infected and coinfected macaques (P = 0.38; Fig. 3A). Moreover, the parasitemia curves for the blood-stage inoculation were very similar between the two groups, especially when comparing the total number of parasites (P = 0.39; Fig. 3B). The average amount of antimalaria drug administered was 112.5 mg/day for coinfected macaques and 93.75 mg/day for malaria-only-infected macaques over a 6-day period.
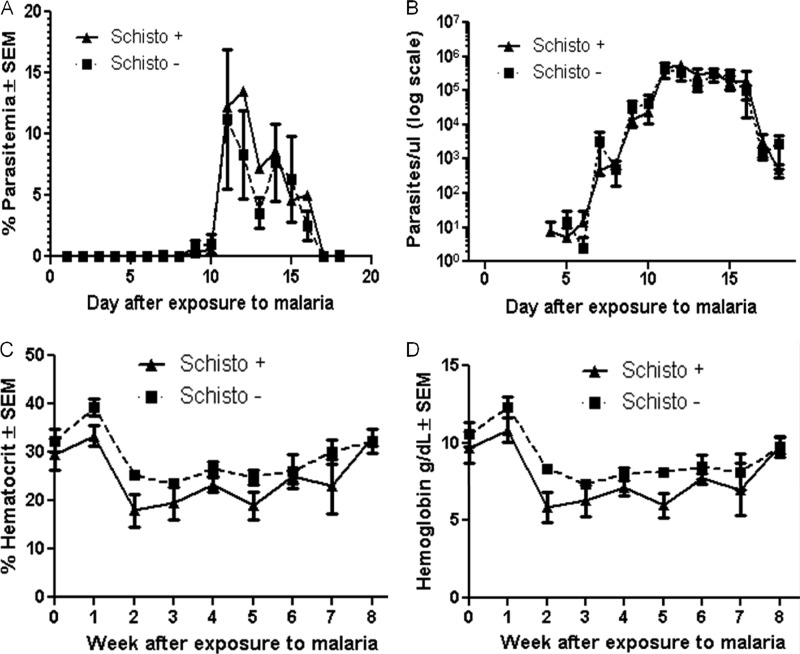
Fig 3.
Parasitemia in malaria blood-stage inoculated macaques. (A) Parasitemia was defined as number of P. coatneyi-infected red blood cells per the total number of uninfected red blood cells. Macaques were treated on days 11, 12, 13, and 15 after exposure to malaria. Parasitemia from day 1 to day 15 is graphed on a linear scale for both coinfected and malaria-only-infected macaques (■, malaria-only or schistosomiasis negative; ▲, coinfected or schistosomiasis positive). Parasitemia is not significantly different between the two groups of macaques (P = 0.38). (B) Parasites per microliter were defined as the total number of parasites in a microliter of blood; this was graphed from day 4 to day 15 on a log scale. The values were not significantly different between the groups (P = 0.39). (C) Hematocrit was determined weekly after exposure to malaria until malaria cure; there is no significant difference between coinfected and malaria-only-infected macaques (P = 0.16). (D) Hemoglobin values (in grams per deciliter) were determined for the same time period as the hematocrit, and there is no significant difference between the groups (P = 0.17).
Severe anemia was again defined as packed-cell volume or hematocrit values below 20%. In comparison to the sporozoite challenge experiments, the average hematocrit values fell below 20% several times for the coinfected macaques infected by blood-stage parasites. In addition, the average hematocrit values for the malaria-only-infected macaques were on average lower than the values for the malaria-only-infected macaques infected through sporozoite challenge. Despite the lower average values in this experiment, the hematocrit and hemoglobin levels between the coinfected and the malaria-only-infected macaques were not significantly different in the experiment where macaques were infected by injection of blood-stage parasites (P = 0.16 and 0.17; Fig. 3C and D, respectively).
Antibody responses (IgG and IgM) in both groups of macaques are similar over the course of blood-stage malaria infection.
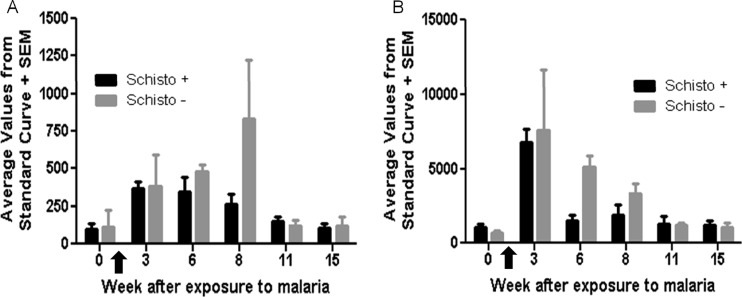
Curative doses of antimalaria drugs were administered 7 weeks after malaria infection. P. coatneyi-specific antibody responses were examined over the course of the infection in the monkeys infected by blood-stage malaria parasites as had been done for monkeys infected by exposure to patent mosquitoes. Plasma IgG antibody levels against P. coatneyi crude antigen were not significantly different between the coinfected and malaria-only-infected macaques (P = 0.34; Fig. 4A). IgM antibody levels were also not significantly different between the groups (P = 0.23; Fig. 4B). The similarities in both IgG and IgM antibodies are in contrast to the significant differences observed for macaques that were infected with malaria by sporozoite challenge.
Fig 4.
P. coatneyi antigen-specific immunoglobulin responses (IgG and IgM) in blood-stage-exposed macaques. Plasma was collected at weeks 0, 3, 6, 8, 11, and 15 after exposure to malaria. Malaria infection was cured at week 7 postexposure. Malaria-specific antibody responses were determined using P. coatneyi crude antigen. The unknown values were determined by assigning units based from a standard curve of P. coatneyi immune sera. The arrows indicate the time when drug treatment was started (day 11). Over the course of the infection, IgG responses (A) and IgM responses (B) to malaria antigen were not significantly different (P = 0.34 and P = 0.23) between the coinfected (black bars) and malaria-only-infected macaques (gray bars).
Comparison of schistosome parasite load between mosquito-borne and blood-stage malaria infection.
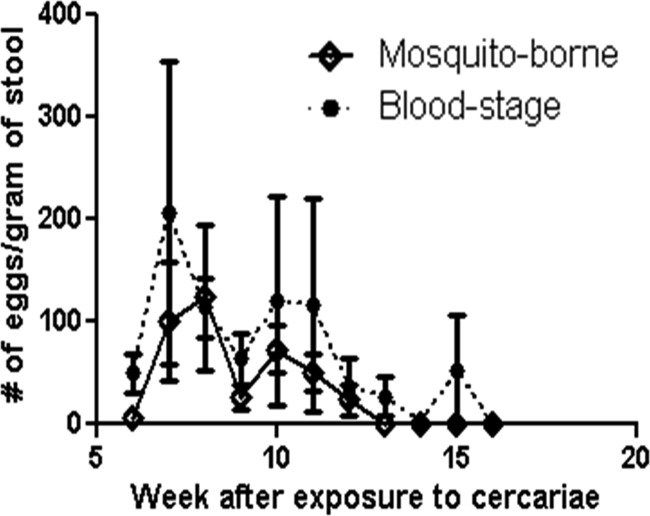
The differences in the effect of schistosome infection on the parasitology, immunology, and pathology of malaria between the two routes of exposure may be due to the route of infection but may also be due to a difference in the schistosome infection. For comparison of the schistosome infections between the sporozoite and blood-stage inoculation, we analyzed the parasite load by comparing the eggs per gram of stool. The average parasite load in both experiments was examined over the course of the schistosome infection until egg counts returned to zero for a minimum of two consecutive weeks. The intensity of the schistosome infections was not significantly different in the two studies (P = 0.20; Fig. 5).
Fig 5.
Schistosome parasite load for sporozoite and blood-stage malaria infection. Egg counts were determined microscopically from processed stool samples collected weekly until egg counts reach zero for a minimum of two consecutive weeks. The graph shows the average number of eggs per gram of stool determined for the four macaques that were exposed to malaria through mosquito bites (◆) and the average number of eggs per gram of stool determined for the four macaques exposed to malaria through blood-stage parasites (●). The difference between schistosome parasite load of the two groups over the course of the schistosomiasis infection is not statistically significant (P = 0.20).
Plasma cytokine levels.
Plasma samples were obtained from the malaria-only and coinfection groups at baseline and various time points following infection. In both the mosquito transmission and blood-stage infection experiments, the coinfected macaque monkeys tended to have higher levels of plasma cytokines than the monkeys infected with malaria alone. However, there was no clear Th1/Th2/Th17 shift pattern between the groups, and any differences between the groups were always higher in the coinfected macaques. Because of the small number of animals per group, the high frequency of plasma cytokine levels below the level of detection of the assay, and the unidirectional aspect of all differential responses, we concluded that plasma cytokine level variances in these experiments were not meaningful.
DISCUSSION
Although there has been a recent surge in the number of research studies investigating polyparasitism, it has been a topic of interest for several decades. In 1978, Buck et al. examined the global epidemiology of polyparasitism, with a focus on the frequency of different combinations of parasites (3), the effects of harboring multiple parasites on accurate diagnosis of infection (4), and the influence of polyparasitism on general health status (5). Recent studies into multiple parasitic infections have expanded on these concepts and have delved into topics such as differential immunologic responses. For example, Hartgers and Yazdanbakhsh recently reviewed immunologic studies on helminth and malaria coinfections in animal models and in humans that highlighted the need to better understand the consequences of malaria and helminth coinfections, especially in terms of their influence on efficacy of potential malaria vaccines (9).
We have demonstrated that S. mansoni infection of rhesus macaques exacerbates concomitant mosquito-borne P. coatneyi infections by worsening parasitemia, decreasing hematocrit levels, and suppressing malaria-specific antibody responses. In contrast, malaria infections initiated by inoculation with blood-stage parasites were not affected by the presence of schistosomes. Our use of a rhesus macaque model in a controlled setting has provided clues to the sometimes disparate results observed in human schistosome-malaria coinfection studies. P. coatneyi is the malaria species of old world monkeys that most closely models human infections with P. falciparum, which does not infect macaques (8). Both P. coatneyi and P. falciparum have knobs and express variant antigens. They both cause severe pathology with hyperparasitemia and deep vascular sequestration in similar organs of their respective hosts. Differences between these species are limited to morphology and development of gametocytes, which were not evaluated in this study.
Our findings corroborate previous studies in mice demonstrating that S. mansoni infection triggered a higher mean Plasmodium yoelii parasitemia, leading to greater mortality in coinfected animals than in mice infected with P. yoelii alone (20). Mice with concomitant P. chabaudi-S. mansoni infections also had higher parasitemias than mice singly infected with P. chabaudi (10). Other studies demonstrated that children infected with S. mansoni are more likely to harbor P. falciparum parasites than children who do not have schistosomiasis (27). Our study, along with others (10, 13, 14, 20, 24, 27), suggests that S. mansoni can decrease host immune responses to malaria parasites and/or the ability to clear infections following antimalarial treatment.
Malarial anemia is an important component of complicated malaria and often leads to deaths, especially in children and in pregnant women (1, 6). Anemia is also a pathological consequence of schistosomiasis (12, 22). We analyzed hematocrit and hemoglobin values over the course of the mosquito-borne malaria transmission experiments to determine if there was an increase in anemia in coinfected macaques. Not surprisingly, the monkeys that demonstrated prolonged malaria parasitemia as a result of coinfection had significantly lower hematocrit and hemoglobin levels than the malaria-only-infected macaques (Fig. 1C and D). Similar results were observed in P. yoelii-S. mansoni-coinfected mice in comparison to mice infected with malaria alone (20). These findings suggest that malaria-schistosomiasis coinfections can exacerbate anemia.
Malaria-specific antibody responses are important for the clearance of blood-stage parasites (7, 16). In coinfected macaques that had higher parasitemia levels for longer time periods than their malaria-only-infected counterparts, the IgG-specific responses to P. coatneyi crude antigen were lower (Fig. 2A). In contrast, the coinfected macaques with higher malaria parasitemias had much higher IgM antibody levels than malaria-only-infected macaques (Fig. 2B). These results suggest that the diminished malaria-specific IgG responses in mosquito-transmitted infections were due to an inability to class switch from IgM to the more effective IgG antibodies rather than an inability of the coinfected macaques to produce any antibodies in response to malaria infection.
In contrast to the parasitological, immunological, and pathological differences observed between coinfected macaques and malaria-infected macaques infected by sporozoite challenge, macaques infected by blood stage parasites did not show any differences in parasitemia (Fig. 3A and B), hematocrit (Fig. 3C), or malaria-specific antibody responses (Fig. 4A and B). The difference in results between the two studies is likely associated with the route of malaria infection rather than differences in the schistosome infections between experiments (Fig. 5). During S. mansoni infections, deposition of schistosome eggs occurs in the liver, which creates a strong T-helper 2 microenvironment. Malaria parasites pass through the liver when the infection is initiated by the bite of an infected mosquito but not when macaques are injected with blood-stage parasites. We hypothesize that the passage of the malaria parasites through the liver with a local Th2 environment during a sporozoite infection may be the cause of the difference in the immunologic and clinical responses to malaria between the two experimental designs. If true, our results may also at least partially explain some of the differences observed in studies of human malaria coinfection with S. mansoni and with S. haematobium. Because S. haematobium eggs are primarily deposited in the urogenital tract of infected humans, the liver environment through which sporozoites pass is less likely to have a strong Th2 shift, and immune responses to parasite antigens may not be as influenced by their schistosome infection. However, a great deal of additional research is necessary to evaluate this possibility and further investigate the impact of different schistosome species on malaria infection, immunology, and pathology.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by an appointment to the Emerging Infectious Diseases Fellowship Program (A.A.S.) administered by the Association of Public Health Laboratories (APHL) and funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
We thank Doug Nace, Tyrone Williams, Pete Augostini, and Brianna Skinner for their technical assistance.
The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 20 August 2012
REFERENCES
- 1. Barnwell JW. 2006. Malaria: death and disappearing erythrocytes. Blood 107:854–855 [Google Scholar]
- 2. Briand V, Watier L, Le Hesran JY, Garcia A, Cot M. 2005. Coinfection with Plasmodium falciparum and Schistosoma haematobium: protective effect of schistosomiasis on malaria in Senegalese children? Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 72:702–707 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Buck AA, Anderson RI, MacRae AA. 1978. Epidemiology of poly-parasitism. II. Types of combinations, relative frequency and associations of multiple infections. Tropenmed. Parasitol. 29:137–144 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Buck AA, Anderson RI, MacRae AA. 1978. Epidemiology of poly-parasitism. III. Effects on the diagnostic capacity of immunological tests. Tropenmed. Parasitol. 29:145–155 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Buck AA, Anderson RI, MacRae AA. 1978. Epidemiology of poly-parasitism. IV. Combined effects on the state of health. Tropenmed. Parasitol. 29:253–268 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Casals-Pascual C, Roberts DJ. 2006. Severe malarial anaemia. Curr. Mol. Med. 6:155–168 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Cohen S, McGregor IA, Carrington S. 1961. Gamma-globulin and acquired immunity to human malaria. Nature 192:733–737 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Craig AG, et al. 2012. The role of animal models for research on severe malaria. PLoS Pathog. 8:e1002401 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Hartgers FC, Yazdanbakhsh M. 2006. Co-infection of helminths and malaria: modulation of the immune responses to malaria. Parasite Immunol. 28:497–506 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Helmby H, Kullberg M, Troye-Blomberg M. 1998. Altered immune responses in mice with concomitant Schistosoma mansoni and Plasmodium chabaudi infections. Infect. Immun. 66:5167–5174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Keusch GT, Migasena P. 1982. Biological implications of polyparasitism. Rev. Infect. Dis. 4:880–882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. King CH, Dangerfield-Cha M. 2008. The unacknowledged impact of chronic schistosomiasis. Chronic Illn. 4:65–79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Laranjeiras RF, Brant LC, Lima AC, Coelho PM, Braga EM. 2008. Reduced protective effect of Plasmodium berghei immunization by concurrent Schistosoma mansoni infection. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 103:674–677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Legesse M, Erko B, Balcha F. 2004. Increased parasitaemia and delayed parasite clearance in Schistosoma mansoni and Plasmodium berghei co-infected mice. Acta Trop. 91:161–166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Lyke KE, et al. 2005. Association of Schistosoma haematobium infection with protection against acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Malian children. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 73:1124–1130 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. McGregor IA. 1964. The passive transfer of human malarial immunity. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 13:237–239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Nookala S, Srinivasan S, Kaliraj P, Narayanan RB, Nutman TB. 2004. Impairment of tetanus-specific cellular and humoral responses following tetanus vaccination in human lymphatic filariasis. Infect. Immun. 72:2598–2604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Reilly L, Magkrioti C, Mduluza T, Cavanagh DR, Mutapi F. 2008. Effect of treating Schistosoma haematobium infection on Plasmodium falciparum-specific antibody responses. BMC Infect. Dis. 8:158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Sabin EA, Araujo MI, Carvalho EM, Pearce EJ. 1996. Impairment of tetanus toxoid-specific Th1-like immune responses in humans infected with Schistosoma mansoni. J. Infect. Dis. 173:269–272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Sangweme D, Shiff C, Kumar N. 2009. Plasmodium yoelii: adverse outcome of non-lethal P. yoelii malaria during co-infection with Schistosoma mansoni in BALB/c mouse model. Exp. Parasitol. 122:254–259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Sangweme DT, et al. 2010. Impact of schistosome infection on Plasmodium falciparum malariometric indices and immune correlates in school age children in Burma Valley, Zimbabwe. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 4:e882 doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000882 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Secor WE. 2005. Immunology of human schistosomiasis: off the beaten path. Parasite Immunol. 27:309–316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Snow RW, Guerra CA, Noor AM, Myint HY, Hay SI. 2005. The global distribution of clinical episodes of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature 434:214–217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Sokhna C, et al. 2004. Increase of malaria attacks among children presenting concomitant infection by Schistosoma mansoni in Senegal. Malar. J. 3:43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Steinmann P, Keiser J, Bos R, Tanner M, Utzinger J. 2006. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect. Dis. 6:411–425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Supali T, et al. 2010. Polyparasitism and its impact on the immune system. Int. J. Parasitol. 40:1171–1176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Verani JR, et al. 2011. Schistosomiasis among young children in Usoma, Kenya. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 84:787–791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. WHO 2010. World health report. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland [Google Scholar]
- 29. Wilson S, Vennervald BJ, Dunne DW. 2011. Chronic hepatosplenomegaly in African school children: a common but neglected morbidity associated with schistosomiasis and malaria. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 5:e1149 doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Wilson S, et al. 2010. Health implications of chronic hepatosplenomegaly in Kenyan school-aged children chronically exposed to malarial infections and Schistosoma mansoni. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 104:110–116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]