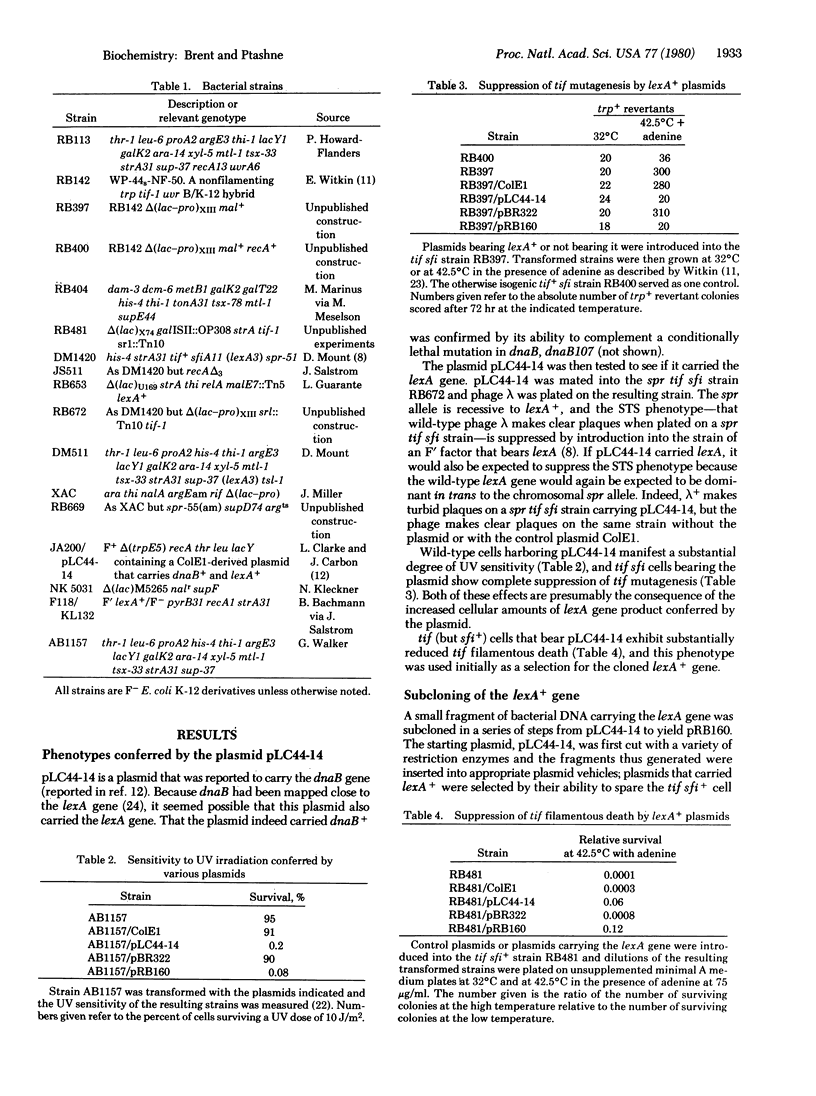
Abstract
The products of the lexA and recA genes of Escherichia coli regulate the cellular response to DNA damage (the SOS response). Here we describe the cloning of the wild-type lexA gene and the identification of its 24,000-dalton protein product. We also describe construction, by recombination in vitro, of a phage that bears the lexA promoter fused to the lacZ gene. Experiments with this fusion phage and with multicopy plasmids that carry the lexA gene showed that the lexA gene product represses of its own promoter. This repression occurs even if the cell has no recA gene, showing that the lexA protein need not be complexed to the recA protein for activity. Moreover, the presence of multicopy plasmids that carry the lexA gene blocks expression of all SOS responses tested. This presumably results from two effects: (i) repression of the recA gene, the product of which is required to activate many of these responses; and (ii) direct repression of other functions involved in the SOS response.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backman K., Ptashne M., Gilbert W. Construction of plasmids carrying the cI gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4174–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Betlach M. C., Boyer H. W. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. I. Ampicillin-resistant derivatives of the plasmid pMB9. Gene. 1977;2(2):75–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Recombination deficient mutants of E. coli and other bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:67–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoret R. Inducible error-prone repair: one of the cellular responses to DNA damage. Biochimie. 1978;60(10):1135–1140. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(79)80347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J., Castellazzi M., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. III. Mutations sfiA and sfiB restore division in tif and lon strains and permit the expression of mutator properties of tif. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Oct 22;140(4):309–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A. Effect of tsl mutations on Col E1 expression in a recA strain of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):775–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.775-776.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C. K. Induction of colicin production by high temperature or inhibition of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):10–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.10-19.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby E. P., Jacob F., Goldthwait D. A. Prophage induction and filament formation in a mutant strain of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1903–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Roth J., Botstein D. Genetic engineering in vivo using translocatable drug-resistance elements. New methods in bacterial genetics. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):125–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Harper J. E. Identification of the lexA gene product of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K. Protein X is the product of the recA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5275–5279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer B. J., Kleid D. G., Ptashne M. Lambda repressor turns off transcription of its own gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4785–4789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W. A mutant of Escherichia coli showing constitutive expression of the lysogenic induction and error-prone DNA repair pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):300–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Kosel C. K., Walker A. Inducible, error-free DNA Repair in tsl recA mutants of E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 5;146(1):37–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00267980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Walker A. C., Kosel C. Effect of tsl mutations in decreasing radiation sensitivity of a recA- strain of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1203–1207. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1203-1207.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp H. J., Szybalski W., Ohashi M., Dove W. F. Gene expression by constitutive mutants of coliphage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(1):80–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00268749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacelli L. Z., Edmiston S. H., Mount D. W. Isolation and characterization of amber mutations in the lexA gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):568–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.568-573.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Backman K., Humayun M. Z., Jeffrey A., Maurer R., Meyer B., Sauer R. T. Autoregulation and function of a repressor in bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):156–161. doi: 10.1126/science.959843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W., Craig N. L., Phizicky E. M. Activity of the Escherichia coli recA-gene product. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):917–920. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Kacich R., Ptashne M. A general method for maximizing the expression of a cloned gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):760–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessman E. S., Gritzmacher C. A., Peterson P. K. Derepression of colicin E1 synthesis in the constitutive tif mutant strain (spr tif sfi) and in a tif sfi mutant strain of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):29–38. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.29-38.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Plasmid (pKM101)-mediated enhancement of repair and mutagenesis: dependence on chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 28;152(1):93–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00264945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. G., Young K. Y., Edlin G. J., Konigsberg W. High-frequency generalised transduction by bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):80–82. doi: 10.1038/280080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Persistence and decay of thermoinducible error-prone repair activity in nonfilamentous derivatives of tif-1, Escherichia coli B/r: the timing of some critical events in ultraviolet mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 29;142(2):87–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00266092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Thermal enhancement of ultraviolet mutability in a tif-1 uvrA derivative of Escherichia coli B-r: evidence that ultraviolet mutagenesis depends upon an inducible function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]