Abstract
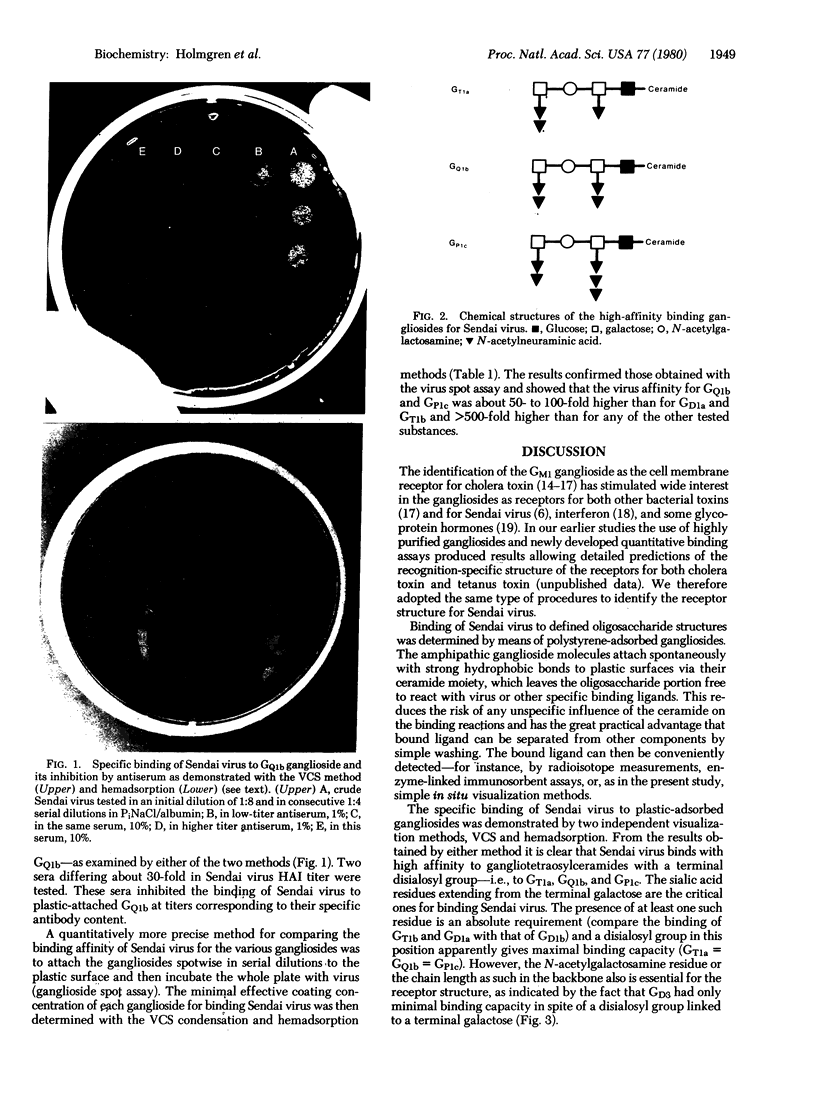
The binding of Sendai virus to polystyrene petri dishes to which various gangliosides of defined structures had been adsorbed was determined. The ganglioside-bound virus was visualized either by a water vapor condensation method or by a hemadsorption method. By either assay, specific virus binding of high affinity was demonstrated to the gangliosides GT1a, GQ1b, and GPlc which have a common end sequence in the oligosaccharide moiety: NeuAc alpha 2 leads to 8NeuAc alpha 2 leads to 3Gal beta 1 leads to 3GalNAc leads to. Binding also occurred to the GD1a and GT1b gangliosides, which have the same end carbohydrate sequence except for the terminal N-acetylneuraminic acid, but the affinity was only 1-9% of that of the gangliosides with a terminal disialosyl linkage. It is proposed that the structure NeuAc alpha 2 leads to 8NeuAc alpha 2 leads to 3Gal beta 1 leads to 3GalNAc is the recognition-specific structure of the receptor for Sendai virus that is present on cell membrane gangliosides and possibly also glycoproteins. Binding tests to plastic-adsorbed glycolipids are suggested to be a useful tool for identification of the receptor recognition structure.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elwing H., Nilsson L. A., Ouchterlony O. A simple spot technique for thin layer immunoassays (TIA) on plastic surfaces. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(1-2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwing H., Nilsson L., Ouchterlony O. Visualization principles in thin-layer immunoassays (TIA) on plastic surfaces. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;51(6):757–762. doi: 10.1159/000231654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood A. M. Characteristics of Sendai virus receptors in a model membrane. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90504-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Svennerholm L. Tissue receptor for cholera exotoxin: postulated structure from studies with GM1 ganglioside and related glycolipids. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):208–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.208-214.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Lee L. T. Virus-erythrocyte interactions. Adv Virus Res. 1972;17:1–50. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60746-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. A., Van Heyningen W. E. Deactivation of cholera toxin by a sialidase-resistant monosialosylganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):639–647. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansson J. E., Vanier M. T., Svennerholm L. Changes in the fatty acid and sphingosine composition of the major gangliosides of human brain with age. J Neurochem. 1978 Jan;30(1):273–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin B. R., Fishman P. H., Lee G., Aloj S. M., Ledley F. D., Winand R. J., Kohn L. D., Brady R. O. Thyrotropin-ganglioside interactions and their relationship to the structure and function of thyrotropin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):842–846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Sadler J. E., Hill R. L. Restoration of specific myxovirus receptors to asialoerythrocytes by incorporation of sialic acid with pure sialyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2120–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rearick J. I., Sadler J. E., Paulson J. C., Hill R. L. Enzymatic characterization of beta D-galactoside alpha2 leads to 3 sialyltransferase from porcine submaxillary gland. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4444–4451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm L., Fredman P. A procedure for the quantitative isolation of brain gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 18;617(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm L., Vanier M. T., Månsson J. E. Krabbe disease: a galactosylsphingosine (psychosine) lipidosis. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jan;21(1):53–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vengris V. E., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Hollenberg M. D., Pitha P. M. Interferon action: role of membrane gangliosides. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):486–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





