Abstract
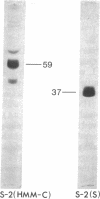
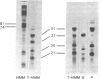
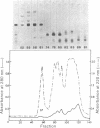
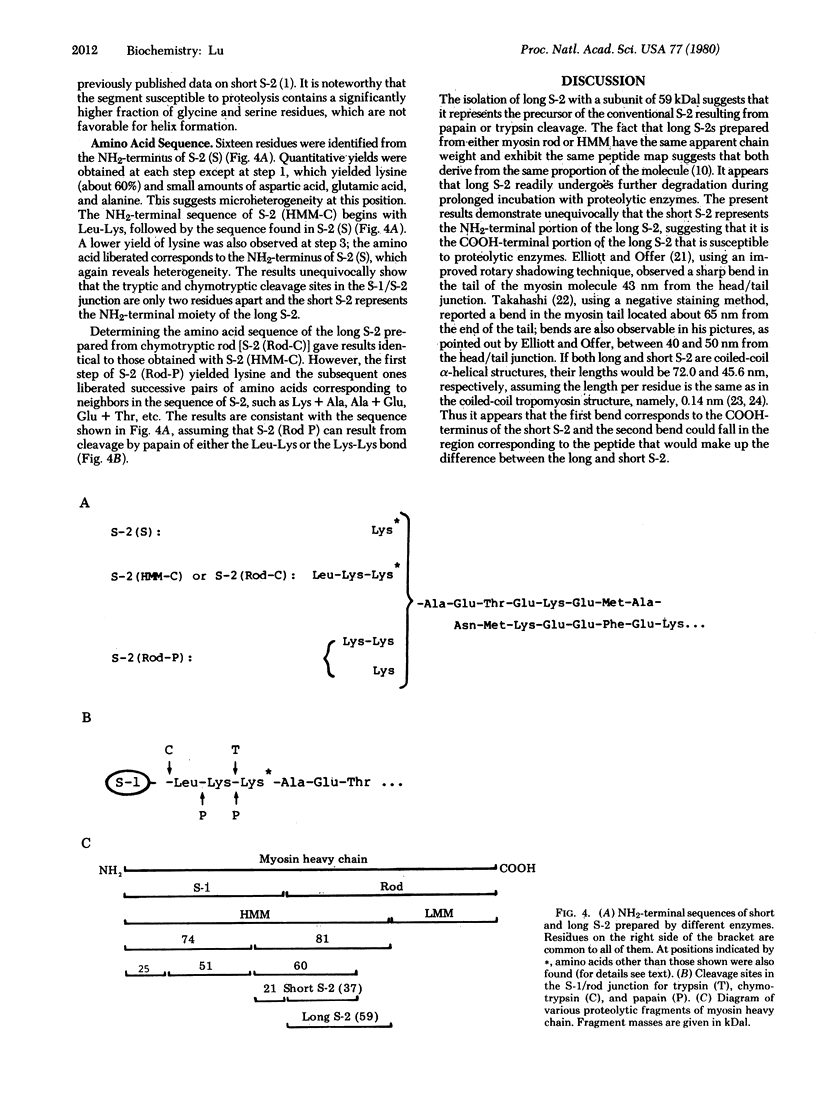
Comparison of the NH2-terminal sequence of myosin short subfragment-2 (Mr of subunit = 37,000) and long subfragment-2 (Mr of subunit = 59,000) demonstrates that the former represents the NH2-terminal portion of the latter and suggests that the hinge region in myosin rod is in the COOH-terminal portion of the long subfragment-2.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bálint M., Sréter F. A., Gergely J. Fragmentation of myosin by papain--studies on myosin from adult fast and slow skeletal and cardiac, and embryonic muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):557–566. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bálint M., Sréter F. A., Wolf I., Nagy B., Gergely J. The substructure of heavy meromyosin. The effect of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on the tryptic fragmentation of heavy meromyosin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6168–6177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Caspar D. L., Parry D. A., Lucas R. M. Tropomyosin crystal dynamics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:205–216. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott A., Offer G. Shape and flexibility of the myosin molecule. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):505–519. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington W. F. A mechanochemical mechanism for muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):685–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S., Kretzschmar K. M., O'Konski C. T., Morales M. F. Flexibility of myosin rod, light meromyosin, and myosin subfragment-2 in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4986–4990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Brown W. The low-angle x-ray diagram of vertebrate striated muscle and its behaviour during contraction and rigor. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):383–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayasi S., Totsuka T. Electric birefringence of myosin subfragments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 17;376(2):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen R. A. Solid-phase Edman degradation. An automatic peptide sequencer. Eur J Biochem. 1971 May 11;20(1):89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson R. A., Morales M. F., Botts J. Segmental flexibility of the S-1 moiety of myosin. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2250–2255. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nihel T., Mendelson R. A., Botts J. The site of force generation in muscle contraction as deduced from fluorescence polarization studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):274–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe F. A. The myosin filament. I. Structural organization from antibody staining observed in electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 28;27(2):203–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Offer G. Polarity of the myosin molecule. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 25;81(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K., Sutoh K., Karr T., Harrington W. F. Isolation and physico-chemical properties of a high molecular weight subfragment-2 of myosin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K. Topography of the myosin molecule as visualized by an improved negative staining method. J Biochem. 1978 Mar;83(3):905–908. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Seidel J. C., Hyde J. S., Gergely J. Motion of subfragment-1 in myosin and its supramolecular complexes: saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1729–1733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Pope B. Studies on the chymotryptic digestion of myosin. Effects of divalent cations on proteolytic susceptibility. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):129–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]