Abstract
A slow reacting substance produced by rat basophilic leukemia cells, treated with ionophore A23187, was characterized by spectroscopic methods, enzymatic conversions, and chemical degradations as 5-hydroxy-6-S-cysteinylglycyl 7,9,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid (leukotriene D). gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase [gamma-glutamyltransferase; (5-glutamyl)-peptide: amino-acid 5-glutamyltransferase, EC 2.3.2.2] converted leukotriene C to a product identical to leukotriene D. This suggests that the stereochemistry of the arachidonyl moiety of leukotrienes C and D is the same [5(S)-6(R)-7,9-trans-11,14-cis]. Leukotriene D induces a faster contraction and, on a molar basis, is more potent than leukotriene C in the isolated guinea pig ileum bioassay.
Full text
PDF
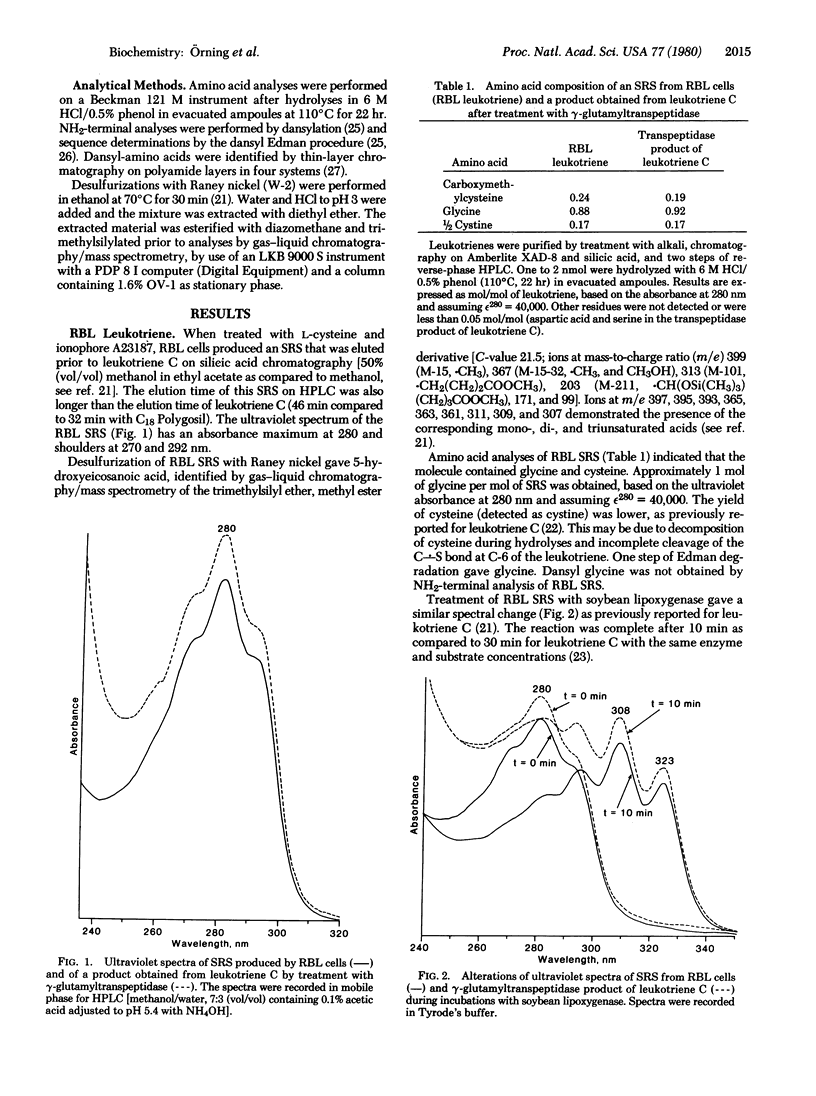
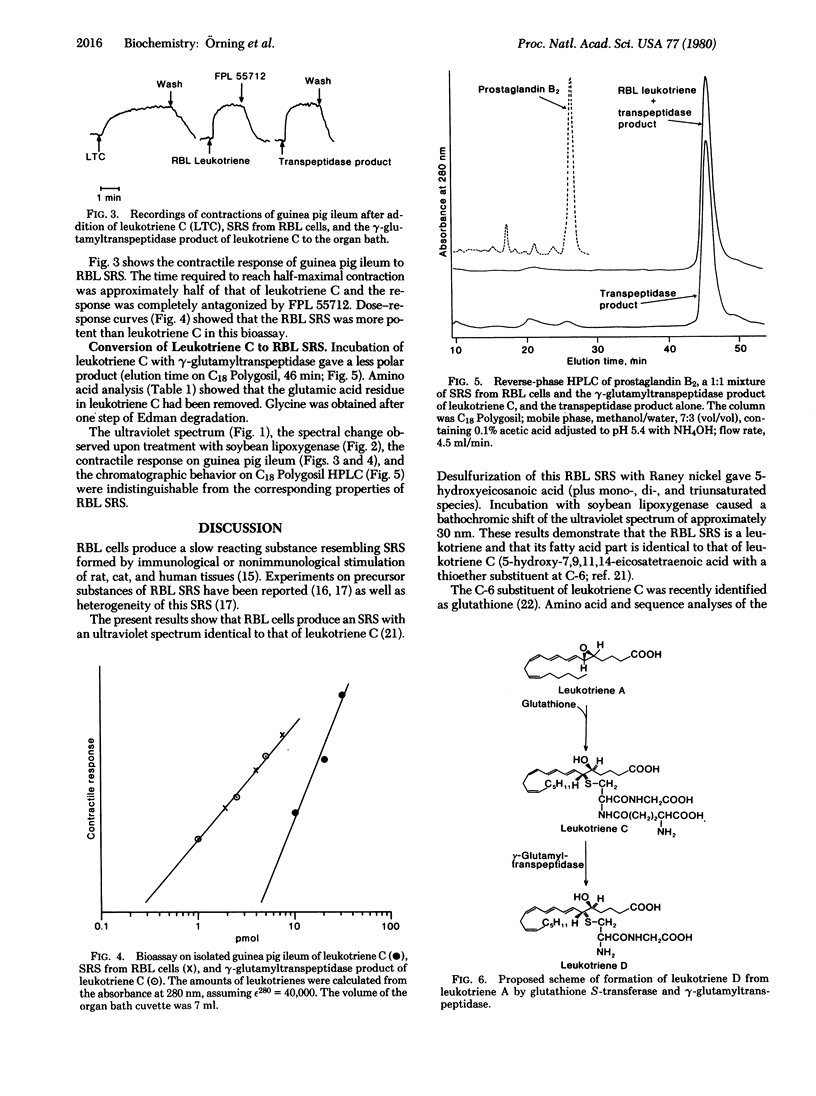

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austen K. F. Homeostasis of effector systems which can also be recruited for immunologic reactions. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):793–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKLEHURST W. E. The release of histamine and formation of a slow-reacting substance (SRS-A) during anaphylactic shock. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:416–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R., Brooks C. D., Neerken A. J. Slow reacting substances: comparison of some properties of human lung SRS-A and two distinct fractions from ionophore-induced rat mononuclear cell SRS. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):160–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R. In vivo and in vitro production of a slow reacting substance in the rat upon treatment with calcium ionophores. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):2040–2044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Arachidonic acid metabolism in polymorphonuclear leukocytes: unstable intermediate in formation of dihydroxy acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conroy M. C., Orange R. P., Lichtenstein L. M. Release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) from human leukocytes by the calcium ionophore A23187. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1677–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Kellaway C. H. Liberation of histamine and formation of lysocithin-like substances by cobra venom. J Physiol. 1938 Nov 14;94(2):187–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY W. R., HARTLEY B. S. THE STRUCTURE OF A CHYMOTRYPTIC PEPTIDE FROM PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:379–380. doi: 10.1042/bj0890379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant J. A., Lichtenstein L. M. Release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis from human leukocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):897–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Murphy R. C., Samuelsson B., Clark D. A., Mioskowski C., Corey E. J. Structure of leukotriene C. Identification of the amino acid part. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 28;91(4):1266–1272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Samuelsson B., Clark D. A., Goto G., Marfat A., Mioskowski C., Corey E. J. Stereochemistry of leukotriene C-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):946–953. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90794-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Orange R. P., Austen K. F. The capacity of human immunoglobulin E to mediate the release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) from monkey lung. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Tomioka H. Release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) by IgE-anti-IgE reactions on monkey mast cells. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):513–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakschik B. A., Falkenhein S., Parker C. W. Precursor role of arachidonic acid in release of slow reacting substance from rat basophilic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4577–4581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakschik B. A., Kulczycki A., Jr, MacDonald H. H., Parker C. W. Release of slow reacting substance (SRS) from rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-1) cells. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):618–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H. Horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase. The primary structure of an N-terminal part of the protein chain of the ethanol-active isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jul;14(3):521–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Taylor G. W., Piper P. J., Sirois P., Tippins J. R. Slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis: purification and characterisation. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 15;87(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80332-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. C., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene C: a slow-reacting substance from murine mastocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Austen K. F. Slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis. Adv Immunol. 1969;10:105–144. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60416-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Chang P. L. The effect of thiols on immunologic release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis. I. Human lung. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1072–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Murphy R. C., Karnovsky M. L., Austen K. F. The physicochemical characteristics and purification of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):760–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. W., Jakschik B. A., Huber M. G., Falkenhein S. F. Characterization of slow reacting substance as a family of thiolipids derived from arachidonic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 28;89(4):1186–1192. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rådmark O., Malmsten C., Samuelsson B., Clark D. A., Goto G., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Leukotriene A: stereochemistry and enzymatic conversion to leukotriene B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):954–961. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90795-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Borgeat P., Hammarström S., Murphy R. C. Introduction of a nomenclature: leukotrienes. Prostaglandins. 1979 Jun;17(6):785–787. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(79)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Borgeat P., Hammarström S., Murphy R. C. Leukotrienes: a new group of biologically active compounds. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1980;6:1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F., Bloch K. J. Antibodies involved in antigen-induced release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) in the guinea pig and rat. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):127–147. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg K., Uvnäs B. Purification and properties of the slow reacting substance formed in the cat paw perfused with compound 48-80. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Jul;82(3):358–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UVNAS B. Lipid spasmogens appearing in connection with histamine liberation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Apr;12:439–443. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



