Abstract
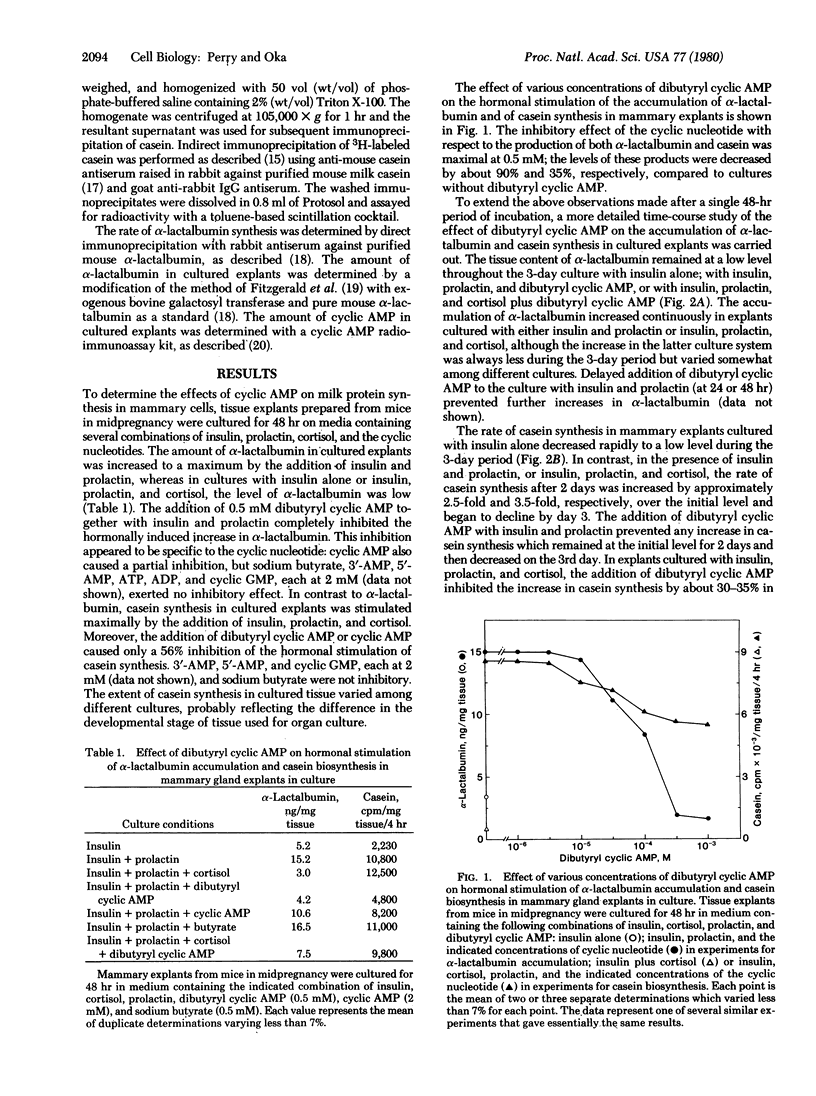
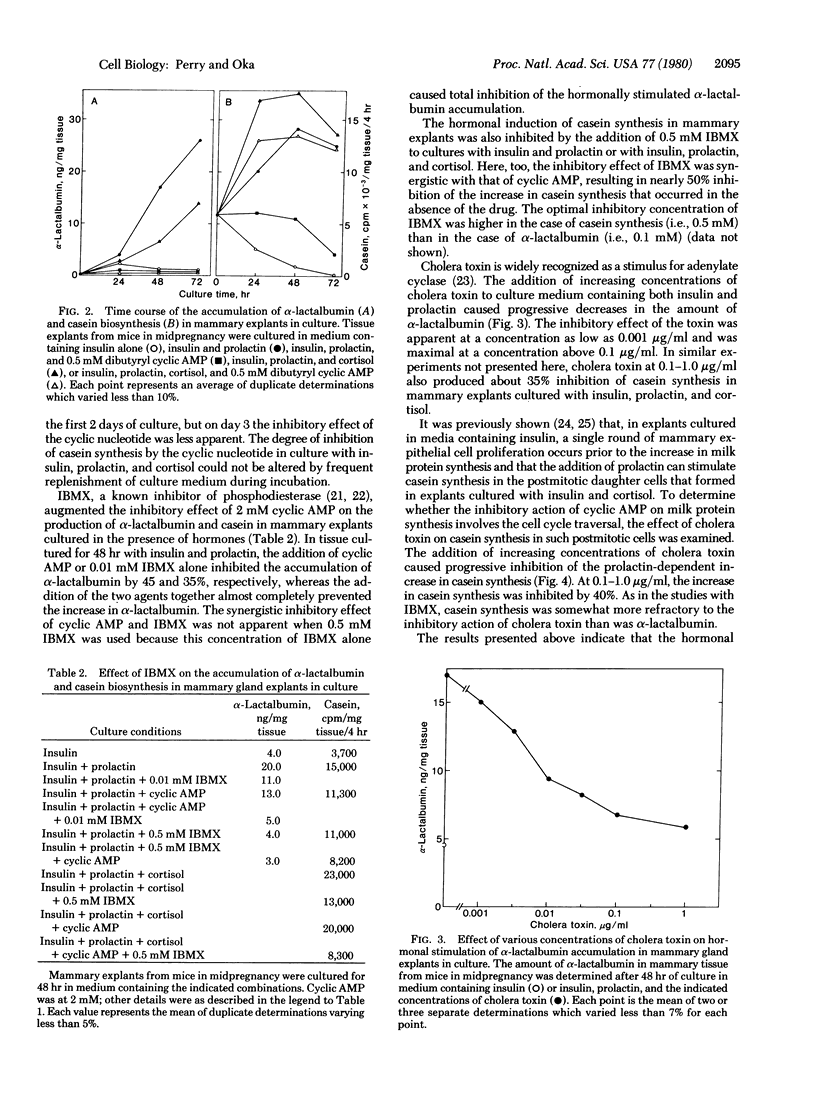
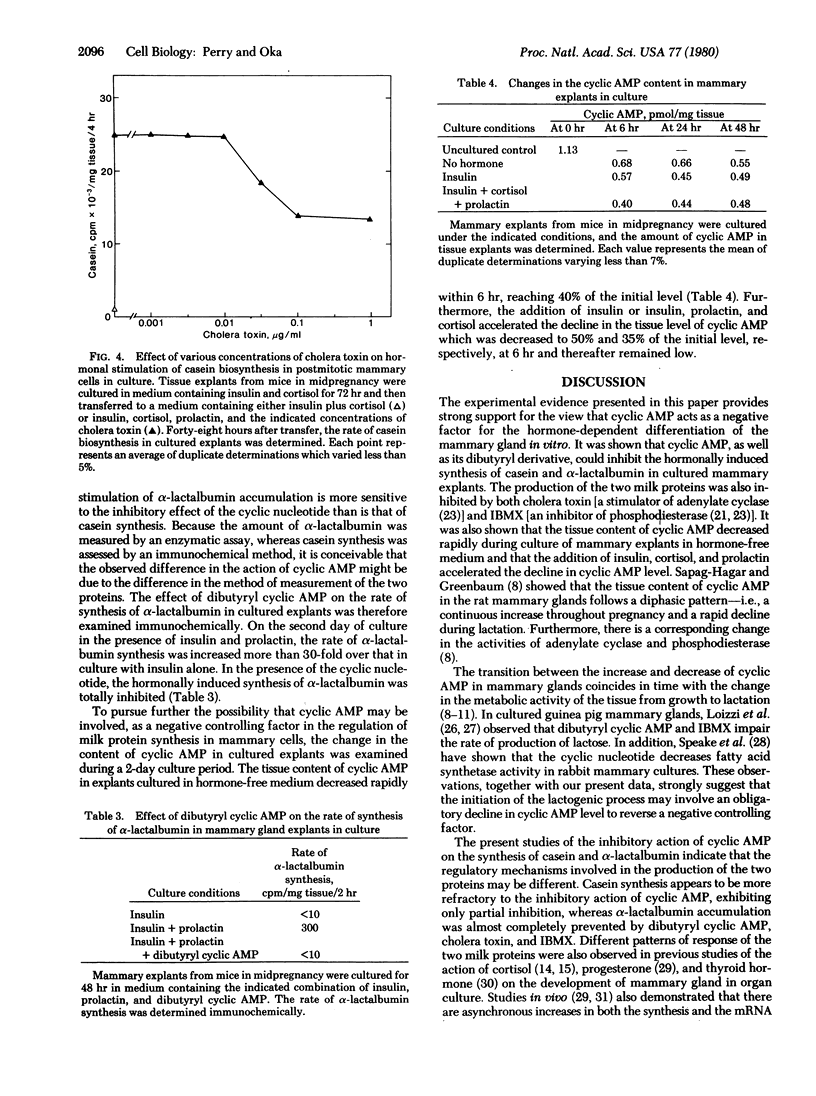
In organ cultures of mammary glands from mice in midpregnancy, addition of both insulin and prolactin induces a marked accumulation of alpha-lactalbumin, whereas the augmentation of casein synthesis requires the presence of insulin, prolactin, and cortisol. Addition of 0.5 mM dibutyryl cyclic AMP resulted in complete inhibition of alpha-lactalbumin accumulation and partial inhibition of casein synthesis. Furthermore, either cholera toxin at 0.1-1.0 microgram/ml (a stimulator of adenylate cyclase) or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase) in combination with 2 mM cyclic AMP, produced a similar pattern of inhibition of alpha-lactalbumin and casein synthesis in cultured tissue. During culture of mammary explants in medium containing no hormone, or insulin alone, or insulin, prolactin, and cortisol, the tissue content of cyclic AMP decreased rapidly, reaching half the initial level in 24-48 hr. These results indicate that cyclic AMP plays "negative" regulatory function in hormonal induction of milk protein synthesis during the development of the mammary gland.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abell C. W., Monahan T. M. The role of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate in the regulation of mammalian cell division. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):549–558. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee M. R. Responses of mammary cells to hormones. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;47:1–97. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Rogers N. L., Crofford O. B., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W., Newman E. V. Effects of xanthine derivatives on lipolysis and on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;6(6):597–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald D. K., Colvin B., Mawal R., Ebner K. E. Enzymic assay for galactosyl transferase activity of lactose synthetase and alpha-lactalbumin in purified and crude systems. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jul;36(1):43–61. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg S. H., Oka T., Topper Y. J. Development of insulin-sensitivity by mouse mammary gland in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1493–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Pastewka J. V. Characterization of major milk proteins from BALB/c and C3H mice. J Dairy Sci. 1976 Feb;59(2):207–215. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(76)84186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Possible role for cyclic nucleotides and phosphorylated membrane proteins in postsynaptic actions of neurotransmitters. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):101–108. doi: 10.1038/260101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizzi R. F. Cylic AMP inhibition of mammary gland lactose synthesis: specificity and potentiation by 1-methyl-3-isobutylxanthine. Horm Metab Res. 1978 Sep;10(5):415–419. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizzi R. F., de Pont J. J., Bonting S. L. Inhibition by cyclic AMP of lactose production in lactating guinea pig mammary gland slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 5;392(1):20–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis S. L., Baldwin R. L. Changes in the cyclic 3', 5'-adenosine monophosphate system of rat mammary gland during lactation cycle. J Dairy Sci. 1975 Jun;58(6):861–869. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(75)84650-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder G. C., Turkington R. W. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent and -independent protein phosphokinase isoenzymes from mammary gland. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2650–2657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder G. C., Turkington R. W. Hormonal regulation of protein kinases and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-binding protein in developing mammary gland. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5545–5554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. T., Greenwald G. S. Progesterone and oestradiol-17beta concentrations in the peripheral plasma during pregnancy in the mouse. J Endocrinol. 1974 Jul;62(1):101–107. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0620101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Cook J. R. The role of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in the regulation of insulin release by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):115–120. doi: 10.1042/bj1220115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamatsu Y., Oka T. Purification and characterization of mouse alpha-lactalbumin and preparation of its antibody. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):227–237. doi: 10.1042/bj1850227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Perry J. W., Kano K. Hormonal regulation of spermidine synthase during the development of mouse mammary epithelium in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Perry J. W. Studies on regulatory factors of ornithine decarboxylase activity during development of mouse mammary epithelium in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1738–1744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Topper Y. J. Hormone-dependent accumulation of rough endoplasmic reticulum in mouse mammary epithelial cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7701–7707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Oka T. The differential actions of cortisol on the accumulation of alpha-lactalbumin and casein in midpregnant mouse mammary gland in culture. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90522-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Oka T. alpha-Lactalbumin-casein induction in virgin mouse mammary explants: dose-dependent differential action of cortisol. Science. 1980 Mar 21;207(4437):1367–1369. doi: 10.1126/science.6986657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. L. Regulation of gene transcription in Escherichia coli by cyclic AMP. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;1:11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rillema J. A. Cyclic nucleotides, adenylate cyclase, and cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in mammary glands from pregnant and lactating mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Apr;151(4):748–751. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W. Cyclic AMP. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:149–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Lundgren D. W., Oka T. Polyamine biosynthesis and DNA synthesis in cultured mammary gland explants from virgin mice. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Jun;95(3):259–267. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040950303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapag-Hagar M., Greenbaum A. L. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and hormone interrelationships in the mammary gland of the rat during pregnancy and lactation. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):303–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapag-Hagar M., Greenbaum A. L. Changes of the activities of adenyl cyclase and cAMP-phosphodiesterase and of the level of 3'5' cyclic adenosine monophosphate in rat mammary gland during pregnancy and lactation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):982–987. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapag-Hagar M., Greenbaum A. L. The role of cyclic nucleotides in the development and function of rat mammary tissue. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 15;46(1):180–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80363-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speake B. K., Dils R., Mayer R. J. Regulation of enzyme turnover during tissue differentiation. Interactions of insulin, prolactin and cortisol in controlling the turnover of fatty acid synthetase in rabbit mammary gland in organ culture. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):359–370. doi: 10.1042/bj1540359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper R. J., Oka T., Vonderhaar B. K. Techniques for studying development of normal mammary epithelial cells in organ culture. Methods Enzymol. 1975;39:443–454. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)39039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper Y. J. Multiple hormone interactions in the development of mammary gland in vitro. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:287–308. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W., Brew K., Vanaman T. C., Hill R. L. The hormonal control of lactose synthetase in the developing mouse mammary gland. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3382–3387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W., Hill R. L. Lactose synthetase: progesterone inhibition of the induction of alpha-lactalbumin. Science. 1969 Mar 28;163(3874):1458–1460. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3874.1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W., Lockwood D. H., Topper Y. J. The induction of milk protein synthesis in post-mitotic mammary epithelial cells exposed to prolactin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):475–480. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan M., Moss J. Mechanism of action of choleragen. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(4):473–488. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderhaar B. K. A role of thyroid hormones in differentiation of mouse mammary gland in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):1219–1225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90803-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderhaar B. K., Topper Y. J. A role of the cell cycle in hormone-dependent differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):707–712. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Brostrom C. O., Brostrom M. A., Chen L., Corbin J. D., Reimann E., Soderling T. R., Krebs E. G. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases from skeletal muscle and liver. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;1:33–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


