Abstract
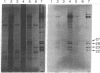
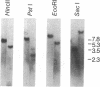
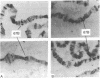
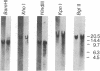
Two plasmids containing cDNA inserts complementary to the messenger RNAs for the 26,000 and 23,000 molecular weight heat-shock-induced proteins from Drosophila melanogaster were identified. Both of these probes hybridized to a site of a major heat-shock-induced puff, 67B. Hybridization by the gel transfer technique with genome DNA that had been cleaved by a restriction endonuclease indicated that the two genes are closely linked. This expectation was validated through isolation of a DNA fragment generated by BamHI endonuclease containing genes for the 26,000 and 23,000 molecular weight heat-shock-induced proteins and also a gene encoding the 27,000 molecular weight heat-shock-induced protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., McCarthy B. J. Induction of the Drosophila heat shock response in isolated polytene nuclei. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J., Wadsworth S. C. Sequence organization of two recombinant plasmids containing genes for the major heat shock-induced protein of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):575–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd B. H., Young M. W. An examination of the one cistron: one chromomere concept. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:573–579. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Mapping of late adenovirus genes by cell-free translation of RNA selected by hybridization to specific DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1344–1348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Goldberg M. L., Karp R. W., Hogness D. S. The organization of the histone genes in Drosophila melanogaster: functional and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1047–1051. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macko V., Staples R. C., Gershon H., Renwick J. A. Self-inhibitor of bean rust uredospores: methyl 3,4-dimethoxycinnamate. Science. 1970 Oct 30;170(3957):539–540. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3957.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. L., Meselson M. Translation in vitro of Drosophila heat-shock messages. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 25;117(1):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Moran L., Arrigo A. P., Tissières A. The effect of heat shock on gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):819–827. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson N. S., Moller G., Mitchell H. K. Genetic mapping of the coding regions for three heat-shock proteins in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1979 Jul;92(3):891–902. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A., Pardue M. L., Penman S. Messenger RNA in heat-shocked Drosophila cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 5;109(4):559–587. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissières A., Mitchell H. K., Tracy U. M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]