Abstract
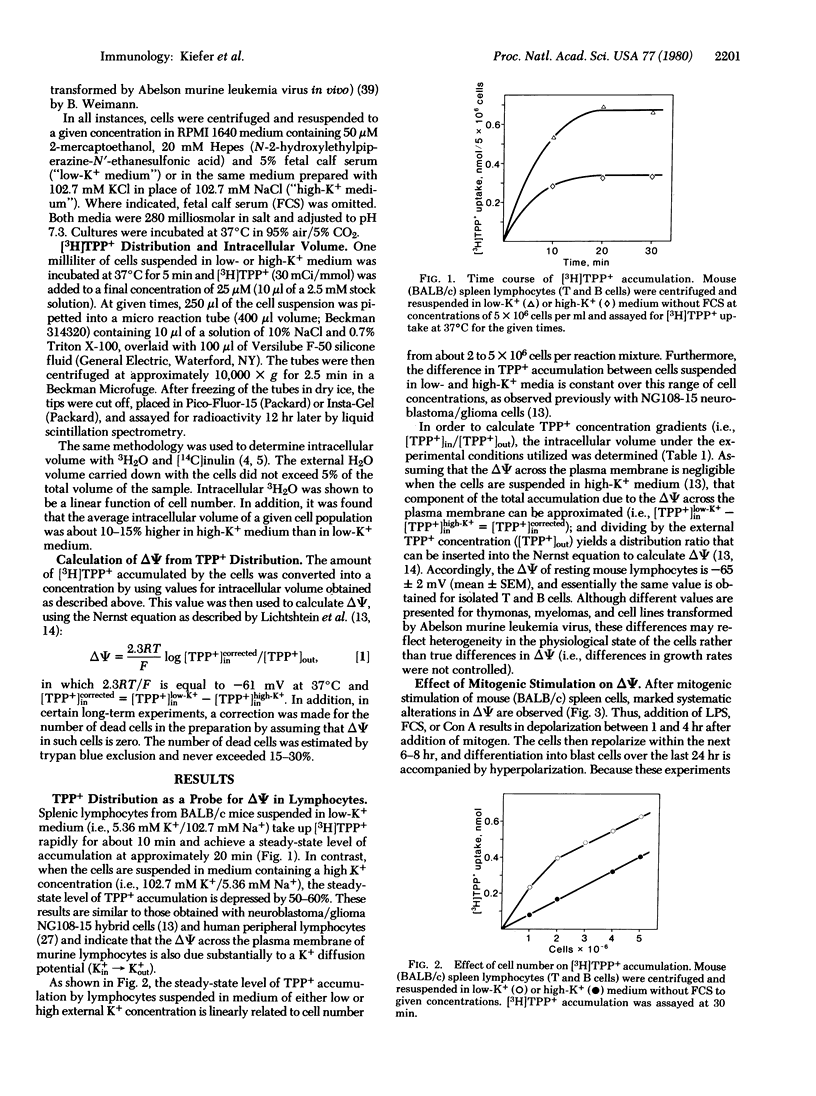
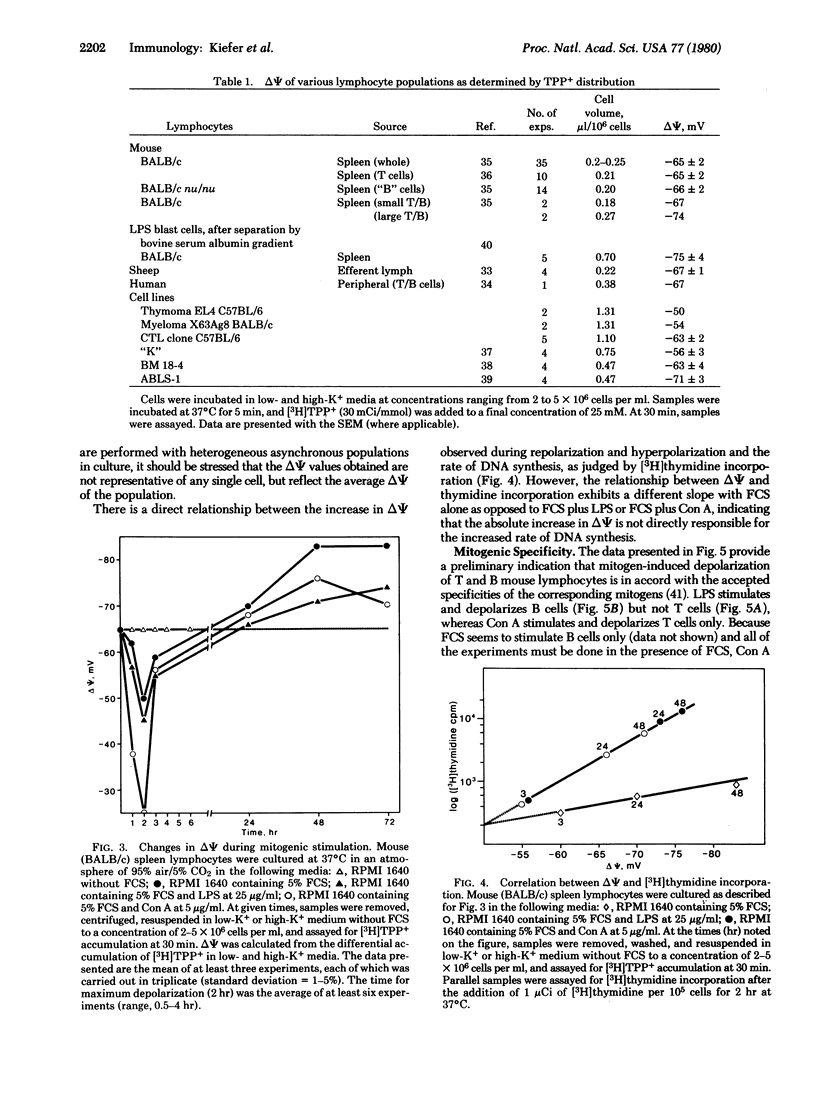
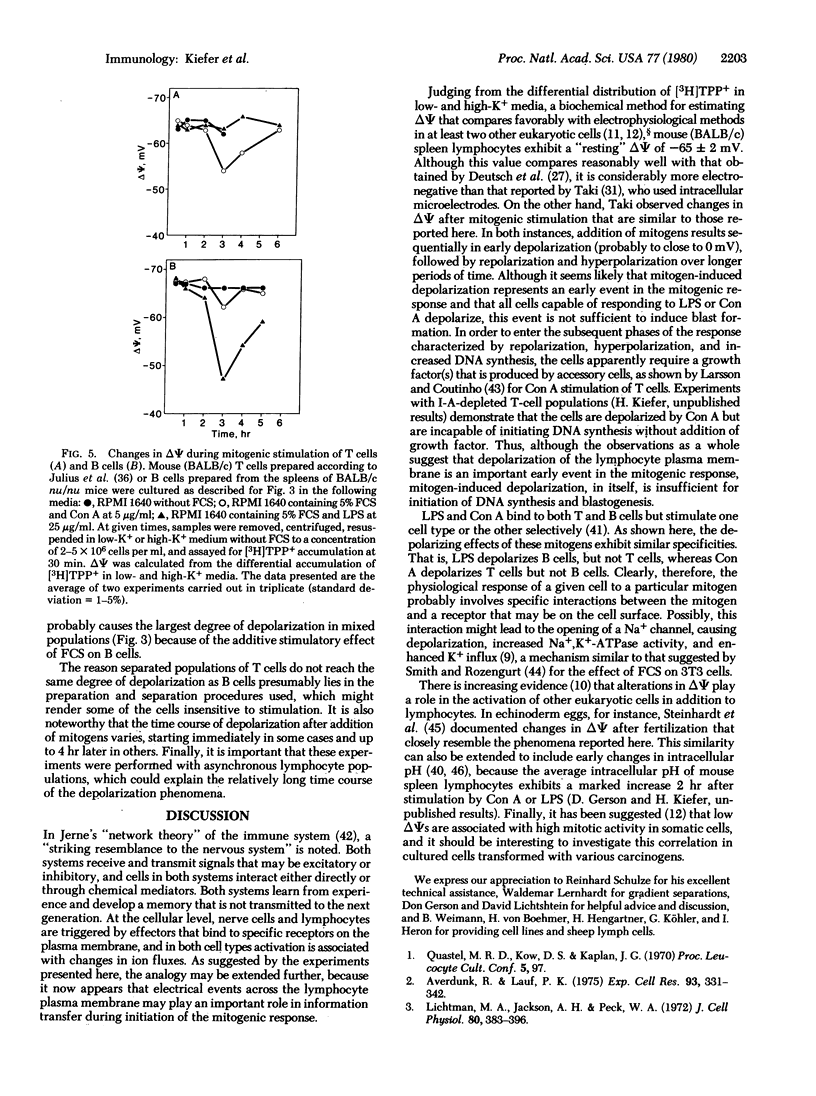
By monitoring differences in accumulation of the lipophilic cation [3H]tetraphenylphosphonium in media containing low or high potassium concentrations [Lichtshtein, D., Kaback, H. R. & Blume, A. J. (1979) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 650-654], the membrane potential of lymphocytes from various sources has been estimated. On the basis of this method, the potential of normal mouse spleen lymphocytes (T and B cells) is -65 ± 2 mV (mean ± SEM, interior negative). During the course of mitogenic stimulation by concanavalin A, lipopolysaccharide, or fetal calf serum, the membrane potential of murine spleen lymphocytes changes systematically according to the following pattern: (i) early depolarization lasting 2-3 hr, (ii) repolarization over the next 7 hr, and (iii) a final hyperpolarization phase during the last 24-48 hr. During repolarization and hyperpolarization, moreover, there is a direct correlation between the membrane potential and DNA synthesis, as judged by [3H]thymidine incorporation. By using isolated T and B cells, it is observed that concanavalin A depolarizes T cells only, whereas lipopolysaccharide depolarizes B cells only. Thus, both mitogens exhibit the same specificity for depolarization as for mitogenic stimulation. On the basis of these observations, it is suggested that the transition of lymphocytes from a resting state to mitotic activity is initiated by depolarization of the plasma membrane.
Keywords: tetraphenylphosphonium, depolarization, hyperpolarization, concanavalin A, lipopolysaccharide
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S., Feldberg S., Nakadomari H., Levy S., McLaughlin S. Electrostatic interactions among hydrophobic ions in lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1978 Jan;21(1):35–70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85507-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averdunk R., Lauf P. K. Effects of mitogens on sodium-potassium transport, 3H-ouabain binding, and adenosine triphosphatase activity in lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Jul;93(2):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90458-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakeeva L. E., Grinius L. L., Jasaitis A. A., Kuliene V. V., Levitsky D. O., Liberman E. A., Severina I. I., Skulachev V. P. Conversion of biomembrane-produced energy into electric form. II. Intact mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone C. D., Jr Unified theory on the basic mechanism of normal mitotic control and oncogenesis. J Theor Biol. 1971 Jan;30(1):151–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniele R. P., Holian S. K. A potassium ionophore (valinomycin) inhibits lymphocyte proliferation by its effects on the cell membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3599–3602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniele R. P., Holian S. K., Nowell P. C. A potassium ionophore (Nigericin) inhibits stimulation of human lymphocytes by mitogens. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):571–581. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cespedes C., Christensen H. N. Complexity in valinomycin effects on amino acid transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch C. J., Holian A., Holian S. K., Daniele R. P., Wilson D. F. Transmembrane electrical and pH gradients across human erythrocytes and human peripheral lymphocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Apr;99(1):79–93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L. L., Jasaitis A. A., Kadziauskas Y. P., Liberman E. A., Skulachev V. P., Topali V. P., Tsofina L. M., Vladimirova M. A. Conversion of biomembrane-produced energy into electric form. I. Submitochondrial particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman E. F., Lee G., Ambesi-Impiombato F. S., Meldolesi M. F., Aloj S. M., Coon H. G., Kaback H. R., Kohn L. D. Effects of thyrotropin on the thyroid cell membrane: hyperpolarization induced by hormone-receptor interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2352–2356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz E., Geck P., Pietrzyk C. Driving forces of amino acid transport in animal cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:428–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Altendorf K., Harold F. M. Role of an electrical potential in the coupling of metabolic energy to active transport by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W. Measurement of membrane potential of chromaffin granules by the accumulation of triphenylmethylphosphonium cation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6703–6709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. Changes in membrane potential of human granulocytes antecede the metabolic responses to surface stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Coutinho A. The role of mitogenic lectins in T-cell triggering. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):239–241. doi: 10.1038/280239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman M. A., Jackson A. H., Peck W. A. Lymphocyte monovalent cation metabolism: cell volume, cation content and cation transport. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Dec;80(3):383–396. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040800309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtshtein D., Dunlop K., Kaback H. R., Blume A. J. Mechanism of monensin-induced hyperpolarization of neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid NG108-15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2580–2584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtshtein D., Kaback H. R., Blume A. J. Use of a lipophilic cation for determination of membrane potential in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cell suspensions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):650–654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F. J., Reeves J. P., Short S. A., Kaback H. R. Evaluation of the chemiosmotic interpretation of active transport in bacterial membrane vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Feb 18;227:312–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Phillips R. A. Separation of cells by velocity sedimentation. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Jun;73(3):191–201. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negendank W. G., Collier C. R. Ion contents of human lymphocytes. The effects of concanavalin A and ouabain. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Aug;101(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90408-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poskitt D. C., Frost H., Cahill R. N., Trnka Z. The appearance of non-specific antibody-forming cells in the efferent lymph draining antigen-stimulated single lymph nodes. Immunology. 1977 Jul;33(1):81–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premkumar E., Potter M., Singer P. A., Sklar M. D. Synthesis, surface deposition, and secretion of immunoglobulins by Abelson virus-transformed lymphosarcoma cell lines. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quastel M. R., Kaplan J. G. Inhibition by ouabain of human lymphocyte transformation induced by phytohaemagglutinin in vitro. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):198–200. doi: 10.1038/219198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Grollman E. F., Lazo P. S., Dyer S. A., Habig W. H., Hardegree M. C., Kaback H. R., Kohn L. D. Effect of tetanus toxin on the accumulation of the permeant lipophilic cation tetraphenylphosphonium by guinea pig brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4783–4787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reenstra W. W., Patel L., Rottenberg H., Kaback H. R. Electrochemical proton gradient in inverted membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 8;19(1):1–9. doi: 10.1021/bi00542a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. A quantitative assay for transformation of bone marrow cells by Abelson murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1453–1463. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H. G., Stambrook P. J., Ebert J. D. Changes in membrane potential during the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Feb;83(2):362–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90350-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. Membrane potential and active transport in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5451–5461. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel G. B., Lichtman M. A. The effect of method on the measurement of K+ concentration in PHA-treated human blood lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Mar 1;112(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Rozengurt E. Serum stimulates the Na+,K+ pump in quiescent fibroblasts by increasing Na+ entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5560–5564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R. A., Lundin L., Mazia D. Bioelectric responses of the echinoderm egg to fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2426–2430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taki M. Studies on blastogenesis of human lymphocytes by phytohemagglutinin, with special reference to changes of membrane potential during blastoid transformation. Mie Med J. 1970 Jan;19(3):245–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truffa-Bachi P., Kaplan J. G., Bona C. The mitogenic effect of lipopolysaccharide. Metabolic processing of lipopolysaccharide by mouse lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1977 Apr;30(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimann B. J. Induction of immunoglobulin synthesis in Abelson murine leukemia virus-transformed mouse lymphoma cells in culture. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 1):163–164. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



