Abstract
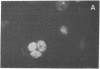
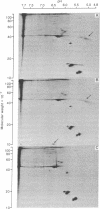
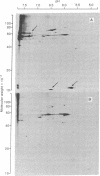
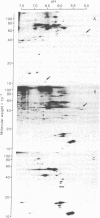
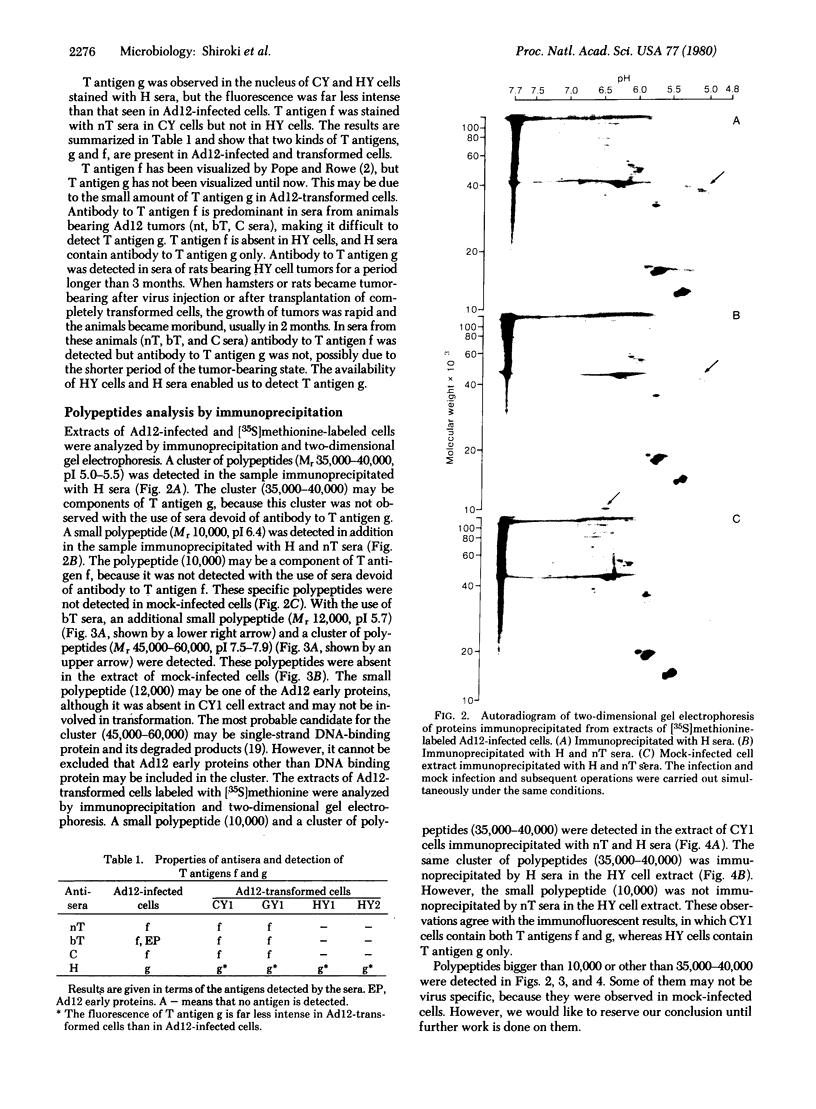
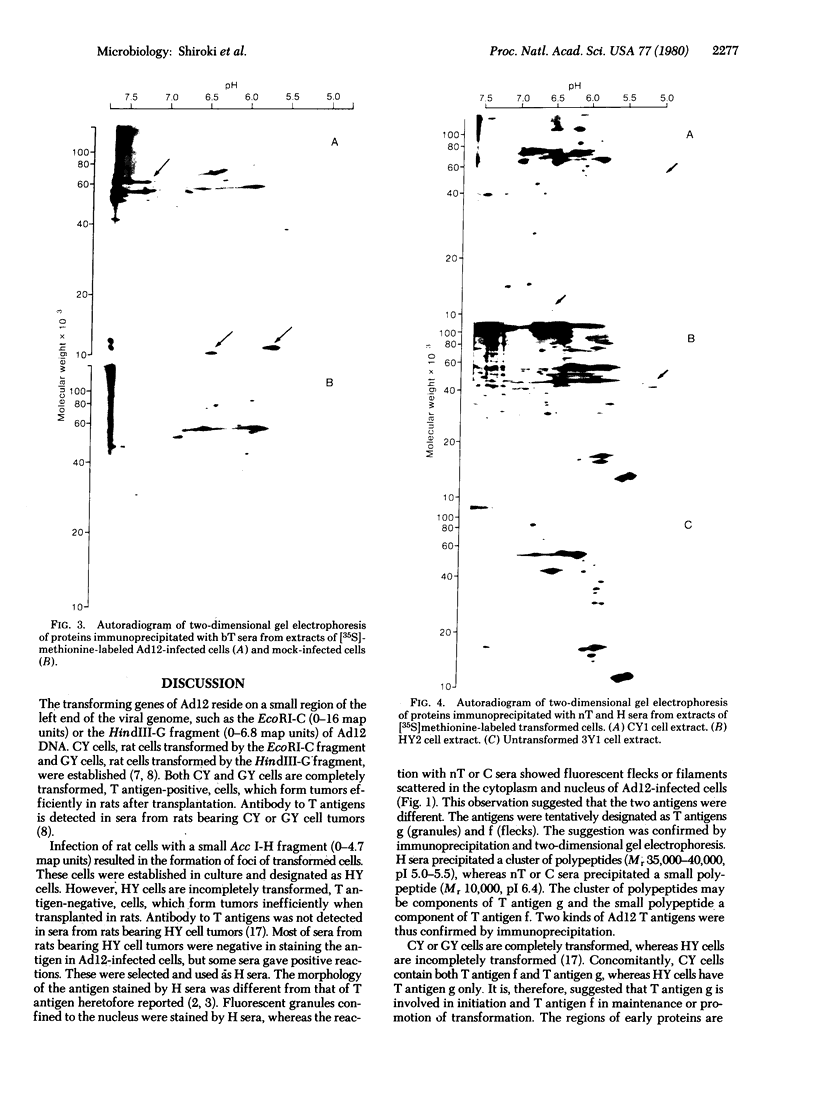
A tumor (T) antigen, designated T antigen g, was visualized as fine fluorescent granules in nuclei of adenovirus type 12 (Ad12)-infected cells by immunofluorescence with sera from rats bearing HY cell tumors (H sera). HY cells are rat cells incompletely transformed by the Acc I-H endonuclease fragment (0-4.7 map units) of Ad12 DNA. The antigen is different from the usually described T antigen, designated T antigen f, which is visualized as fluorescent flecks or filaments in both nucleus and cytoplasm of Ad12-infected cells when tested with narrowly reacting T sera. Extracts of [35S]methioninelabeled infected cells were immunoprecipitated with H sera, and the resultant precipitate was analyzed by the two-dimensional gel electrophoresis technique of O'Farrell. The autoradiogram showed the presence of a cluster of several polypeptides (Mr 35,000-40,000, pI 5.0-5.5) that was absent in extracts of mock-infected cells. A similar autoradiogram of infected cells analyzed with narrowly reacting T sera showed the presence of a small polypeptide (Mr 10,000, pI 6.4), that was absent in extracts of mock-infected cells. The results show that Mr 35,000-40,000 polypeptides are components of T antigen g and a Mr 10,000 polypeptide is a component of T antigen f. Ad12-transformed cells showed a similar result. T antigen g was present and T antigen f was absent in HY cells. Both T antigen g and T antigen f were present in CY cells, which are rat cells completely transformed by the EcoRI-C endonuclease fragment (0-16 map units) of Ad12 DNA. The possible functions of these proteins are discussed.
Keywords: indirect immunofluorescence, immunoprecipitation, transforming gene product
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron K. K., Morrongiello M. P., Rasková J., Raska K., Jr Adenovirus type 12 tumor antigen. I. Separation from DNA polymerase alpha and immunoprecipitation of tumor-antigen polypeptides. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):464–474. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90453-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G., Jeng Y. H., Gilead Z., Green M. Identification of early proteins induced by highly oncogenic human adenovirus 12 during lytic infection and in hamster tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):1199–1205. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91645-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Berget S. M., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus transcription. III. Mapping of viral RNA sequences in cells productively infected by adenovirus type 5. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):443–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Gallimore P. H., Sharp P. A. Comparison of viral RNA sequences in adenovirus 2-transformed and lytically infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):47–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H. Viral DNA in transformed cells. II. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA IN NINE LINES OF TRANSFORMED RAT CELLS USING SPECIFIC FRAGMENTS OF THE VIRAL GENOME;. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilead Z., Jeng Y. H., Wold W. S., Sugawara K., Rho H. M., Harter M. L., Green M. Immunological identification of two adenovirus 2-induced early proteins possibly involved in cell transformation. Nature. 1976 Nov 18;264(5583):263–266. doi: 10.1038/264263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Abrahams P. J., Mulder C., Heijneker H. L., Warnaar S. O., De Vries F. A., Fiers W., Van Der Eb A. J. Studies on in vitro transformation by DNA and DNA fragments of human adenoviruses and simian virus 40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):637–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUEBNER R. J., ROWE W. P., TURNER H. C., LANE W. T. SPECIFIC ADENOVIRUS COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGENS IN VIRUS-FREE HAMSTER AND RAT TUMORS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50:379–389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Lewis J. B. Adenovirus type 2 early proteins synthesized in vitro and in vivo: identification in infected cells of the 38,000- to 50,000- molecular-weight protein encoded by the left end of the adenovirus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):736–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.736-749.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Spurr N., Dulbecco R. Characterization of polyoma virus T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1259–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G., Itagaki A., Summers J. Rat cell line 3y1 and its virogenic polyoma- and sv40- transformed derivatives. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):694–706. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu T., Shiroki K., Shimojo H. Detection of adenovirus 12-induced DNA-binding protein in infected and transformed cells with monkey antisera. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(6):339–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Levine A. J. The group C adenovirus tumor antigens: identification in infected and transformed cells and a peptide map analysis. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):871–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A., Levine A. J. The isolation and identification of the adenovirus group C tumor antigens. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Baum P. R., Solem R., Gesteland R. F., Anderson C. W. Location and identification of the genes for adenovirus type 2 early polypeptides. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortin J., Scheidtmann K. H., Greenberg R., Westphal M., Doerfler W. Transcription of the genome of adenovirus type 12. III. Maps of stable RNA from productively infected human cells and abortively infected and transformed hamster cells. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):355–372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.355-372.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STUDIES OF ADENOVIRUS 12 TUMORS AND OF CELLS TRANSFORMED OR INFECTED BY ADENOVIRUSES. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:577–588. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwirth B., Shiroki K., Levine A. J., Shimojo H. Isolation and characterization of adenovirus type 12 DNA binding proteins. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):14–23. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90399-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekikawa K., Shiroki K., Shimojo H., Ojima S., Fujinaga K. Transformation of a rat cell line by an adenovirus 7 DNA fragment. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Gallimore P. H., Flint S. J. Mapping of adenovirus 2 RNA sequences in lytically infected cells and transformed cell lines. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):457–474. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimojo H., Yamamoto H., Abe C. Differentiation of adenovirus 12 antigens in cultured cells with immunofluorescent analysis. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):748–752. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroki K., Handa H., Shimojo H., Yano S., Ojima S., Fujinaga K. Establishment and characterization of rat cell lines transformed by restriction endonuclease fragments of adenovirus 12 DNA. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):462–471. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroki K., Shimojo H., Sawada Y., Uemizu Y., Fujinaga K. Incomplete transformation of rat cells by a small fragment of adenovirus 12 DNA. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90407-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano S., Ojima S., Fujinaga K., Shiroki K., Shimojo H. Transformation of a rat cell line by an adenovirus type 12 DNA fragment. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]