Abstract
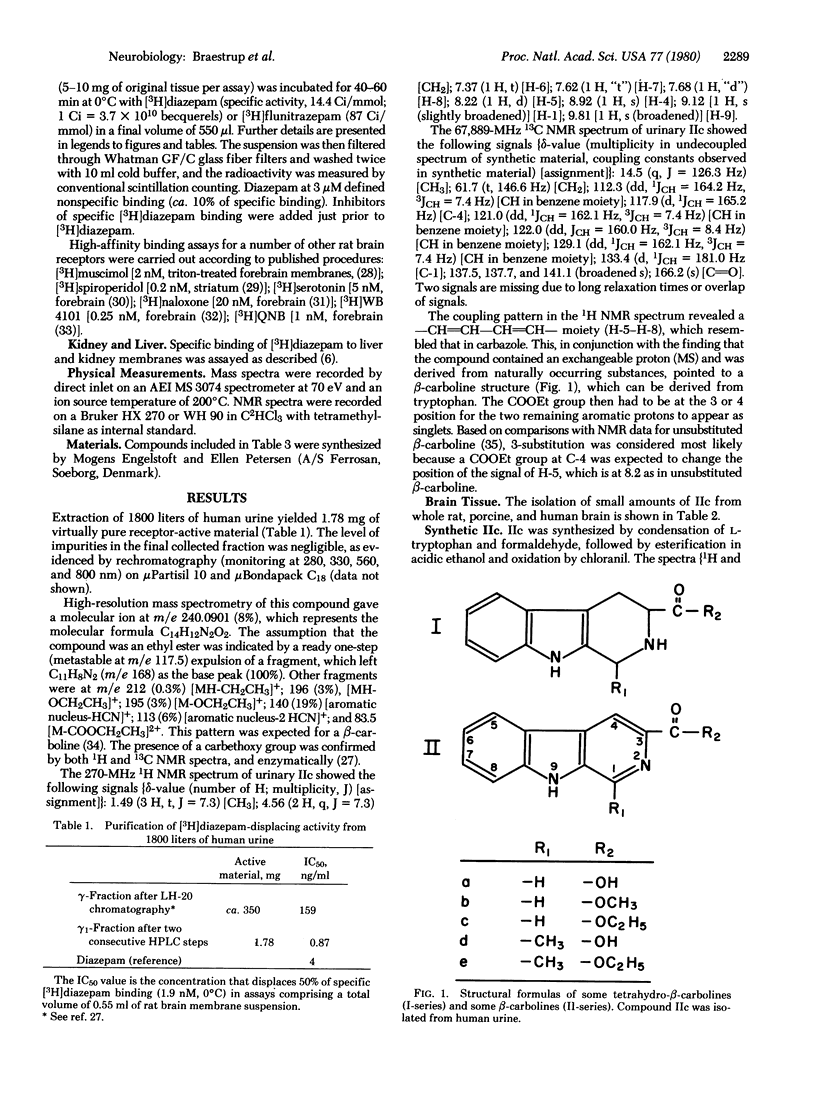
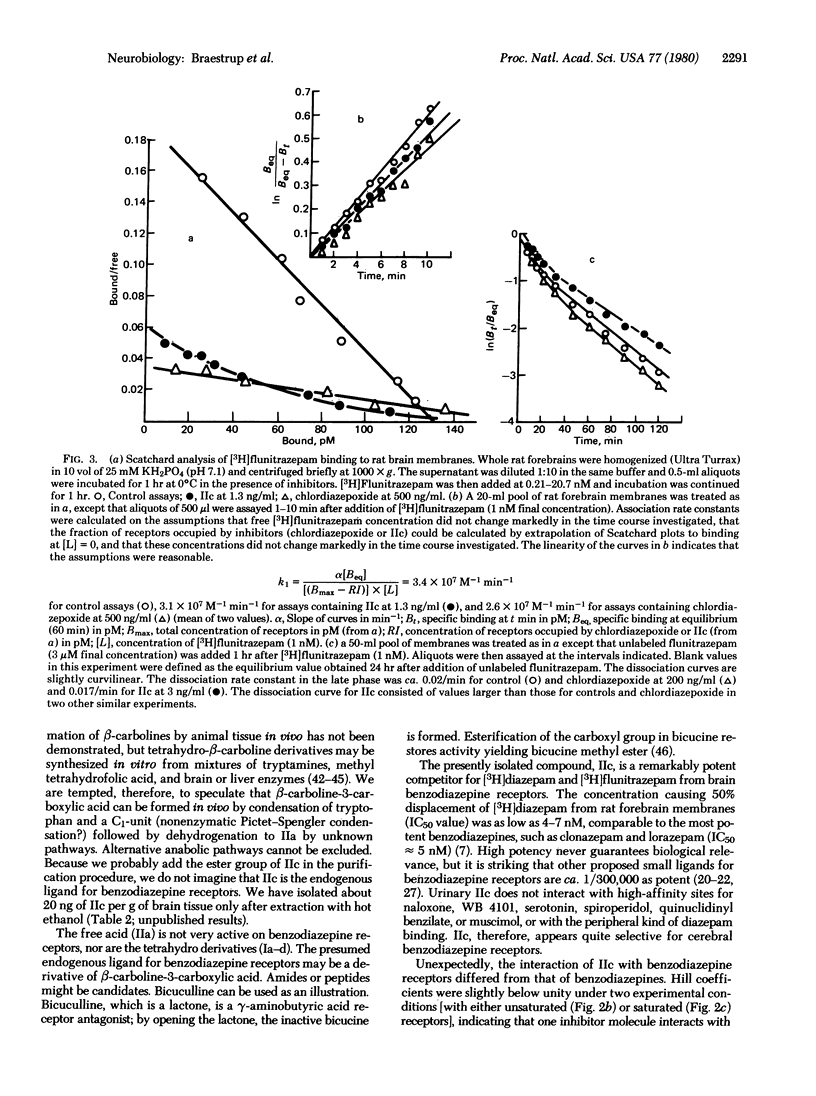
Benzodiazepines probably exert their anxiolytic, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant effects by interacting with brain-specific high-affinity benzodiazepine receptors. In searching for possible endogenous ligands for these receptors we have purified a compound 10(7)-fold from human urine by extractions, treatment with hot ethanol, and column chromatography. The compound was identified as beta-carboline-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (IIc) by mass spectrometry, NMR spectrometry, and synthesis; IIc was also isolated from brain tissues (20 ng/g) by similar procedures. Very small concentrations of IIc displaced [3H]diazepam completely from specific cerebral receptors, but not from liver and kidney binding sites; the concentration causing 50% inhibition of specific [3H]diazepam binding (IC50) was 4-7 nM compared to ca. 5 nM for the potent benzodiazepine lorazepam. Specific binding sites for quinuclidinyl benzilate, naloxone, spiroperidol, serotonin, muscimol, and WB 4101 were not affected by IIc. In contrast to benzodiazepines, IIc exhibits "mixed type" competitive inhibition of forebrain benzodiazepine receptors (negative cooperativity). We surmise that an endogenous ligand for benzodiazepine receptors may be a derivative of beta-carboline-3-carboxylic acid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramovitch R. A., Spenser I. D. The carbolines. Adv Heterocycl Chem. 1964;3:79–207. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2725(08)60542-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Spector S. Identification of inosine and hypoxanthine as endogenous ligands for the brain benzodiazepine-binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):977–981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battersby M. K., Richards J. G., Möhler H. Benzodiazepine receptor: photoaffinity labeling and localization. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug 1;57(2-3):277–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont K., Chilton W. S., Yamamura H. I., Enna S. J. Muscimol binding in rat brain: association with synaptic GABA receptors. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 9;148(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. P., Jr, Snyder S. H. Serotonin and lysergic acid diethylamide binding in rat brain membranes: relationship to postsynaptic serotonin receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 May;12(3):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. The binding of agonists to brain muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Sep;14(5):723–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B., Case K. R., DiStefano P. Diazepam receptor characterization: specific binding of a benzodiazepine to macromolecules in various areas of rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80623-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Albrechtsen R., Squires R. F. High densities of benzodiazepine receptors in human cortical areas. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):702–704. doi: 10.1038/269702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M., Nielsen E. B., Lyon M. Benzodiazepine receptors in the brain as affected by different experimental stresses: the changes are small and not undirectional. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979 Nov;65(3):273–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00492215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Brain specific benzodiazepine receptors. Br J Psychiatry. 1978 Sep;133:249–260. doi: 10.1192/bjp.133.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Pharmacological characterization of benzodiazepine receptors in the brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Apr 1;48(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckholtz N. S. Neurochemical and behavior effects of beta-carbolines. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1979 Jan;15(1):56–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colello G. D., Hockenbery D. M., Bosmann H. B., Fuchs S., Folkers K. Competitive inhibition of benzodiazepine binding by fractions from porcine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6319–6323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillion G. M., Rousselle J. C., Fillion M. P., Beaudoin D. M., Goiny M. R., Deniau J. M., Jacob J. J. High-affinity binding of (3H) 5-hydroxytryptamine to brain synaptosomal membranes: comparison with (3H) lysergic acid diethylamide binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;14(1):50–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Prichard D. C., Snyder S. H. Alpha-noradrenergic receptor binding in mammalian brain: differential labeling of agonist and antagonist states. Life Sci. 1976 Jul 1;19(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Toffano G., Costa E. An endogenous protein modulates the affinity of GABA and benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):553–555. doi: 10.1038/275553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. L., Mandell A. J. Enzymatic formation of tetrahydro-beta-carboline from tryptamine and 5-methyltetrahydrofolic acid in rat brain fractions: regional and subcellular distribution. J Neurochem. 1975 Apr;24(4):631–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karobath M., Sperk G., Schönbeck G. Evidence for an endogenous factor interfering with 3H-diazepam binding to rat brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jun 1;49(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippa A. S., Sano M. C., Coupet J., Klepner C. A., Beer B. Evidence that benzodiazepine receptors reside on cerebellar purkinje cells: studies with "nervous" mutant mice. Life Sci. 1978 Nov 27;23(22):2213–2217. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackerer C. R., Kochman R. L., Bierschenk B. A., Bremner S. S. The binding of [3H]diazepam to rat brain homogenates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Aug;206(2):405–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maelicke A., Fulpius B. W., Klett R. P., Reich E. Acetylcholine receptor. Responses to drug binding. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4811–4830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel L. R., Rosegay A., Walker R. W., Vandenheuvel W. J., Rokach J. 5-methyltetrahydrofolic Acid as a mediator in the formation of pyridoindoles. Science. 1974 Nov 22;186(4165):741–743. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4165.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Properties of 3H-diazepam binding to benzodiazepine receptors in rat cerebral cortex. Life Sci. 1977 Jun 15;20(12):2101–2110. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. The benzodiazepine receptor in normal and pathological human brain. Br J Psychiatry. 1978 Sep;133:261–268. doi: 10.1192/bjp.133.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Polc P., Cumin R., Pieri L., Kettler R. Nicotinamide is a brain constituent with benzodiazepine-like actions. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):563–565. doi: 10.1038/278563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Evidence for a late evolutionary appearance of brain-specific benzodiazepine receptors: an investigation of 18 vertebrate and 5 invertebrate species. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 10;141(2):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Gredal O., Braestrup C. Some properties of 3H-diazepam displacing activity from human urine. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 20;25(8):679–686. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. M., Skolnick P. Rapid changes in brain benzodiazepine receptors after experimental seizures. Science. 1978 Nov 24;202(4370):892–894. doi: 10.1126/science.715447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelspacher H., Coper H., Strauss S. On the mode of formation of tetrahydro-beta carbolines. Life Sci. 1976 Jan 1;18(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90277-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick P., Marangos P. J., Goodwin F. K., Edwards M., Paul S. Identification of inosine and hypoxanthine as endogenous inhibitors of [3H] diazepam binding in the central nervous system. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 9;23(14):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick P., Syapin P. J., Paugh B. A., Moncada V., Marangos P. J., Paul S. M. Inosine, an endogenous ligand of the brain benzodiazepine receptor, antagonizes pentylenetetrazole-evoked seizures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1515–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperk G., Schlögl E. Reduction of number of benzodiazepine binding sites in the caudate nucleus of the rat after kainic acid injections. Brain Res. 1979 Jul 20;170(3):563–567. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90976-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth R. C., Wastek G. J., Johnson P. C., Yamamura H. I. Benzodiazepine binding in human brain: characterization using [3H]flunitrazepam. Life Sci. 1978 Mar;22(10):859–866. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90610-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Benson D. I., Braestrup C., Coupet J., Klepner C. A., Myers V., Beer B. Some properties of brain specific benzodiazepine receptors: new evidence for multiple receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1979 May;10(5):825–830. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(79)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Braestrup C. Characteristics and regional distributions of two distinct [3H]naloxone binding sites in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1978 Jan;30(1):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Brastrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):732–734. doi: 10.1038/266732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. J., Erdelyi E., DoAmaral J. R., Elliott G. R., Renson J., Barchas J. D. Tryptoline formation by a preparation from brain with 5-methyltetrahydrofolic acid and tryptamine. Science. 1975 Mar 7;187(4179):853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.234627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. Muscarinic cholinergic binding in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



