Abstract
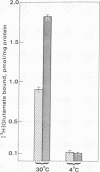
Specific [3H]glutamate binding to rat hippocampal membranes and the calcium-induced increase in this binding are markedly temperature-sensitive and are inhibited by alkylating or reducing agents as well as by various protease inhibitors. N-Ethylmaleimide, chloromethyl ketone derivatives of lysine and phenylalanine, and tosylarginine methyl ester decrease the maximum number of [3H]glutamate binding sites without changing their affinity for glutamate. Preincubation of the membranes with glutamate does not protect the glutamate "receptors" from the suppressive effects of these agents. The proteases trypsin and alpha-chymotrypsin increase the maximum number of [3H]glutamate binding sites. The effects of calcium on glutamate binding are different across brain regions. Cerebellar membranes are almost insensitive whereas hippocampal and striatal membranes exhibit a strong increase in the number of binding sites after exposure to even low concentrations of calcium. These results suggest that an endogenous membrane-associated thiol protease regulates the number of [3H]glutamate-associated thiol protease regulates the number of [3H]glutamate binding sites in hippocampal membranes and that this is the mechanism by which calcium stimulates glutamate binding. The possibility is discussed that the postulated mechanisms participate in synaptic physiology and in particular may be related to the long-term potentiation of transmission found in hippocampus under certain conditions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudry M., Lynch G. Regulation of glutamate receptors by cations. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):748–750. doi: 10.1038/282748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Lynch G. Two glutamate binding sites in rat hippocampal membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug 1;57(2-3):283–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K. J., Harwood J. P., Aguilera G., Dufau M. L. Hormonal regulation of peptide receptors and target cell responses. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):109–116. doi: 10.1038/280109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Davies J. An evaluation of D-alpha-aminoadipate and D-(and DL-)alpha-aminosuberate as selective antagonists of excitatory amino acids in the substantia nigra and mesencephalic reticular formation of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Feb;18(2):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costentin J., Marçais H., Protais P., Baudry M., De La Baume S., Martres M. P., Schwartz J. C. Rapid development of hypersensitivity of striatal dopamine receptors induced by alpha-methylparatyrosine and its prevention by protein synthesis inhibitors. Life Sci. 1977 Aug 1;21(3):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie T. V., Lynch G. The relationship between extracellular calcium concentrations and the induction of hippocampal long-term potentiation. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 15;169(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding in rat brain synaptic membrane fractions. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):81–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Roberts P. J. High affinity l-[3h]glutamate binding to postsynaptic receptor sites on rat cerebellar membranes. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1467–1477. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. S., Newby B. J. Neurofilament disguise, destruction and discipline. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):586–589. doi: 10.1038/256586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotson J. R., Prince D. A., Schwartzkroin P. A. Anomalous inward rectification in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1979 May;42(3):889–895. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.3.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Zatz M., Romero J. A., Axelrod J. Rapid changes in rat pineal beta-adrenergic receptor: alterations in l-(3H)alprenolol binding and adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3735–3739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe J. Transformation by concanavalin A of the response of molluscan neurones to L-glutamate. Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):866–869. doi: 10.1038/274866a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer A., Gani V., Jiménez J. S., Shaltiel S. Affinity labeling of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by N alpha-tosyl-L-lysine chloromethyl ketone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3073–3077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martres M. P., Costentin J., Baudry M., Marcais H., Protais P., Schwartz J. C. Long-term changes in the sensitivity of pre-and postsynaptic dopamine receptors in mouse striatum evidenced by behavioural and biochemical studies. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 11;136(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90806-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notides A. C., Hamilton D. E., Rudolph J. H. The action of a human uterine protease on the estrogen receptor. Endocrinology. 1973 Jul;93(1):210–216. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-1-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONG E. B., SHAW E., SCHOELLMANN G. THE IDENTIFICATION OF THE HISTIDINE RESIDUE AT THE ACTIVE CENTER OF CHYMOTRYPSIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:694–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts P. J. Glutamate receptors in the rat central nervous system. Nature. 1974 Nov 29;252(5482):399–401. doi: 10.1038/252399a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochefort H., Baulieu E. E. Effect of KCl, CaCl 2 , temperature and oestradiol on the uterine cytosol receptor of oestradiol. Biochimie. 1971;53(8):893–907. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer W. W., Hasler M. B. Characterization of the calcium-induced disruption of neurofilaments in rat peripheral nerve. Brain Res. 1979 May 25;168(2):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Costentin J., Martres M. P., Protais P., Baudry M. Modulation of receptor mechanisms in the CNS: hyper- and hyposensitivity to catecholamines. Neuropharmacology. 1978 Sep;17(9):665–685. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(78)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw E. Selective chemical modification of proteins. Physiol Rev. 1970 Apr;50(2):244–296. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siman R. G., Klein W. L. Cholinergic activity regulates muscarinic receptors in central nervous system cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4141–4145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Bennett J. P., Jr Neurotransmitter receptors in the brain: biochemical identification. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:153–175. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. F., Nadler J. V., Hamberger A., Cotman C. W., Cummins J. T. Glutamate as transmitter of hippocampal perforant path. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):356–357. doi: 10.1038/270356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A., Basbaum A. I. Intradendritic recordings from hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):986–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]