Abstract
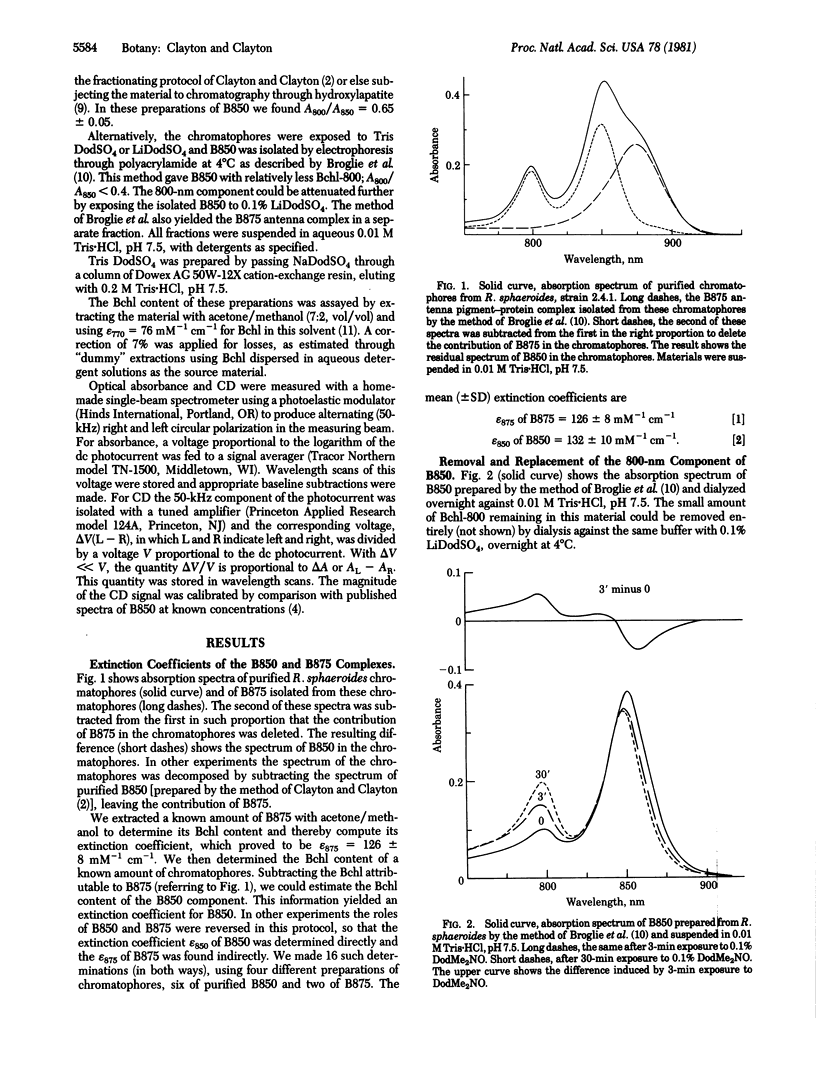
Chromatophores of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides yield the antenna complex B850 in either of two states, depending on the method of isolation. Methods using dodecyl (= lauryl) dimethylamine oxide yield B850 with an absorption spectrum like that in vivo: the bands at 800 and 850 nm, due to the bacteriochlorophyll (Bchl) components Bchl-800 and Bchl-850, are in ratio A800/A850 = 0.65 ± 0.05. When B850 is isolated by methods using dodecyl sulfate, the Bchl-800 is attenuated or absent. Bchl assays of these materials and of the isolated antenna complex B875 yielded the following extinction coefficients, ±SD, on the basis of the molarity of Bchl: For B875, ε875 = 126 ± 8 mM-1 cm-1. For B850 in the normal (high-Bchl-800) state, ε850 = 132 ± 10 mM-1 cm-1. For the individual components of Bchl in B850, ε850 of Bchl-850 = 184 ± 13 mM-1 cm-1 and ε800 of Bchl-800 = 213 ± 28 mM-1 cm-1. With these coefficients the molecular ratio of Bchl-850 to Bchl-800 equals 1.8 ± 0.4 for B850 in the high-Bchl-800 state. Starting with B850 depleted of Bchl-800, the addition of dodecyldimethylamine oxide restored the 800-nm absorption band. The 850-nm band became shifted toward the blue, narrowed, and slightly attenuated, and its associated circular dichroism became 20% more intense. Free Bchl added with dodecyldimethylamine oxide accelerated the restoration of Bchl-800 and retarded the attenuation of Bchl-850. We conclude that free Bchl can interact reversibly with a binding site for Bchl-800 in the B850 complex, with dodecyl sulfate favoring dissociation and dodecyldimethylamine oxide promoting association. Thus the reversible dissociation of a native chlorophyll-protein complex has now been demonstrated.
Keywords: photosynthetic bacteria, antenna complexes, pigment-protein interactions
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolt J., Sauer K. Linear dichroism of light harvesting bacteriochlorophyll proteins from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides in stretched polyvinyl alcohol films. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 11;546(1):54–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broglie R. M., Hunter C. N., Delepelaire P., Niederman R. A., Chua N. H., Clayton R. K. Isolation and characterization of the pigment-protein complexes of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides by lithium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):87–91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton B. J., Clayton R. K. Properties of photochemical reaction centers purified from Rhodopseudomonas gelatinosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 13;501(3):470–477. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton R. K., Clayton B. J. Relations between pigments and proteins in the photosynthetic membranes of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 14;283(3):492–504. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogdell R. J., Thornber J. P. The preparation and characterization of different types of light-harvesting pigment-protein complexes from some purple bacteria. Ciba Found Symp. 1978 Feb 7;(61):61–79. doi: 10.1002/9780470720431.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feick R., Drews G. Isolation and characterization of light harvesting bacteriochlorophyll.protein complexes from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 13;501(3):499–513. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer K., Austin L. A. Bacteriochlorophyll-protein complexes from the light-harvesting antenna of photosynthetic bacteria. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):2011–2019. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster G. D., Cogdell R. J., Lindsay G. J. The location of the carotenoid in the B800--850 light-harvesting pigment--protein complex from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 10;111(2):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80834-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



